蚁群优化算法模拟了自然界中蚂蚁的觅食行为,信息素浓度的大小表征路径的远近,信息素浓度越高,表示对应的路径距离越短。同时,路径上的信息素浓度会随着时间的推进而逐渐衰减。
1.过程
(1)初始化参数
蚁群规模、信息素因子α、启发函数因子β、信息素挥发因子ρ、信息素释放总量q、最大迭代次数等。
(2)构建解空间
起初把蚂蚁随机放到不同城市,对于每一个蚂蚁,采用轮盘赌找出下一个要访问的城市,直到访问完所有城市。
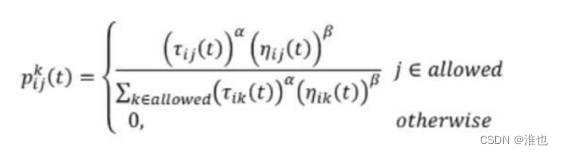
(3)更新信息素
计算各个蚂蚁经过的路径长度,找出本次迭代中的最短路径,并更新城市路径的信息素浓度。更新信息素浓度分为三种策略:蚁周、蚁量、蚁密。
蚁周是完成一次路径循环后,蚂蚁才释放信息素。
蚁量是一只蚂蚁从一个城市到达另一个城市后,直接释放信息素。
蚁密是一只蚂蚁从一个城市到达另一个城市后,释放的信息素需要除以城市间的路径距离。
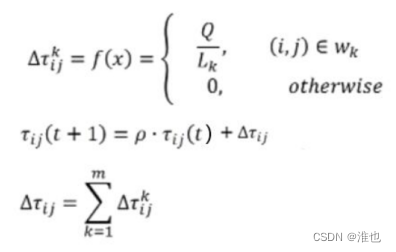
(4)判断是否终止
迭代次数到达最大迭代次数后,终止。否则,回到(2)。
2.流程图

3.代码
from utils import draw_picture, get_next_pos, init_pos, save_best_result
import tqdmimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')class ACO(object):def __init__(self, ant_count: int, generations: int, alpha: float, beta: float, rho: float, q: int,strategy: int, distance, points):""":param ant_count::param generations::param alpha: relative importance of pheromone:param beta: relative importance of heuristic information:param rho: pheromone residual coefficient:param q: pheromone intensity:param strategy: pheromone update strategy. 0 - ant-cycle, 1 - ant-quality, 2 - ant-density:param distance: distance between each points"""self.Q = qself.rho = rhoself.beta = betaself.alpha = alphaself.ant_count = ant_countself.generations = generationsself.update_strategy = strategyself.points = pointsself.distance = distance# 路径数目self.rank = len(distance)#self.eta = [[0 if i == j else 1 / distance[i][j] for j in range(self.rank)] for i inrange(self.rank)]# 每条路径上的信息素浓度self.pheromone_content = [[1 for _ in range(self.rank)] for _ in range(self.rank)]# 初始化def initialization(self):self.memory_vector = [] # 记录每个蚂蚁的总路径for _ in range(self.ant_count): # 不关心i,可以用_代替iself.memory_vector.append([init_pos(self.rank)]) # 随机初始化每个蚂蚁位置# 用轮盘赌计算蚂蚁要去的下一个城市def roulette(self, id, pos):possibility = []for i in range(self.rank):if i in self.memory_vector[id]:# 如果蚂蚁访问过这个城市,则不去possibility.append(0)else:possibility.append(self.pheromone_content[pos][i]**self.alpha*(self.eta[pos][i]**self.beta))next_pos = get_next_pos(possibility)return next_pos# 增加信息素浓度:三种策略,这里还有点问题def update_pheromone_delta(self, ant_path):if self.update_strategy == 0:for i in range(self.ant_count):self.pheromone_content[ant_path[i][0]][ant_path[i][1]] += self.Qself.pheromone_content[ant_path[i][1]][ant_path[i][0]] += self.Qif len(self.memory_vector[0]) == self.rank:self.pheromone_content[self.memory_vector[i][-1]][self.memory_vector[i][0]] += self.Qself.pheromone_content[self.memory_vector[i][0]][self.memory_vector[i][-1]] += self.Qelif self.update_strategy == 1:for i in range(self.ant_count):self.pheromone_content[ant_path[i][0]][ant_path[i][1]] += (self.Q/self.distance[ant_path[i][0]][ant_path[i][1]])self.pheromone_content[ant_path[i][1]][ant_path[i][0]] += (self.Q/self.distance[ant_path[i][0]][ant_path[i][1]])if len(self.memory_vector[0]) == self.rank:self.pheromone_content[self.memory_vector[i][-1]][self.memory_vector[i][0]]+=self.Q/self.distance[self.memory_vector[i][0]][self.memory_vector[i][-1]]self.pheromone_content[self.memory_vector[i][0]][self.memory_vector[i][-1]]+=self.Q/self.distance[self.memory_vector[i][0]][self.memory_vector[i][-1]]elif self.update_strategy == 2:# 完成一次循环后if len(self.memory_vector[0]) == self.rank:# 计算每个蚂蚁本次的总路程total_cost = []for i in range(self.ant_count):cost = 0for j in range(1, self.rank):cost += self.distance[self.memory_vector[i][j-1]][self.memory_vector[i][j]]cost += self.distance[self.memory_vector[i][0]][self.memory_vector[i][-1]]total_cost.append(cost)# 更新信息素浓度for i in range(self.ant_count):delta = self.Q/total_cost[i]for j in range(1, self.rank):# 双向路径self.pheromone_content[self.memory_vector[i][j-1]][self.memory_vector[i][j]] += deltaself.pheromone_content[self.memory_vector[i][j]][self.memory_vector[i][j-1]] += delta# 蚂蚁最初的那条路self.pheromone_content[self.memory_vector[i][0]][self.memory_vector[i][-1]] += deltaself.pheromone_content[self.memory_vector[i][-1]][self.memory_vector[i][0]] += deltaelse:# 没有完成一次循环passelse:raise KeyError# 减少信息素浓度def update_pheromone(self):for i in range(self.rank):for j in range(self.rank):self.pheromone_content[i][j] = self.pheromone_content[i][j] * (1 - self.rho)# 更新蚂蚁本次迭代找到的路径def update_memory_vector(self, ant_path):for i in range(self.ant_count):self.memory_vector[i].append(ant_path[i][1])# 执行算法def run(self):self.cost = 0self.path = []plt.ion() # 启用交互模式(动态图)# tqdm进度条for iteration in tqdm.tqdm(range(self.generations), desc='Processing'):# print(f'-----start iteration {iteration+1} of ACO-----')self.initialization()for steps in range(self.rank - 1):# 在一次新的迭代中,蚂蚁选择一条路径从pos到next_posant_path = []for i in range(self.ant_count): # 对于每一只蚂蚁pos = self.memory_vector[i][-1]next_pos = self.roulette(i, pos)ant_path.append([pos, next_pos])self.update_memory_vector(ant_path) # 更新蚂蚁本次迭代的路径self.update_pheromone_delta(ant_path) # 增加路径上的信息素浓度self.update_pheromone() # 减少信息素浓度plt.cla()plt.title("ant colony algorithm")self.cost, self.path = draw_picture(self.points, self.distance, self.memory_vector, iteration)plt.pause(0.01) # 暂停运行一段时间,能将内存中的图像显示出来# 保存数据def save(self, seed):save_best_result(self.path, self.points, seed)plt.ioff() # 关闭交互模式plt.show() # 显示图片,会阻塞后面代码运行,适用于静态图# 开发时间:2023/12/13 19:50
import random
import math
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')def random_init(points_num ,min_x ,max_x, min_y, max_y):points = []while len(points) != points_num:x = random.randint(min_x, max_x)y = random.randint(min_y, max_y)if [x, y] in points:continuepoints.append([x, y])file = open("temp.txt", "w")for i in range(len(points)):file.write(f'{points[i][0]}{points[i][1]}\n')file.close()print("Data running time was saved in file [temp.txt]")return pointsdef dis(point1, point2):return math.sqrt((point1[0]-point2[0]) ** 2 + (point1[1]-point2[1]) ** 2)def calculate_distance(points):distance = []for i in range(len(points)):list = []for j in range(len(points)):list.append(dis(points[i], points[j]))distance.append(list)return distancedef get_next_pos(possibility):n = sum(possibility)for i in range(len(possibility)):possibility[i] /= nn = sum(possibility)r = random.uniform(0, n)pos = 0while True:if possibility[pos] == 0:pos += 1elif r-possibility[pos] < 0:return poselse:r -= possibility[pos]pos += 1def init_pos(rank):pos = random.randint(0, rank-1)return posdef load_example(text_name):file = open(text_name, 'r')content = file.readlines()points = []for data in content:x, y = data.split(" ")points.append([int(x), int(y)])distance = calculate_distance(points)return points, distancedef draw_picture(points, distance, path, iteration):rank = len(points)ant_number = len(path)x = []y = []for i in range(rank):x.append(points[i][0])y.append(points[i][1])plt.scatter(x, y)min_cost = np.inffor i in range(ant_number):temp_cost = 0for j in range(1, rank):temp_cost += distance[path[i][j-1]][path[i][j]]temp_cost += distance[path[i][0]][path[i][-1]]if temp_cost < min_cost:min_cost = temp_costbest_path = path[i]for i in range(ant_number):for j in range(rank):x[j] = points[path[i][j]][0]y[j] = points[path[i][j]][1]plt.plot(x, y)plt.text(0, 0, f'iteration:{iteration} min_cost = {round(min_cost, 2)}', family='fantasy', fontsize=12,style='italic',color='mediumvioletred')return round(min_cost, 2), best_pathdef save_best_result(path, points, seed):for i in range(1, len(path)):x1 = points[path[i - 1]][0]y1 = points[path[i - 1]][1]x2 = points[path[i]][0]y2 = points[path[i]][1]plt.arrow(x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1, width=0.05, color='r', length_includes_head=True)plt.arrow(x2, y2, points[path[0]][0] - x2, points[path[0]][1] - y2, width=0.05, color='r',length_includes_head=True)plt.gcf().set_size_inches(20, 12) # get current figureplt.savefig("result.png")print("画图呀")plt.close()print('\n')print("-" * 50)print(f"[Best Path](random seed [{seed}])")print(show_path(path))print("Last result picture was saved in [result.png]")print(f"If you want to get this result again please add '-s {seed}'")print("-" * 50)print('\n')def show_path(path):route = str(path[0])for i in range(1, len(path)):route = route + "->"+str(path[i])route = route + "->"+str(path[0])return route
import argparse
from ACO import ACO
import random
from utils import random_init,calculate_distance,load_exampleimport matplotlib
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')def default_argument_parser():# ArgumentParser 编写命令行接口# 创建对象(解析器)parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="ant colony algorithm")# 添加参数parser.add_argument("--test", nargs="?") # 参数可设置0或1个parser.add_argument('--ant', default=5, type=int) # 蚂蚁数parser.add_argument('--points', default=20, type=int) # 城市数parser.add_argument('--generation', default=50,type=int) # 迭代次数parser.add_argument('--alpha', default=2.0,type=float) # 信息素因子parser.add_argument('--beta', default=3.0,type=float) # 启发函数因子parser.add_argument('--rho', default=0.5,type=float) # 信息素挥发因子parser.add_argument('--q', default=100,type=float) # 信息素浓度parser.add_argument('--strategy', default=2,type=int) # 信息素更新策略parser.add_argument('--min_x', default=0,type=int) # 范围parser.add_argument('--max_x', default=100,type=int)parser.add_argument('--min_y', default=0,type=int)parser.add_argument('--max_y', default=100,type=int)parser.add_argument('-s', '--seed', type=int)'''信息素三种更新策略0: 蚁量:加浓度1: 蚁密:加浓度/城市间的路径距离2: 蚁周:蚂蚁全走完再更新信息素浓度'''return parserdef main():# 解析参数args = default_argument_parser().parse_args()if(args.seed == None):seed = random.randint(1, 10000)random.seed(seed) # 随机数种子print("no random seed found")args.seed = seedelse:print(f"set random seed {args.seed}")random.seed(args.seed)if args.test != None:points, distance = load_example(args.test)else:points = random_init(args.points, args.min_x, args.max_x, args.min_y, args.max_y)distance = calculate_distance(points)aco = ACO(ant_count=args.ant,generations=args.generation,alpha=args.alpha,beta=args.beta,rho=args.rho,q=args.q,strategy=args.strategy,points=points,distance=distance,)aco.run() # 执行算法aco.save(args.seed) # 保存数据# 当.py文件被直接运行时,下面代码会执行;当.py文件以模块形式被导入则不会执行
if __name__ == '__main__':main()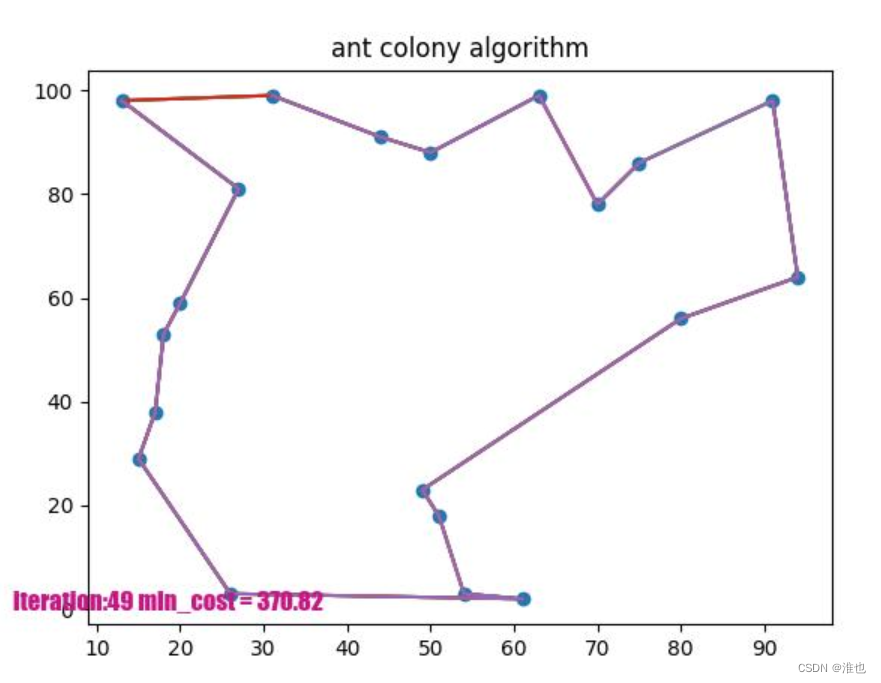
4.优缺点
优点:采用正反馈机制进行更新,使得结果不断收敛;可以并行计算。
缺点:收敛速度慢;不适用于解空间是连续的优化问题。


)
)
真题解析)






)





)

