1.pair
pair用于存储两个不同类型的值(元素)作为一个单元。它通常用于将两个值捆绑在一起,以便一起传递或返回。
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
int main() {pair<int, string> person = make_pair(25, "jack");//存储一对值并初始化
//可简写为 pair<int, string> person(25, "jack");cout << person.first << " " << person.second;//25 jack
}
嵌套
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
int main() {pair<int, pair<int, int>> people=make_pair(3, make_pair(4, 5));cout << people.second.first;//4return 0;
}
排序规则
优先考虑first,若相等再比较second…
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {pair<int, std::string> people[] = {make_pair(25, "Alice"),make_pair(30, "Bob"),};sort(people, people + 2);for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {cout << people[i].first<< people[i].second << endl;}return 0;
}
2.vector
提供了动态数组(可变大小数组)的实现,存储的事一系列相同类型的元素
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {vector<int> a;//定义整型a容器a.push_back(1);a.push_back(2);a.push_back(3);cout << a[0]<<endl;//首元素:1a.pop_back();//删除尾部元素cout << a.size();//元素个数:2
}
元素插入操作
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {vector<int> a = { 5,4,3 };a.insert(a.begin() + 1, 999);cout << a[1];//999
}
初始化与排序
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {//初始化vector<int> a(5, 1);//对容器a初始化为{1,1,1,1,1}vector<int> b = { 5,4,3,2,1 };//排序sort(b.begin(), b.end());for (int i = 0; i < b.size(); i++) {cout << b[i];//12345}
}
去重排序
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {vector<int> a = { 5,4,3,2,1,5,5 };sort(a.begin(), a.end());//unique只能去掉相邻重复元素,所以先sort//auto用于自动推导 unique 函数返回的迭代器类型auto b = unique(a.begin(), a.end());auto n = distance(a.begin(), b);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cout << a[i];//12345}
}
另一种去重排序方式
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {vector<int> a = { 5,4,3,2,1,5,5 };sort(a.begin(), a.end());//1 2 3 4 5 5 5auto b = unique(a.begin(), a.end());//b指向了多余元素的起始位置(排序完成后的第二个5的位置)a.erase(b, a.end());//擦除从b到末尾的元素,a的大小也同时修改了。即删除了后面的两个5for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) {cout << a[i];//12345}
}
输出可以使用以下方式
循环变量 i 依次取 a 容器中的每个元素的值
const 保证了元素不会被修改
auto 使编译器自动推断元素的类型
& 表示使用引用来避免不必要的复制
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {vector<int> a = { 5,4,3,2,1,5,5 };sort(a.begin(), a.end());auto b = unique(a.begin(), a.end());a.erase(b, a.end());for (const auto& i : a) {cout << i;//12345}
}
3.list
较少使用
以节点存储,以指针链接的链表结构
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {// 创建一个空的 list,存储整数list<int> myList;// 在列表末尾插入元素myList.push_back(1);myList.push_back(2);myList.push_back(3);//列表元素为123// 在列表开头插入元素myList.push_front(6);//列表元素为6123// 遍历列表并打印元素for (const auto& i : myList) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;//输出了:6 1 2 3// 删除列表中的元素myList.pop_back();myList.pop_front();//列表元素为12
}

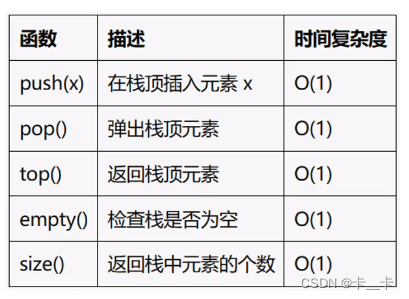
4.stack
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {stack<int> myStack;// 压栈操作myStack.push(1);myStack.push(2);myStack.push(3);//栈内(从下到上):123// 访问栈顶元素cout << myStack.top();//3// 弹栈操作myStack.pop();//3被弹出// 再次访问栈顶元素cout << myStack.top();//2//栈内(从下到上):12// 获取栈中元素的数量cout << "Stack size: " << myStack.size() << endl;//2// 检查栈是否为空if (myStack.empty()) {cout << "Stack is empty." << endl;}else {cout << "Stack is not empty." << endl;}
}
5.queue
(1)普通队列
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {queue<int> myQueue;// 入队操作myQueue.push(1);myQueue.push(2);myQueue.push(3);//队列(从头到尾):123// 访问队头元素cout << myQueue.front();//1// 出队操作myQueue.pop();//1出// 再次访问队头元素cout <<myQueue.front();//2//队列(从头到尾):23// 获取队列中元素的数量cout << myQueue.size();//2// 检查队列是否为空if (myQueue.empty()) {cout << "Queue is empty." << endl;}else {cout << "Queue is not empty." << endl;}
}
(2)优先队列/堆
队列中的元素是按照一定优先级进行排序的,默认情况下是从小到大排序的,即最大元素位于队列的前面。在插入元素时会插入到指定位置,确保队内有序。(大根堆)
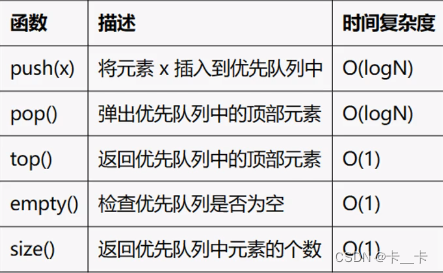
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {priority_queue<int> maxHeap;// 插入元素maxHeap.push(3);maxHeap.push(1);maxHeap.push(4);maxHeap.push(2);while (!maxHeap.empty()) {cout << maxHeap.top()<<" ";maxHeap.pop();}//4 3 2 1
}
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {priority_queue<int> maxHeap;// 插入元素maxHeap.push(3);maxHeap.push(1);maxHeap.push(4);maxHeap.push(2);队列元素:4 3 2 1// 访问队头元素(最大元素)cout << maxHeap.top();//4// 弹出队头元素maxHeap.pop();//4出//队列元素:3 2 1// 再次访问队头元素cout << maxHeap.top();//3// 获取队列中元素的数量cout << maxHeap.size();//3// 检查队列是否为空if (maxHeap.empty()) {cout << "Priority queue is empty." << endl;}else {cout << "Priority queue is not empty." << endl;}
}
小根堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> minHeap
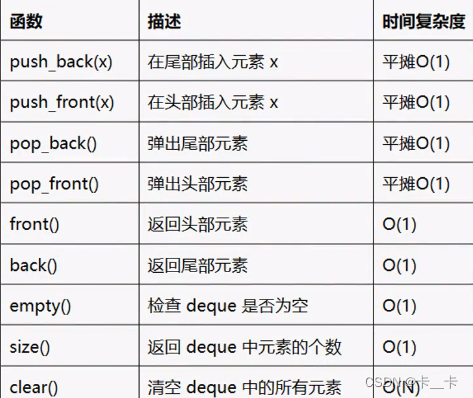
(3)双端队列
#include <deque>
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
int main() {// 创建一个双端队列deque<int> deque;// 向双端队列的尾部添加元素deque.push_back(1);//队列元素:1deque.push_back(2);//队列元素:1(头) 2(尾)// 向双端队列的头部添加元素deque.push_front(3);//队列元素:3 1 2deque.push_front(4);//队列元素:4 3 1 2// 打印双端队列的元素for (int n : deque) {cout << n;}// 4 3 1 2// 从双端队列的尾部删除元素deque.pop_back();//队列元素:4 3 1// 从双端队列的头部删除元素deque.pop_front();//队列元素:3 1
}
[例1] CLZ银行问题


评测系统
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {int num;cin >> num;//操作数量queue<string> vipQueue;queue<string> normalQueue;for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) {string operation,name;cin >> operation;if (operation == "IN") {cin >> name;char type;cin >> type;if (type == 'V') {vipQueue.push(name);}else {normalQueue.push(name);}}else {char type;cin >> type;if (type == 'V'&&!vipQueue.empty()) {vipQueue.pop();}else if(type=='N'&&!normalQueue.empty()) {normalQueue.pop();}}}while (!vipQueue.empty()) {cout << vipQueue.front()<<endl;vipQueue.pop();}while (!normalQueue.empty()) {cout << normalQueue.front() << endl;normalQueue.pop();}
}
[例2] 合并果子


评测系统
每次选择两个最小的数合并(贪心),并将合并后的新数重新放入堆中
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {int kind;cin >> kind;priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> minHeap;for (int i = 0; i < kind; ++i) {int num;cin >> num;minHeap.push(num);}int sum = 0;while (minHeap.size() > 1) {int heapone=minHeap.top();minHeap.pop();int heaptwo = minHeap.top();minHeap.pop();sum += heapone + heaptwo;minHeap.push(heapone + heaptwo);}cout << sum;
}
[例3] 建筑抢修


评测系统
我们对建筑按照截止时间进行排序,并使用一个最大堆(优先队列)来动态管理当前的修理计划。每次当总修理时间超过当前考虑的建筑的截止时间时,我们从堆中移除修理时间最长的建筑。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct building {int repairtime;int deadline;
};
int cmp(building a, building b) {return a.deadline < b.deadline;
}
int main()
{int total = 0;int n;cin >> n;vector<building> a(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {cin >> a[i].repairtime >> a[i].deadline;}sort(a.begin(), a.end(), cmp);priority_queue<int> q;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {q.push(a[i].repairtime);//一定修,因为马上deadline了total += a[i].repairtime;if (total > a[i].deadline) {//如果超时,那么根据大根堆,队列中维修时长最大的移除total -= q.top();q.pop();}}cout << q.size();return 0;
}
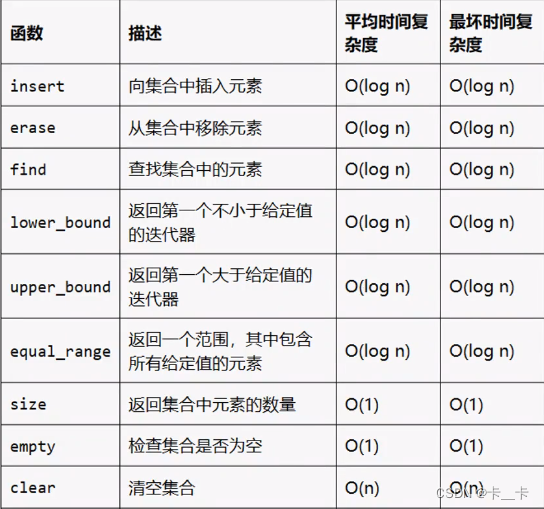
6.set
set存储唯一元素,默认升序
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;int main() {set<int> s;s.insert(3);s.insert(1);s.insert(4);s.insert(2);s.insert(2); // 这个操作没有效果,因为 2 已存在cout << "Set contains:";for (int x : s) {cout << " " << x;}cout << endl;//输出:1 2 3 4
}
降序排列
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;int main() {set<int,greater<int>> s;//改为降序排列s.insert(3);s.insert(1);s.insert(4);s.insert(2);s.insert(2);cout << "Set contains:";for (int x : s) {cout << " " << x;}cout << endl;//输出:4 3 2 1
}

multiset允许重复元素
#include <iostream>
#include <set>using namespace std;int main() {multiset<int> ms;ms.insert(3);ms.insert(1);ms.insert(4);ms.insert(2);ms.insert(2); // 可以插入重复元素// 输出 multiset 的内容cout << "Multiset contains:";for (int x : ms) {cout << " " << x;}//输出:1 2 2 3 4// 计算某个值在 multiset 中出现的次数int count = ms.count(2);cout <<count;//2
}

7.map
map存储键值对,键是唯一的,键值对是根据键排序的(自动排序,默认升序排列),可以直接使用键访问对应的值;在插入新元素时,若键已存在,则更新其对应的值
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;int main() {// 创建一个 mapmap<string, int> marks;// 插入键值对marks["Alice"] = 88;marks["Bob"] = 95;marks["Charlie"] = 72;// 更新键对应的值marks["Alice"] = 91;// 遍历并打印 mapfor (const auto& pair : marks) {cout << pair.first << pair.second << endl;}/*输出Alice91Bob95Charlie72*/// 查找并访问元素if (marks.find("Bob") != marks.end()) {cout << marks["Bob"];//95}
}

8.练习
(1)宝藏排序

评测系统
#include <iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {int n;cin >> n;priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> pq;while (n--) {int x;cin >> x;pq.push(x);}while(!pq.empty()) {cout<<pq.top()<<" ";pq.pop();}
}
(2)小蓝吃糖果

评测系统
找出糖果数量最多的种类,其余糖果进行插空。
若最多种类的糖果数量是max,一共有max-1个空,第二大种类的糖果数一定不超过max-1,越插空越多,以此类推。只有当所有糖果加起来也没有填满max-1个空时,失败。
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {int n;cin >> n;long long int total=0;priority_queue<int> a;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int x;cin >> x;a.push(x);total += x;}int max = a.top();total -= max;if (max - 1 <= total)cout << "Yes";elsecout << "No";
}
(3)小蓝的括号串


评测系统
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {stack<char> s;int n;cin >> n;while (n--) {char x;cin >> x;if (x == '(') {s.push(x);}else {if (!s.empty()) {s.pop();}else {cout << "No";return 0;}}}if (!s.empty()) {cout << "No";}else {cout << "Yes";}
}
(4)快递分拣


评测系统
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {int n;cin >> n;map<string, vector<string>> m;//一对多的关系,一个键对应多个值vector<string> vm;//记录城市出现顺序while (n--) {string s, p;cin >> s >> p;if (m.find(p) == m.end()) {//当前城市首次出现,可改为if(m.count(p)==0)vm.push_back(p);}m[p].push_back(s);}for (const auto& x : vm) {cout << x <<" " << m[x].size() << endl;for (const auto& x2 : m[x]) {cout << x2 << endl;}}
}
(5)顺子日期

答案:14
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int panduanmonth(int x) {if (x == 1 || x == 3 || x == 5 || x == 7 || x == 8 || x == 10 || x == 12)return 31;else if (x == 4 || x == 6 || x == 9 || x == 11)return 30;else {return 28;}
}
string formatDate(int a, int b, int c) {string s = "2022";if (b < 10) {s+= "0"+to_string(b);}else {s+= to_string(b);}if (c < 10) {s += "0" + to_string(c);}else {s += to_string(c);}return s;
}
bool isSequentialDate(string s) {for (int i = 0; i <= 5; ++i) {if (s[i] + 1 == s[i + 1] && s[i + 1] + 1 == s[i + 2])return true;}return false;
}
int main() {int count = 0;for (int month = 1; month <= 12; month++) {for (int day = 1; day <= panduanmonth(month); day++) {string date = formatDate(2022, month, day);if (isSequentialDate(date)) {count++;}}}cout << count;
}
(6)小明和完美序列

评测系统
对于序列中的每个数字,计算它出现的次数。比较其值和出现的次数。如果出现次数大于数字的值,则需要删除多余的出现。如果出现次数小于数字的值,则需要全部删除。计算总共需要删除的数字数量。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main() {int n;cin >> n;map<int, int> count;int num;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {cin >> num;count[num]++;}int deletecount = 0;for (const auto& x : count) {int a = x.first;int b = x.second;if (a > b) {deletecount += b;}else if (a < b) {deletecount += b - a;}}cout << deletecount;
}


Echarts使用bmap.js实现轨迹动画效果)
)

)
)











之后执行的方法)
