8. Web Ontology Language (OWL)
在RDFs不可能实现:
Property cardinalities, Functional properties, Class disjointness, we cannot produce contradictions, circumvent the Non Unique Naming Assumption, circumvent the Open World Assumption
8.1 OWL
Trade-off: Expressive power, Complexity of reasoning, Decidability
Solution: different variants of OWL, e.g.,OWL Lite, OWL DL, OWL Full; Profiles in OWL2
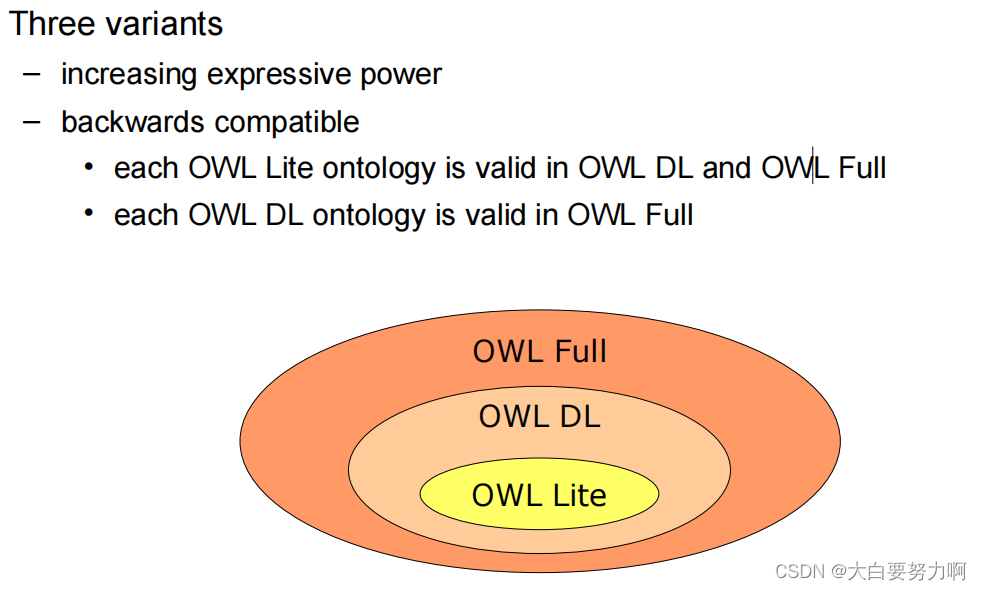
OWL and RDF Schema
both are based on RDF
OWL ontologies can also be expressed in RDF
as triples or in XML notation
Compatibility
OWL Lite(more stricted) and OWL DL are not fully compatible to RDF Schema but reuse some parts of RDF Schema
OWL Full and RDF Schema are fully compatible
8.2 OWL: Classes
Basic concept (owl:Class)
owl:Class rdfs:subClassOf rdfs:Class .
Two predefined classes
# top
owl:Thing
# bottom
owl:Nothing# Nothing is empty set, a subset of any class
c rdfs:subClassOf owl:Thing
owl:Nothing rdfs:subClassOf c
Classes can be intersections of others
# (:SwimmingAnimals :Mammals): 表示:SwimmingMammals 类是 :SwimmingAnimals 和:Mammals 两个类的交集。
:SwimmingMammals owl:intersectionOf (:SwimmingAnimals :Mammals) .
There are also set unions and set differences but not in OWL Lite
8.2 OWL: Properties
RDF Schema does not distinguish literal and object valued properties
:name a rdf:Property .
:name rdfs:range xsd:string .:knows a rdf:Property .
:knows rdfs:range foaf:Person .
Without specifying the range, “dual use” of an RDF property is not forbidden.
:peter :knows :john .
:peter :knows "mary"^^xsd:string .
“dual use” (双重使用)的意思是,:knows 这个属性既可以与另一个资源(如 :john)关联,也可以与字面量(如 “mary”)关联,而没有明确规定它们的类型。
In contrast, OWL distinguishes literal and object valued properties
– owl:DatatypeProperty
– owl:ObjectProperty– owl:DatatypeProperty rdfs:subClassOf rdf:Property .
– owl:ObjectProperty rdfs:subClassOf rdf:Property .
实际上,rdf:Property包含这两种,但是在RDFs中没有进一步明确
Hierarchy
in RDFs
:capitalOf rdfs:subPropertyOf :locatedIn
In OWL, with the restrions, can only have two disjoint hierarchies: 1. hierarchy of DatatypeProperty 2. hierarchy of ObjectProperty. 但DatatypeProperty不能是subPropertyOf ObjectProperty,反之也不可以。
Domains
only classes for OWL Lite, classes or restrictions* for OWL DL/Full
:name rdfs:domain foaf:Person .
Ranges
XML Datatypes for owl:DatatypeProperty
Classes or restrictions* for owl:ObjectProperty
:name rdfs:range xsd:string .
:knows rdfs:range foaf:Person .
8.3 Equality and Inequality
8.3.1 Equality between individuals
Allows using multiple definitions/descriptions of an entity, in other datasets as well -> solves some problems of the Non unique naming assumption
:Muenchen owl:sameAs :Munich .
# as a means to establish links between datasets
myDataset:Mannheim owl:sameAs dbpedia:Mannheim .
8.3.2 Equality between classes and properties
allows for relations between datasets on the schema level, gives way to more complex constructs
:UniversityTeachers owl:equivalentClass :Lecturers .
:teaches owl:equivalentProperty :lecturerFor .# Also useful for Linked Open Data:
my:createdBy owl:equivalentProperty foaf:maker .
8.3.3 Inequality between individuals
Allows some useful reasoning
:Munich owl:differentFrom :Hamburg .# Shorthand notation for multiple entities: 不仅是两者之间不同,而是一个和多个都不同
owl:AllDifferent owl:distinctMembers (:Munich :Hamburg :Berlin :Darmstadt :Mannheim) .
Why can’t we Simply Use only owl:sameAs?
In OWL (Lite+DL), we must not mix classes, properties, and instances. 必须区分开来
owl:sameAs has owl:Thing as domain/range
owl:equivalentClass has rdfs:Class as domain/range (recap: owl:Class rdfs:subClassOf rdfs:Class)
owl:equivalentProperty has rdf:Property
as domain/range
owl:ObjectProperty rdfs:subClassOf rdf:Property
owl:DatatypeProperty rdfs:subClassOf rdf:Property
8.3.4 Special Properties in OWL
# Symmetric Properties
:sitsOppositeOf a owl:SymmetricProperty .
:Tom :sitsOppositeOf :Sarah .
→ :Sarah :sitsOppositeOf :Tom .# Inverse Properties
:supervises owl:inverseOf :supervisedBy .
:Tom :supervises :Julia .
→ :Julia :supervisedBy :Tom .# Transitive Properties
:hasOfficeMate a owl:TransitiveProperty .
:Tom :hasOfficeMate :Jon . :Jon :hasOfficeMate :Kim .
→ :Tom :hasOfficeMate :Kim# Reflexive, irreflexive, and asymmetric properties
# Everybody is a relative of him/herself
:relativeOf a owl:ReflexiveProperty .# Nobody can be his/her own parent
:parentOf a owl:IrreflexiveProperty .# If I am taller than you, you cannot be taller than me
:tallerThan a owl:AsymmetricProperty .
8.3.5 Restrictions on Property Types
Only ObjectProperties may be transitive, symmetric, inverse, and reflexive. DataProperties may not be because “Literals can only be objects, never subjects or predicates.”
# Example:
:samePerson a owl:DatatypeProperty .
:samePerson rdfs:range xsd:string .
:samePerson a owl:SymmetricProperty .
:Peter :samePerson "Peter" .
→"Peter" :samePerson :Peter . #违反Literals不能是subjects:hasName a owl:DatatypeProperty .
:hasName rdfs:range xsd:string .
:hasName owl:inverseOf :nameOf .
:Peter :hasName "Peter" .
→"Peter" :nameOf :Peter . #违反Literals不能是subjects# owl:TransitiveProperty is also restricted to ObjectProperties
:hasPseudonym a owl:DatatypeProperty .
:hasPseudonym rdfs:range xsd:string .
:hasPseudonym a owl:TransitiveProperty .
:Thomas :hasPseudonym "Dr. Evil" .
+ "Dr. Evil" :hasPseudonym "Skullhead" . #在reasoning procee中必定违反
→:Thomas :hasPseudonym "Skullhead" .Which statement would we need here to make the conclusion via the owl:TransitiveProperty?
8.3.6 Functional Properties & Inverse Functional Properties
Functional Properties
If A and B are related via fp and A and C are related via fp, then, B and C are equal. Simply speaking: fp(x) is unique for each x. [Only one object]
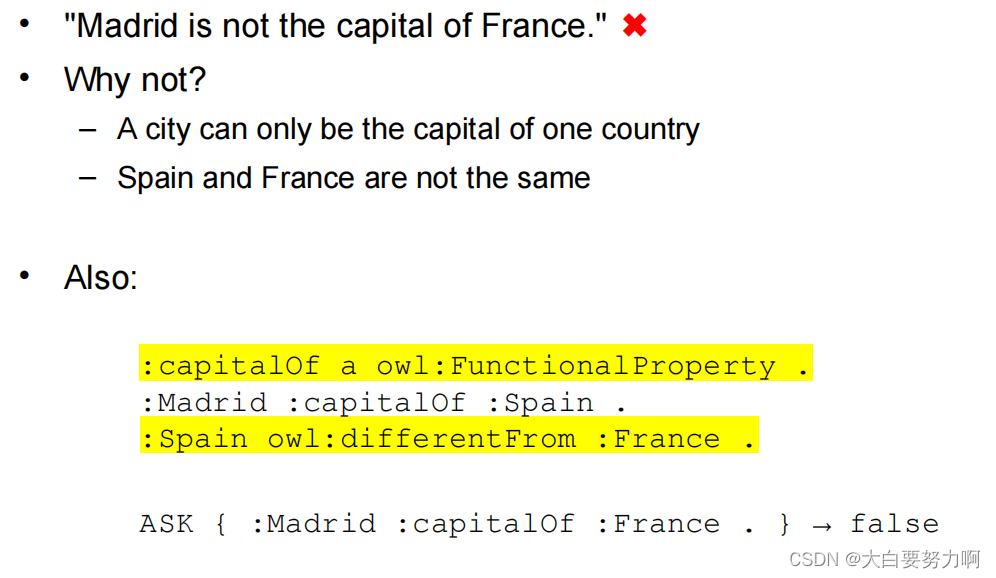
:hasCapital a owl:FunctionalProperty .
:Finland :hasCapital :Helsinki .
:Finland :hasCapital :Helsingfors .
→:Helsinki owl:sameAs :Helsingfors .
Inverse Functional Properties
– if A and C are in relation ifp and B and C are in relation ifp, then, A and B are the same. ifp(x) is a unique identifier for x. [Only one subject]
:capitalOf a owl:InverseFunctionalProperty .
:Helsinki :capitalOf :Finland .
:Helsingfors :capitalOf :Finland .
→:Helsinki owl:sameAs :Helsingfors .
8.4 Expressive Ontologies using OWL

8.5 Restrictions
8.5.1 Define characteristics of a class
A powerful and important concept in OWL
# Example: Vegan recipes only contain vegetables as ingredients
:VeganRecipe rdfs:subClassOf :Recipe .
:VeganRecipe rdfs:subClassOf [
a owl:Restriction ;
owl:onProperty :hasIngredient ;
owl:allValuesFrom :Vegetable .
] .# Every human as exactly one mother
:Human rdfs:subClassOf [
a owl:Restriction ;
owl:onProperty :hasMother ;
owl:cardinality 1^^xsd:integer .
] .# Standard bicycles are vehicles without a motor
:StandardBicycle rdfs:subClassOf :Vehicle .
:StandardBicycle rdfs:subClassOf [
a owl:Restriction ;
owl:onProperty :hasMotor ;
owl:cardinality 0^^xsd:integer .
]
8.5.2 Restrictions(local) vs. Ranges(global)
Restrictions are local to a class
:VeganRecipe rdfs:subClassOf [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :hasIngredient ;owl:allValuesFrom :Vegetable .
] .
# other classes may use hasIngredient with meat or fish
Range: a global restriction
:hasIngredient rdfs:range :Food
# this holds once and for all whenever hasIngredient is used
8.5.3 The Anatomy of a Restriction
on Property – defines the property on which the restriction should hold
Restriction of values
owl:allValuesFrom – all values must be in this class
owl:someValuesFrom – at least one value must be in this class
Restriction of cardinalities
OWL Lite: only n=0 or n=1
owl:minCardinality – at least n values
owl:maxCardinality – at most n values
owl:cardinality – exactly n values
Both cannot be combined
# Example
# All ball sports require a ball
:BallSports rdfs:subClassOf [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :requires ;owl:someValuesFrom :Ball .
] .# All sports for which a ball is required are ball sports
:BallSports owl:equivalentClass [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :requires ;owl:someValuesFrom :Ball .
] .# Difference
:BallSports owl:equivalentClass [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :requires ;owl:someValuesFrom :Ball .
] .
:Soccer :requires :soccerBall .
:soccerBall a :Ball.
# A reasoner may conclude that soccer is a ball sports
# This would not work with subClassOf
# Caveat: gymnastics with a ball are also recognized as ball sports
8.5.4 Qualified Restrictions in OWL2
In OWL, cardinalities and value restrictions may not be combined, use either all/someValuesFrom or min/maxCardinality
OWL 2 introduces qualified restrictions
# Example: a literate person has to have read at least 1,000 books (newspapers and magazines do not count!)
:LiteratePerson rdfs:subClassOf [
a owl:Restriction ;
owl:onProperty :hasRead;
owl:minQualifiedCardinality "1000"^^xsd:integer ;
owl:onClass :Book . ] .# Analogously, there are also
owl:maxQualifiedCardinality
owl:qualifiedCardinality
在OWL中,只能分开,但是意义不一样,变成一个有文化的人读1000个东西 + 一个有文化的人读书,但是可能是1本书+999个杂志,无法表达必须是1000本书的意思
8.5.5 Using Restriction Classes as Ranges
Restrictions can also be used in other contexts
# Example: books, newspapers, and posters can be read, essentially: everything that contains letters
# Range of the predicate reads:
:reads rdfs:range [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :containsLetter ;owl:minCardinality 1^^xsd:integer .
] .
8.5.6 Using Restriction as Domains
If it works for ranges, it also works for domains
Note: only in OWL DL/Full
# to think about something, a brain is required
# Domain of the thinksAbout property:
:thinksAbout rdfs:domain [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :hasBodyPart ;owl:someValuesFrom :Brain .
] .
8.5.7 Nesting Restrictions
It is always possible to make things more complex
grandparents have children who themselves have at least one child
:GrandParent owl:equivalentClass [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :hasChild ;owl:someValuesFrom [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :hasChild ;owl:minCardinality 1^^xsd:integer .] .
] .
8.6 OWL DL
DL stands for “Description Logics” — a subset of first order logics
OWL DL introduces
- the full set of cardinality restrictions (OWL Lite allows only 0 and 1)
- more set operators
- closed classes
- value based restrictions
- restrictions on datatypes
- …
8.6.1 Complex Set Definitions
# Set union
:FacultyMembers owl:unionOf (:Students, :Professors) .# Complement set
:LivingThings owl:complementOf :InanimateThings .# Disjoint sets
:EdibleMushrooms owl:disjointWith :PoisonousMushrooms .# We can combine class definitions and restrictions:
:VegetarianRecipe rdfs:subClassOf [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :hasIngredient ;owl:allValuesFrom [a owl:Class .owl:complementOf [owl:unionOf (:Meat :Fish)]]
] .

8.6.2 Closed Classes



Basic semantic principles of RDF:
AAA: Anybody can say Anything about Anything
Non-unique name assumption -> we can control it with owl:sameAs and owl:differentFrom
The Open World Assumption says:
– everything we do not know could be true
–> so far, we have to live with it
# Example:
:Tim a :PeopleInOfficeD219 .
:John a :PeopleInOfficeD219 .
:Mary a :PeopleInOfficeD219 .
# This does not mean that there cannot be more people in D219
:Mike a :PeopleInD219 .# Sometimes, this is exactly what we want to say
# Works with owl:oneOf in OWL DL
:PeopleInOfficeD219 owl:oneOf (:Tim :John :Mary) .
:Mike a :PeopleInD219 . # Mike maybe just a name of these three people, but if it's different, then this is a contradiction
8.6.3 OWL DL: Restrictions with Single Values
# For ObjectProperties:
:AfricanStates owl:subClassOf [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :locatedOnContinentowl:hasValue :Africa] .# For DatatypeProperties:
:AlbumsFromTheEarly80s owl:subClassOf [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :yearowl:dataRange (1980^^xsd:integer 1981^^xsd:integer 1982^^xsd:integer) ]
8.6.4 OWL Lite/DL vs. OWL Full
OWL Lite/DL: a resource is either an instance or a class or a property
OWL Full does not have such restrictions
:Elephant a owl:Class .
:Elephant a :Species .
:Elephant :livesIn :Africa .
:Species a owl:Class .
OWL Lite/DL: classes are only instances of owl:Class
OWL Lite/DL: classes and properties can only have a predefined set of relations (e.g., rdfs:subClassOf)
8.7 OWL2
New Constructs and More (Syntactic sugar, New language constructs, OWL profiles)
8.7.1 OWL2: Syntactic Sugar


without syntactic sugar, how to construct before?

8.7.2 OWL2: Reflexive Class Restrictions
Using hasSelf
# Example: defining the set of all autodidacts(a self-taught person.):
:AutoDidact owl:equivalentClass [a owl:Restriction ;owl:onProperty :teaches ;owl:hasSelf "true"^^xsd:boolean ].
8.7.3 OWL2: Property Chains
Typically used for defining rule-like constructs,
# hasParent(X,Y) and hasParent(Y,Z) → hasGrandParent(X,Z)
# OWL Syntax:
:hasGrandparent owl:propertyChainAxiom ( :hasParent :hasParent ) .# Can be combined with inverse properties and others
# hasParent(X,Y) and hasParent(Z,Y) → hasSibling(X,Z) at least share one of parents
# This is not a proper chain yet, so we have to rephrase it to
# hasParent(X,Y) and hasParent-1(Y,Z) → hasSibling(X,Z)
# OWL Syntax:
:hasSibling owl:propertyChainAxiom ( :hasParent [ owl:inverseOf:hasParent ] ) .
8.7.4 OWL2 Profile
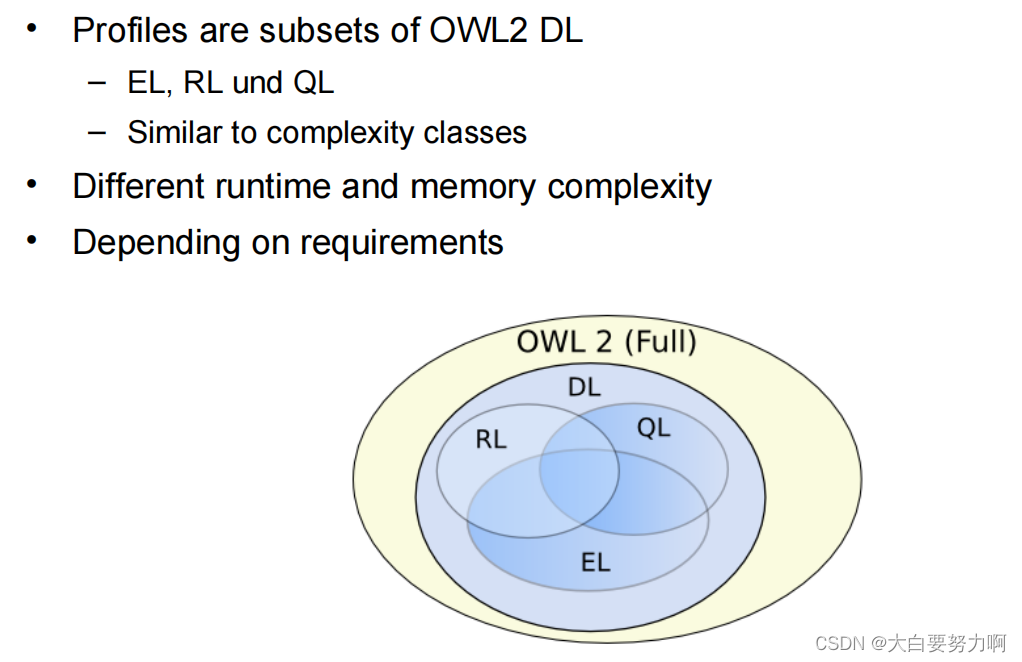
1. OWL2 EL (Expressive Language)
Fast reasoning on many standard ontologies
Restrictions, e.g.:
- someValuesFrom, but not allValuesFrom
- No inverse and symmetric properties
- No unionOf and complementOf
2. OWL2 QL (Query Language)
Fast query answering on relational databases
Restrictions, e.g.:
- No unionOf, allValuesFrom, hasSelf, …
- No cardinalities and functional properties
3. OWL2 RL (Rule Language)
- Subset similar to rule languages such as datalog
subClassOf is translated to a rule (Person ← Student) - Restrictions, e.g.:
Only qualified restrictions with 0 or 1
Some restrictions for head and body
The following holds for all three profiles:
Reasoning can be implemented in polynomial time for each of the three
Reasoning on the union of two profiles only possible in exponential time
OWL2 Example: Russell’s Paradox
8.7.5 Reasoning in OWL DL

Reasoning for OWL DL is more difficult
Forward chaining may have scalability issues
Conjunction (e.g., unionOf) is not supported by forward chaining (same holds for some other constructs, no negation)
Different approach: Tableau Reasoning
Underlying idea: find contradictions in ontology. i.e., both a statement and its opposite can be derived from the ontology
8.8 Typical Reasoning Tasks

basic idea: contradiction checking
Contradiction


8.8.1 Subclass Relations



8.8.2 Class equivalence

8.8.3 Class Consistency

8.8.4 Class Instantiation & Class enumeration

All reasoning tasks can be reduced to the same basic task i.e., consistency checking
This means: for building a reasoner that can solve those tasks, we only need a reasoner capable of consistency checking.
8.9 OWL DL
8.9.1 Ontologies in Description Logics Notation


8.9.2 Global Statements in Description Logic

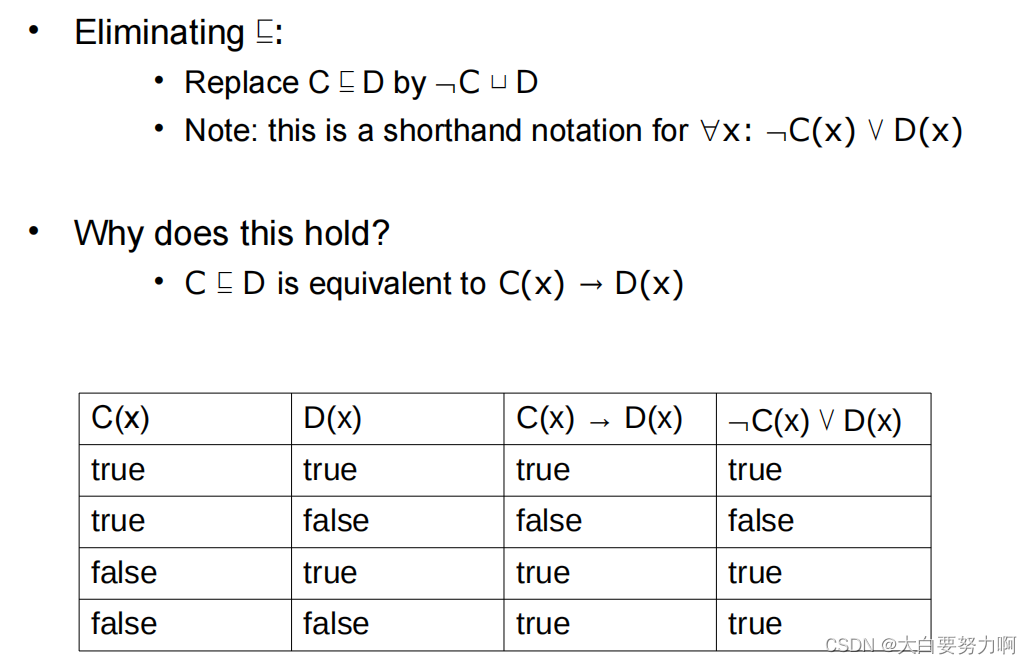
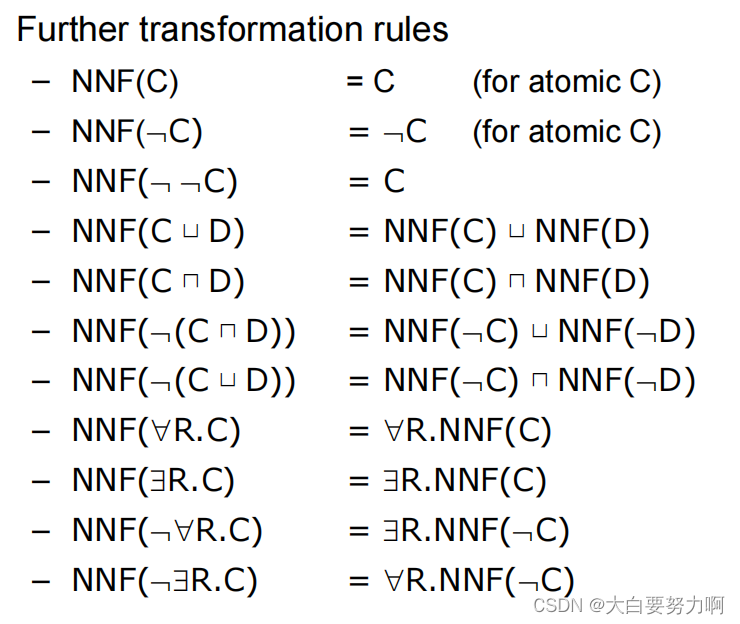
8.9.3 Negation Normal Form (NNF)

eliminate subclass
C(x) → D(x)
C(x): Predicate or property indicating that x belongs to class C.
D(x): Predicate or property indicating that x belongs to class D.
→: Logical implication, meaning “implies” or “if…then.”
eliminate equivalence

8.10 The Basic Tableau Algorithm
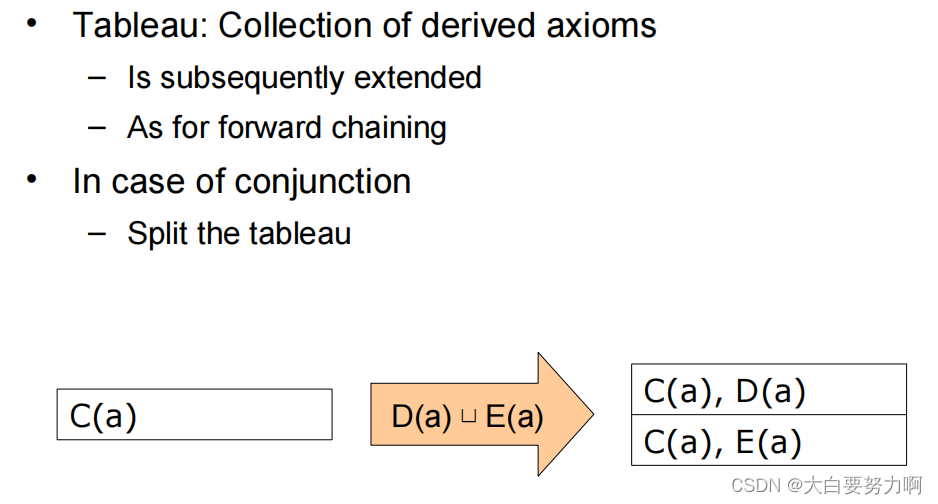
Tableau算法通过在逐步扩展的过程中不断检查矛盾来判断本体是否一致。当不再有新的公理可以添加,或者至少有一个部分的Tableau没有矛盾时,可以确保本体是一致的。如果任何一个部分的Tableau同时包含一个公理及其否定,那么这个部分就被认为包含矛盾,因此整个算法会停止在这个分支上的扩展。

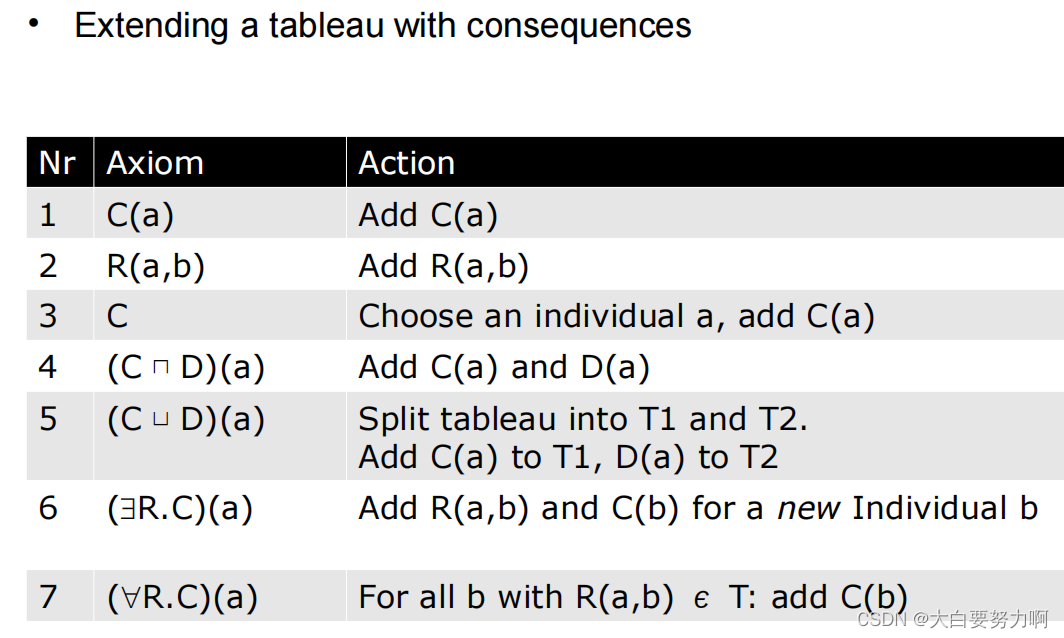
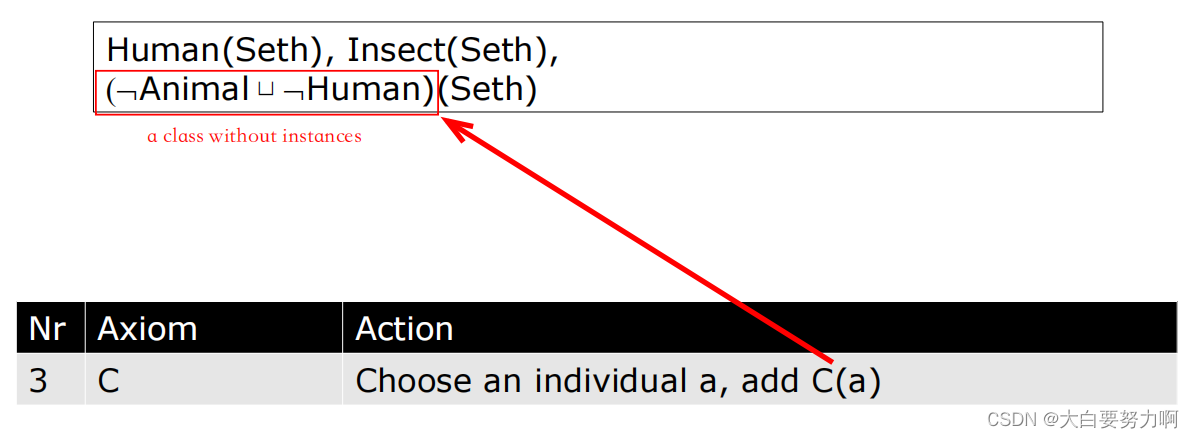
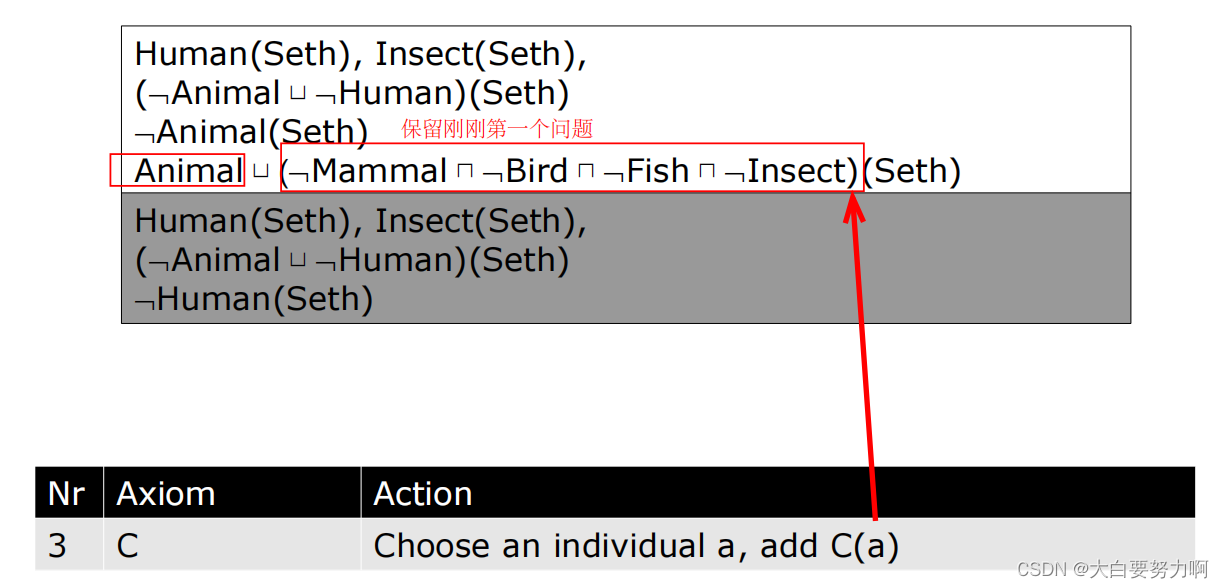
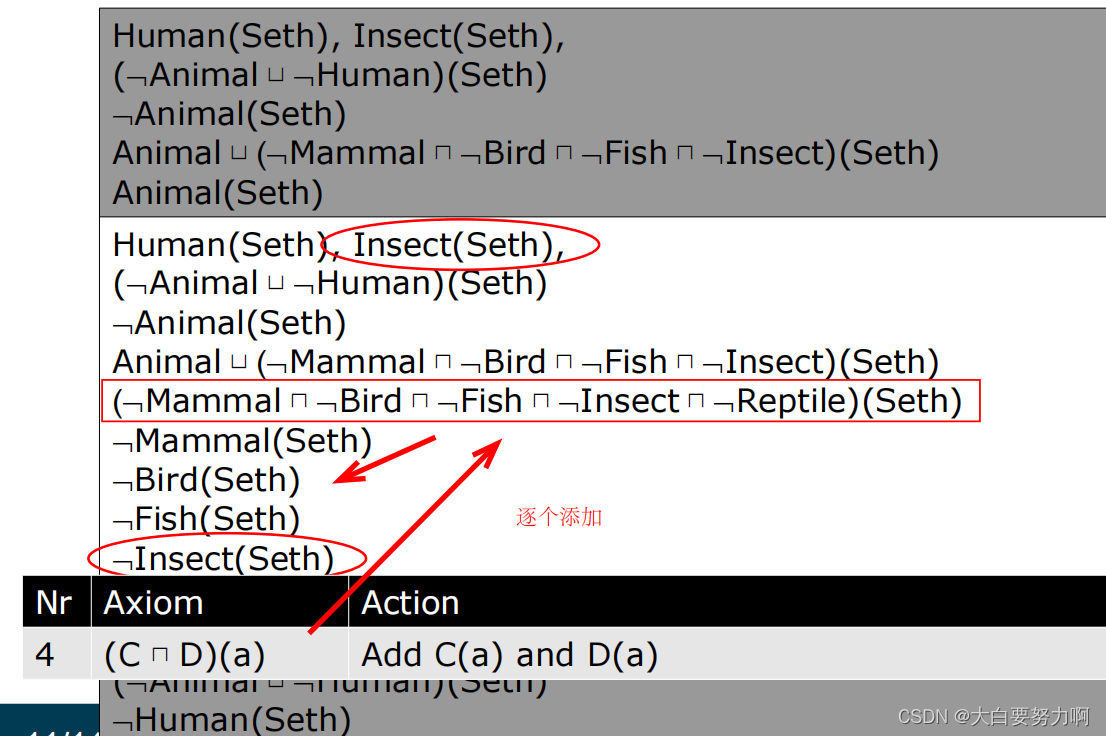
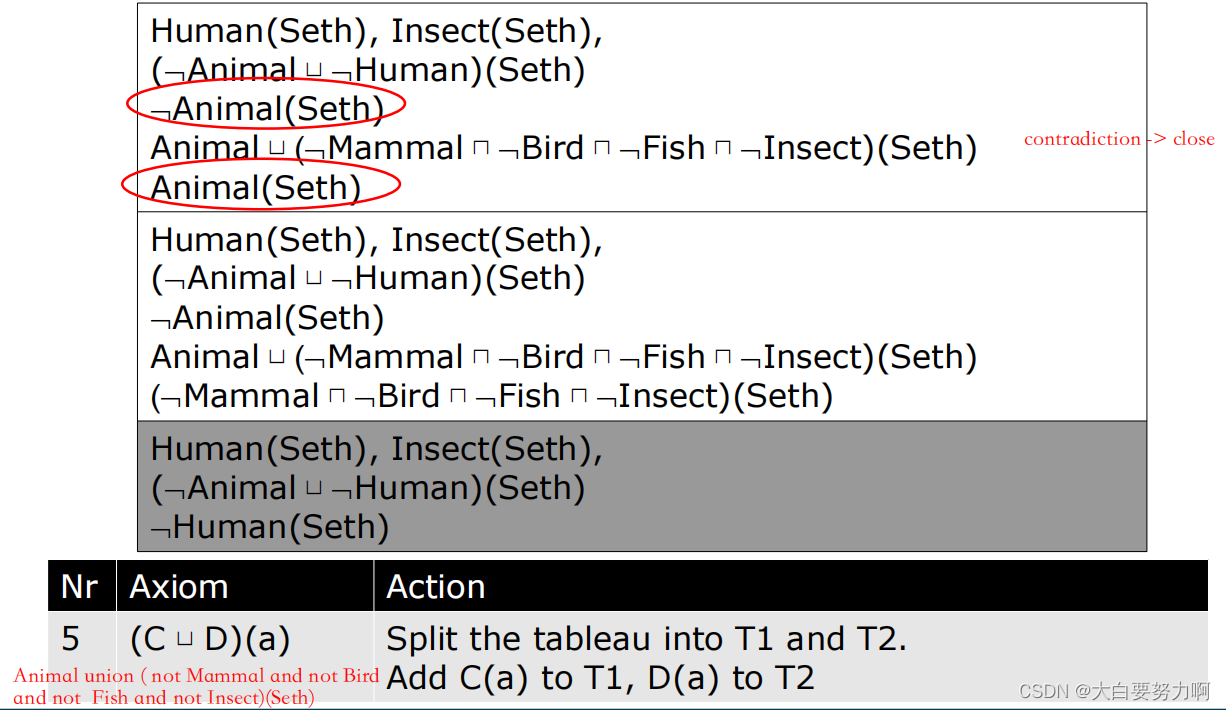
Algorithm
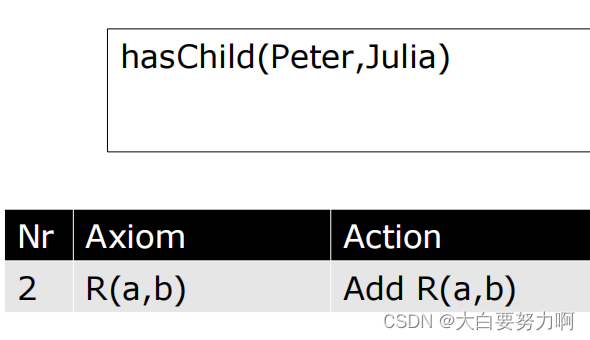
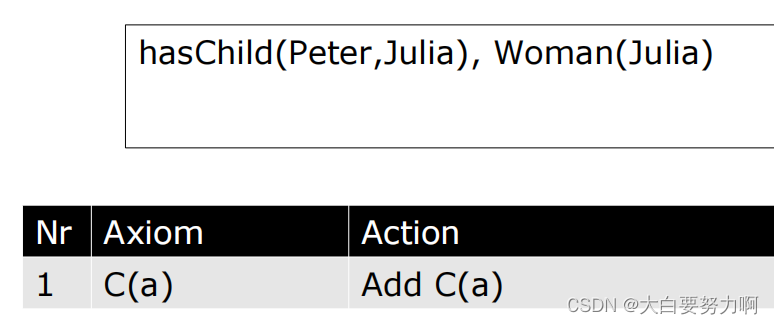
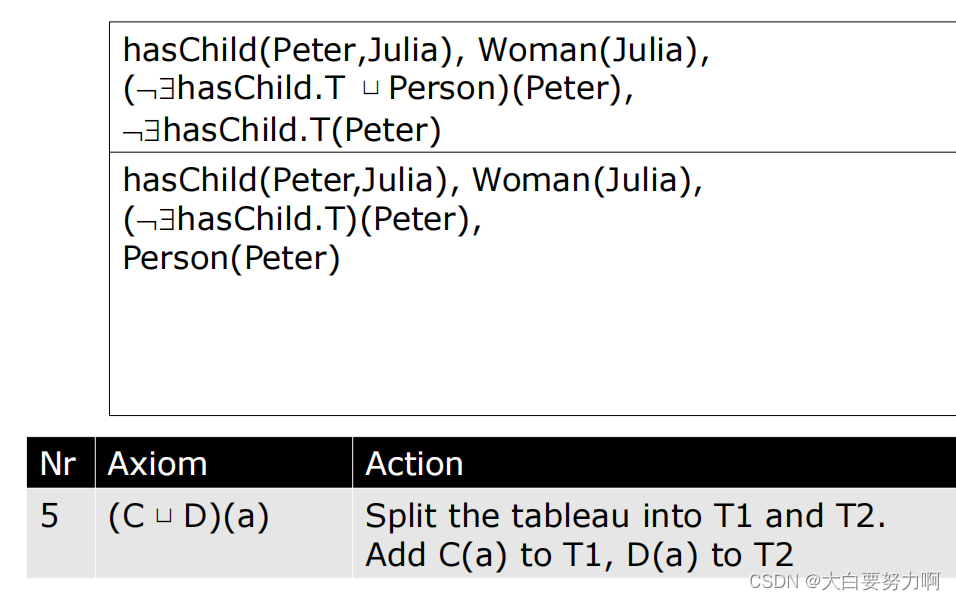
Axiom(公理):
Axiom 指的是本体中的一条陈述,它描述了某种关于个体、类、属性或关系的事实或规则。在Tableau算法中,Axiom 是用来构建和扩展表格的基本元素。通过引入新的Axiom,算法可以逐步探索可能的解释空间。
Action(动作):
Action 是指在Tableau算法的执行过程中,为了展开表格而执行的具体操作。这些操作包括对Axiom的分解、对个体的引入、对存在量词的展开等。通过执行这些Action,算法可以逐步构建具体的解释。

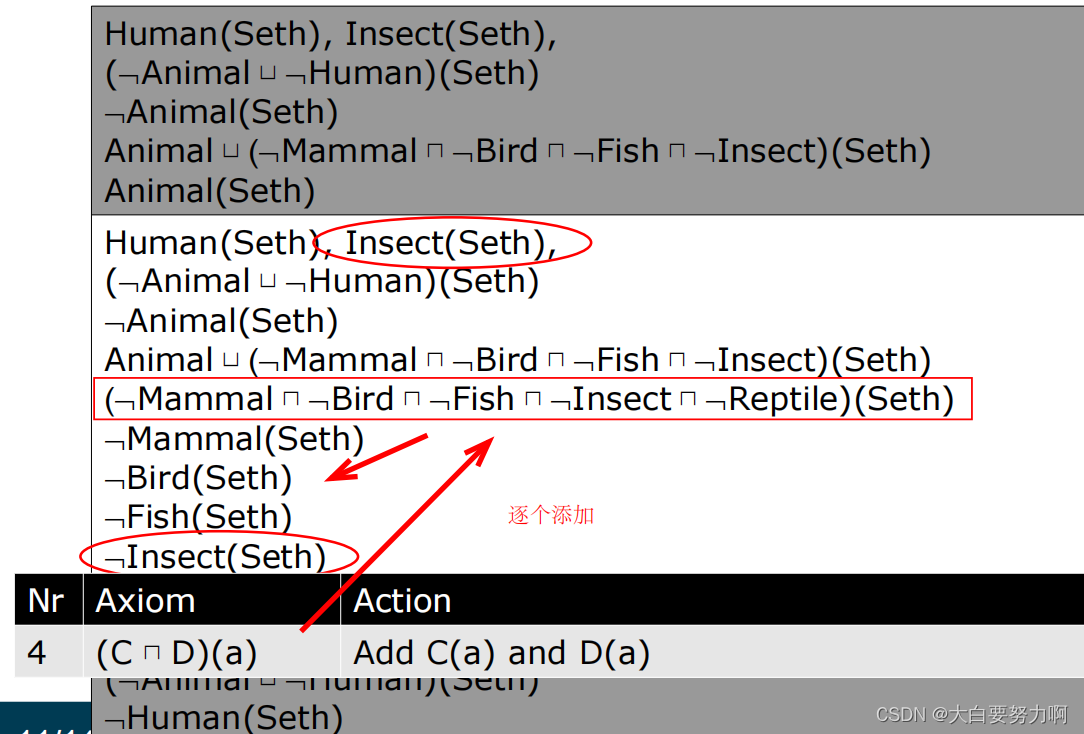
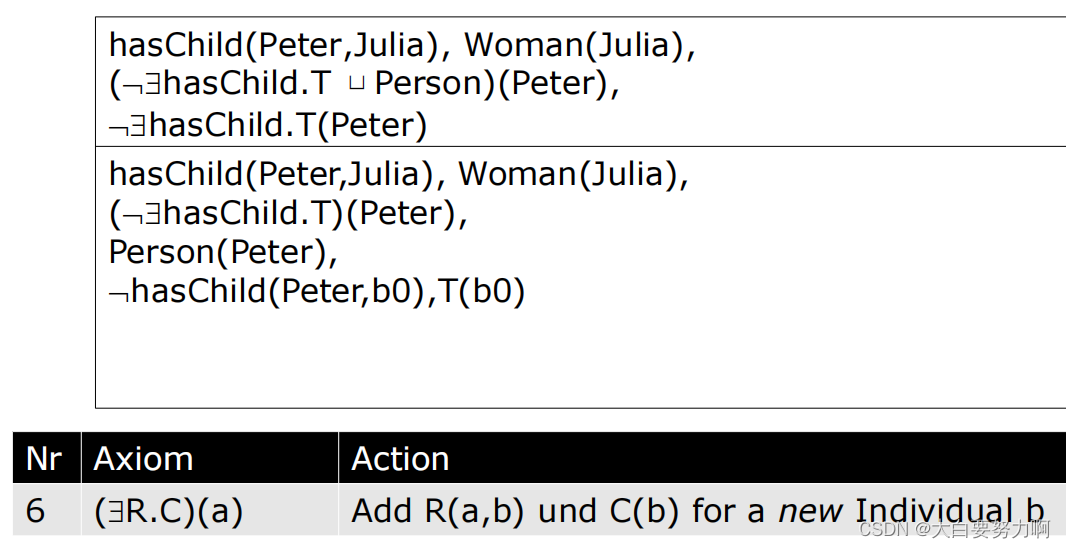
Example1


DL-NNF是一种形式化的逻辑表示,其中否定只作用于概念的基本成分上,而不涉及复合概念。尽管使用DL-NNF并非强制性要求,但它有一些优势:
简化推理:
DL-NNF形式的表达式更容易处理,有助于简化推理过程。这是因为否定的使用受到了限制,使得在算法中处理表达式更加直观和高效。
易于理解和实现:
DL-NNF形式的表达式更符合直观,更易于理解。这有助于实现和维护Tableau算法,使其更具可读性。
减少冗余计算:
使用DL-NNF形式可以减少在推理过程中进行的冗余计算。简化的表达形式避免了对复合概念进行重复的否定操作。
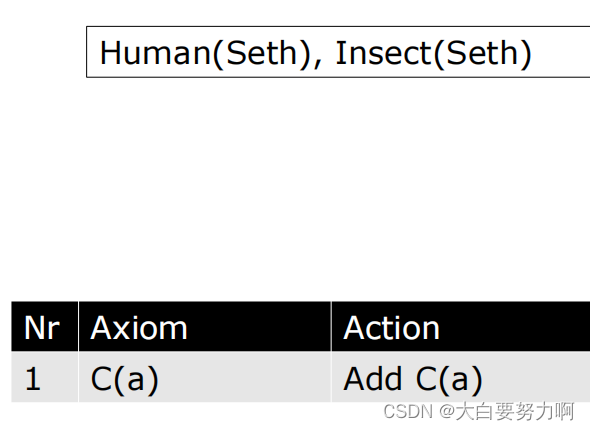
在表达式 “C(a)” 中,C 是一个概念,而 a 是一个个体。

Example2




Introducing Rule Blocking

Tableau Algorithm with Rule Blocking

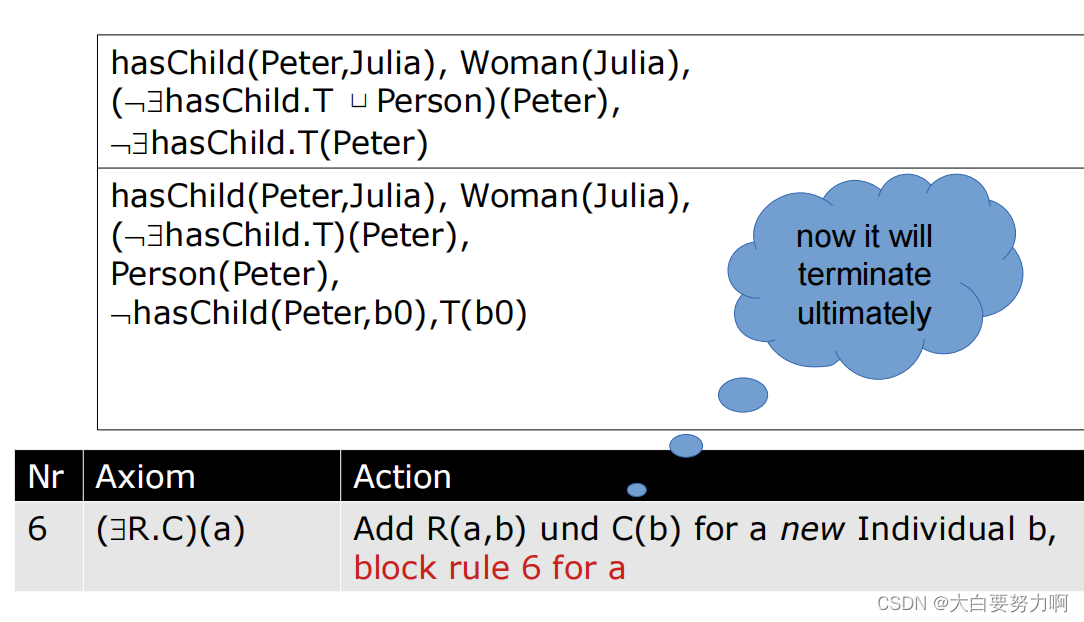
Tableau Algorithm: Wrap Up
An algorithm for description logic based ontologies, works for OWL Lite and DL
We have seen examples for some OWL expressions, Other OWL DL expressions can be “translated” to DL as well
And they come with their own expansion rules
Reasoning may become more difficult. e.g., dynamic blocking and unblocking
Optimizing Tableau Reasoners

8.11 OWL Lite vs DL

8.12 Complexity of Ontologies
Reasoning performance depends on ontology complexity
Rule of thumb: the more complexity, the more costly
Most useful ontologies are in OWL DL
But there are differences.
In detail: complexity classes
OWL DL是Web Ontology Language(OWL)的一个子语言,它在描述逻辑方面提供了丰富的表达能力。这意味着许多有用的本体都采用OWL DL进行建模,因为它能够更准确地表达复杂的概念和关系。尽管大多数有用的本体采用OWL DL,但实际上还存在其他本体语言和表示方法。这些语言可能具有不同的表达能力和语法结构,因此在推理性能和成本方面可能存在差异。本体的复杂性类,即用于描述本体中所包含信息复杂性的类别。不同的本体可以属于不同的复杂性类,而这些类别会对推理的复杂性和成本产生影响。
8.13 Simple Ontologies: ALC
ALC: Attribute Language with Complement
Allowed:
– subClassOf, equivalentClass
– unionOf, complementOf, disjointWith
– Restrictions: allValuesFrom, someValuesFrom
– domain, range
– Definition of individuals
8.14 SHIQ, SHOIN & co
Complexity classes are noted as letter sequences
Using
– S = ALC plus transitive properties (basis for most ontologies)
– H = Property hierarchies (subPropertyOf)
– O = closed classes (oneOf)
– I = inverse properties (inversePropertyOf)
– N = numeric restrictions (min/maxCardinality)
– F = functional properties
– Q = qualified numerical restrictions (OWL2)
– (D) = Usage of datatype properties
8.15 Some Tableau Reasoners
Fact
– University of Manchester, free
– SHIQ
Fact++/JFact
– Extension of Fact, free
– SHOIQ(and a little D), OWL-DL + OWL2
Pellet
– Clark & Parsia, free for academic use
– SHOIN(D), OWL-DL + OWL2
RacerPro
– Racer Systems, commercial
– SHIQ(D)

8.16 Limitations of OWL
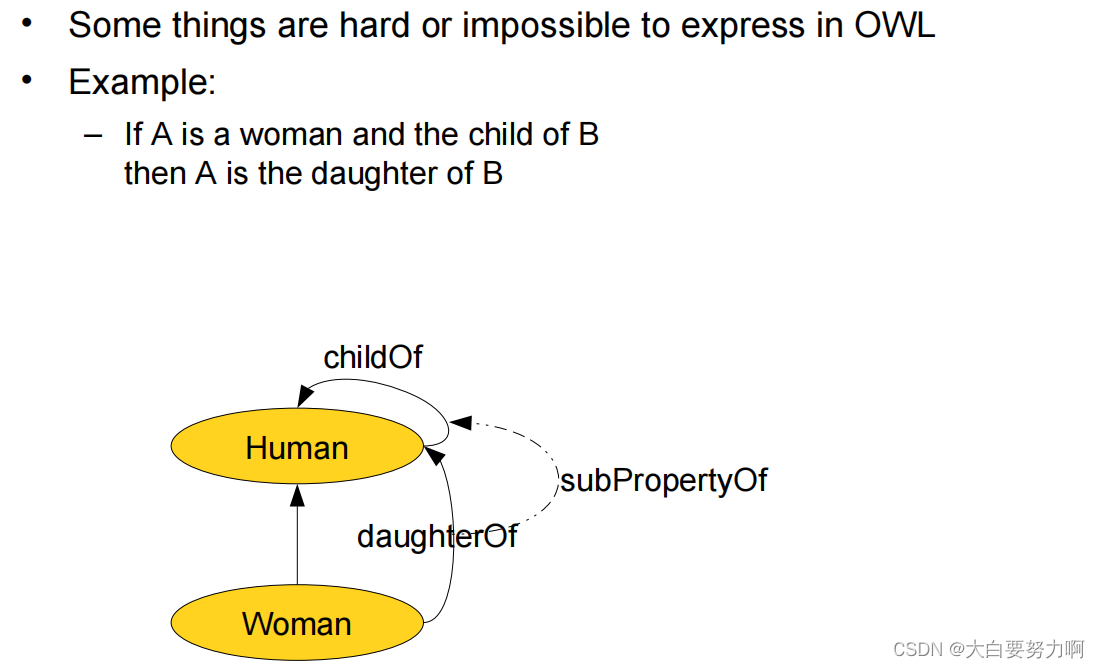



8.17Wrap Up



-docker的基本使用)


![[NCTF2019]Fake XML cookbook1](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[NCTF2019]Fake XML cookbook1)













