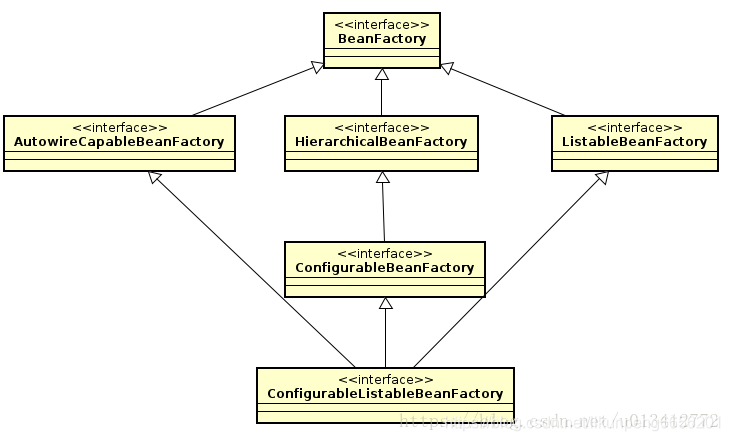
ListableBeanFactory获取bean时,Spring 鼓励使用这个接口定义的api. 还有个Beanfactory方便使用.其他的4个接口都是不鼓励使用的.
提供容器中bean迭代的功能,不再需要一个个bean地查找.比如可以一次获取全部的bean(太暴力了),根据类型获取bean.在看SpringMVC时,扫描包路径下的具体实现策略就是使用的这种方式(那边使用的是BeanFactoryUtils封装的api).
如果同时实现了HierarchicalBeanFactory,返回值不会考虑父类BeanFactory,只考虑当前factory定义的类.当然也可以使用BeanFactoryUtils辅助类来查找祖先工厂中的类. 即ListableBeanFactory是beanFactory接口的扩展接口,它可以枚举所有的bean实例,而不是客户端通过名称一个一个的查询得出所有的实例。要预加载所有的bean定义的beanfactory可以实现这个接口来。该 接口定义了访问容器中Bean基本信息的若干方法,如查看Bean的个数、获取某一类型Bean的配置名、查看容器中是否包括某一Bean等方法.
这个接口中的方法只会考虑本factory定义的bean.这些方法会忽略ConfigurableBeanFactory的registerSingleton注册的单例bean(getBeanNamesOfType和getBeansOfType是例外,一样会考虑手动注册的单例).当然BeanFactory的getBean一样可以透明访问这些特殊bean.当然在典型情况下,所有的bean都是由external bean定义,所以应用不需要顾虑这些差别.
注意:getBeanDefinitionCount和containsBeanDefinition的实现方法因为效率比较低,还是少用为好.
ListableBeanFactory源码具体:
1、3个跟BeanDefinition有关的总体操作。包括BeanDefinition的总数、名字的集合、指定类型的名字的集合。(这里指出,BeanDefinition是Spring中非常重要的一个类,每个BeanDefinition实例都包含一个类在Spring工厂中所有属性。)
2、2个getBeanNamesForType重载方法。根据指定类型(包括子类)获取其对应的所有Bean名字。
3、2个getBeansOfType重载方法。根据类型(包括子类)返回指定Bean名和Bean的Map。
4、2个跟注解查找有关的方法。根据注解类型,查找Bean名和Bean的Map。以及根据指定Bean名和注解类型查找指定的Bean。
总结:
正如这个工厂接口的名字所示,这个工厂接口最大的特点就是可以列出工厂可以生产的所有实例。当然,工厂并没有直接提供返回所有实例的方法,也没这个必要。它可以返回指定类型的所有的实例。而且你可以通过getBeanDefinitionNames()得到工厂所有bean的名字,然后根据这些名字得到所有的Bean。这个工厂接口扩展了BeanFactory的功能,作为上文指出的BeanFactory二级接口,有9个独有的方法,扩展了跟BeanDefinition的功能,提供了BeanDefinition、BeanName、注解有关的各种操作。它可以根据条件返回Bean的集合,这就是它名字的由来——ListableBeanFactory。
/*** * @author DemoTransfer* @since 4.3*/
public interface ListableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {//-------------------------------------------------------------------------// 暴力获取全部bean的属性//-------------------------------------------------------------------------/*** Check if this bean factory contains a bean definition with the given name.* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in,* and ignores any singleton beans that have been registered by* other means than bean definitions.* @param beanName the name of the bean to look for* @return if this bean factory contains a bean definition with the given name* @see #containsBean*/// 对于给定的名字是否含有BeanDefinitionboolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);/*** Return the number of beans defined in the factory.* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in,* and ignores any singleton beans that have been registered by* other means than bean definitions.* @return the number of beans defined in the factory*/// 返回工厂的BeanDefinition总数int getBeanDefinitionCount();/*** Return the names of all beans defined in this factory.* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in,* and ignores any singleton beans that have been registered by* other means than bean definitions.* @return the names of all beans defined in this factory,* or an empty array if none defined*/// 返回工厂中所有Bean的名字String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();//-------------------------------------------------------------------------// 根据bean 的类型获取bean//// 这边的方法仅检查顶级bean.它不会检查嵌套的bean.FactoryBean创建的bean会匹配为FactoryBean而不是原始类型.// 一样不会考虑父factory中的bean,非要用可以通过BeanFactoryUtils中的beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors.// 其他方式注册的单例这边会纳入判断.// 这个版本的getBeanNamesForType会匹配所有类型的bean,包括单例,原型,FactoryBean.返回的bean names会根据backend 配置的进行排序.//-------------------------------------------------------------------------/*** Return the names of beans matching the given type (including subclasses),* judging from either bean definitions or the value of {@code getObjectType}* in the case of FactoryBeans.* <p><b>NOTE: This method introspects top-level beans only.</b> It does <i>not</i>* check nested beans which might match the specified type as well.* <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans, which means that FactoryBeans* will get initialized. If the object created by the FactoryBean doesn't match,* the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the type.* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in.* Use BeanFactoryUtils' {@code beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors}* to include beans in ancestor factories too.* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> ignore singleton beans that have been registered* by other means than bean definitions.* <p>This version of {@code getBeanNamesForType} matches all kinds of beans,* be it singletons, prototypes, or FactoryBeans. In most implementations, the* result will be the same as for {@code getBeanNamesForType(type, true, true)}.* <p>Bean names returned by this method should always return bean names <i>in the* order of definition</i> in the backend configuration, as far as possible.* @param type the class or interface to match, or {@code null} for all bean names* @return the names of beans (or objects created by FactoryBeans) matching* the given object type (including subclasses), or an empty array if none* @since 4.2* @see #isTypeMatch(String, ResolvableType)* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType* @see BeanFactoryUtils#beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory, ResolvableType)*/String[] getBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType type);/*** Return the names of beans matching the given type (including subclasses),* judging from either bean definitions or the value of {@code getObjectType}* in the case of FactoryBeans.* <p><b>NOTE: This method introspects top-level beans only.</b> It does <i>not</i>* check nested beans which might match the specified type as well.* <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans, which means that FactoryBeans* will get initialized. If the object created by the FactoryBean doesn't match,* the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the type.* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in.* Use BeanFactoryUtils' {@code beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors}* to include beans in ancestor factories too.* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> ignore singleton beans that have been registered* by other means than bean definitions.* <p>This version of {@code getBeanNamesForType} matches all kinds of beans,* be it singletons, prototypes, or FactoryBeans. In most implementations, the* result will be the same as for {@code getBeanNamesForType(type, true, true)}.* <p>Bean names returned by this method should always return bean names <i>in the* order of definition</i> in the backend configuration, as far as possible.* @param type the class or interface to match, or {@code null} for all bean names* @return the names of beans (or objects created by FactoryBeans) matching* the given object type (including subclasses), or an empty array if none* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType* @see BeanFactoryUtils#beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory, Class)*/// 获取给定类型的bean names(包括子类),通过bean 定义或者FactoryBean的getObjectType判断.// 返回对于指定类型Bean(包括子类)的所有名字String[] getBeanNamesForType(Class<?> type);/*** Return the names of beans matching the given type (including subclasses),* judging from either bean definitions or the value of {@code getObjectType}* in the case of FactoryBeans.* <p><b>NOTE: This method introspects top-level beans only.</b> It does <i>not</i>* check nested beans which might match the specified type as well.* <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans if the "allowEagerInit" flag is set,* which means that FactoryBeans will get initialized. If the object created by the* FactoryBean doesn't match, the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the* type. If "allowEagerInit" is not set, only raw FactoryBeans will be checked* (which doesn't require initialization of each FactoryBean).* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in.* Use BeanFactoryUtils' {@code beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors}* to include beans in ancestor factories too.* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> ignore singleton beans that have been registered* by other means than bean definitions.* <p>Bean names returned by this method should always return bean names <i>in the* order of definition</i> in the backend configuration, as far as possible.* @param type the class or interface to match, or {@code null} for all bean names* @param includeNonSingletons whether to include prototype or scoped beans too* or just singletons (also applies to FactoryBeans)* @param allowEagerInit whether to initialize <i>lazy-init singletons</i> and* <i>objects created by FactoryBeans</i> (or by factory methods with a* "factory-bean" reference) for the type check. Note that FactoryBeans need to be* eagerly initialized to determine their type: So be aware that passing in "true"* for this flag will initialize FactoryBeans and "factory-bean" references.* @return the names of beans (or objects created by FactoryBeans) matching* the given object type (including subclasses), or an empty array if none* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType* @see BeanFactoryUtils#beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory, Class, boolean, boolean)*//** 返回指定类型的名字 includeNonSingletons为false表示只取单例Bean,true则不是* allowEagerInit为true表示立刻加载,false表示延迟加载。 注意:FactoryBeans都是立刻加载的。*/String[] getBeanNamesForType(Class<?> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit);/*** Return the bean instances that match the given object type (including* subclasses), judging from either bean definitions or the value of* {@code getObjectType} in the case of FactoryBeans.* <p><b>NOTE: This method introspects top-level beans only.</b> It does <i>not</i>* check nested beans which might match the specified type as well.* <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans, which means that FactoryBeans* will get initialized. If the object created by the FactoryBean doesn't match,* the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the type.* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in.* Use BeanFactoryUtils' {@code beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors}* to include beans in ancestor factories too.* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> ignore singleton beans that have been registered* by other means than bean definitions.* <p>This version of getBeansOfType matches all kinds of beans, be it* singletons, prototypes, or FactoryBeans. In most implementations, the* result will be the same as for {@code getBeansOfType(type, true, true)}.* <p>The Map returned by this method should always return bean names and* corresponding bean instances <i>in the order of definition</i> in the* backend configuration, as far as possible.* @param type the class or interface to match, or {@code null} for all concrete beans* @return a Map with the matching beans, containing the bean names as* keys and the corresponding bean instances as values* @throws BeansException if a bean could not be created* @since 1.1.2* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType* @see BeanFactoryUtils#beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory, Class)*/// 如果保护懒加载的类,FactoryBean初始化的类和工厂方法初始化的类会被初始化.就是说执行这个方法会执行对应的初始化.// 根据类型(包括子类)返回指定Bean名和Bean的Map<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> type) throws BeansException;/*** Return the bean instances that match the given object type (including* subclasses), judging from either bean definitions or the value of* {@code getObjectType} in the case of FactoryBeans.* <p><b>NOTE: This method introspects top-level beans only.</b> It does <i>not</i>* check nested beans which might match the specified type as well.* <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans if the "allowEagerInit" flag is set,* which means that FactoryBeans will get initialized. If the object created by the* FactoryBean doesn't match, the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the* type. If "allowEagerInit" is not set, only raw FactoryBeans will be checked* (which doesn't require initialization of each FactoryBean).* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in.* Use BeanFactoryUtils' {@code beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors}* to include beans in ancestor factories too.* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> ignore singleton beans that have been registered* by other means than bean definitions.* <p>The Map returned by this method should always return bean names and* corresponding bean instances <i>in the order of definition</i> in the* backend configuration, as far as possible.* @param type the class or interface to match, or {@code null} for all concrete beans* @param includeNonSingletons whether to include prototype or scoped beans too* or just singletons (also applies to FactoryBeans)* @param allowEagerInit whether to initialize <i>lazy-init singletons</i> and* <i>objects created by FactoryBeans</i> (or by factory methods with a* "factory-bean" reference) for the type check. Note that FactoryBeans need to be* eagerly initialized to determine their type: So be aware that passing in "true"* for this flag will initialize FactoryBeans and "factory-bean" references.* @return a Map with the matching beans, containing the bean names as* keys and the corresponding bean instances as values* @throws BeansException if a bean could not be created* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType* @see BeanFactoryUtils#beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory, Class, boolean, boolean)*/<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit)throws BeansException;//-------------------------------------------------------------------------// 查找使用注解的类//-------------------------------------------------------------------------/*** Find all names of beans whose {@code Class} has the supplied {@link Annotation}* type, without creating any bean instances yet.* @param annotationType the type of annotation to look for* @return the names of all matching beans* @since 4.0*/String[] getBeanNamesForAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType);/*** Find all beans whose {@code Class} has the supplied {@link Annotation} type,* returning a Map of bean names with corresponding bean instances.* @param annotationType the type of annotation to look for* @return a Map with the matching beans, containing the bean names as* keys and the corresponding bean instances as values* @throws BeansException if a bean could not be created* @since 3.0*/// 根据注解类型,查找所有有这个注解的Bean名和Bean的MapMap<String, Object> getBeansWithAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType) throws BeansException;//-------------------------------------------------------------------------// 查找一个类上的注解,如果找不到,父类,接口使用注解也算.//-------------------------------------------------------------------------/*** Find an {@link Annotation} of {@code annotationType} on the specified* bean, traversing its interfaces and super classes if no annotation can be* found on the given class itself.* @param beanName the name of the bean to look for annotations on* @param annotationType the annotation class to look for* @return the annotation of the given type if found, or {@code null}* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name* @since 3.0*/// 根据指定Bean名和注解类型查找指定的Bean<A extends Annotation> A findAnnotationOnBean(String beanName, Class<A> annotationType)throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;}







)










