一、问题描述
题目九:出租车计价器设计(平台实现)★★
完成简易出租车计价器设计,选做停车等待计价功能。
1、基本功能:
(1)起步8元/3km,此后2元/km;
(2)里程指示信号为每前进50米一个高电平脉冲,上升沿有效;显示行驶公里数,精确到0.1km。(模拟时速40km/h)
(3)前进里程开始之前显示价钱,精确到0.1元;
(4)用两个按键分别表示开始行程和结束行程。
2、选做功能:
(1)增加一个停车等待/恢复行程按钮,用2个数码管显示等待时间,精确到0.1分钟。
(2)等候费1元/min,计价精度为0.1元。
二、设计方案
根据题设分析得到出租车的计费工作原理分成以下4个阶段:
(1)出租车起步开始计费,首先显示起步价(设计起步费为8.0元),当出租车在3km的行驶里程以内,只收起步价8.0元;
(2)出租车行驶超过3km后,按每公里2元计费(在8.0元基础上每行驶1km车费加2.0元),车费依次累加;
(3)出租车暂停行驶(如行驶中遇红灯或中途由于堵车等意外情况而停车),按停止时间进行计费,每1分钟计费1.0元;
(4)若行程终止,则车费清零,等待下一次计费的开始。
对应主要可分为以下三大模块去实现:
(1)秒分频模块:
脉冲生成模块保证整个系统的同步工作,对于电路板上提供的100Hz时钟脉冲信号进行分频处理,得到题目中需要用到的秒分频信号,便于后续计量数据模块对于信号的处理。
(2)计量控制模块:
计量数据模块主要有三个部分组成,分别是计价部分、计时部分和计程部分,这三个部分是出租车计价器系统多功能实现的基础与保证。
计价部分又可以分为两个内容,其一是在出租车正常行驶的过程中根据不同的收费标准分段将里程数折算为对应的价格费用,如本题中在起步3km以内固定收费8.0元,而超出3km起步里程后对后续的每公里里程折算为2元的价格费用;其二是在出租车暂停行驶的情况下,将等候时间折算为对应的价格费用,如本题中将每分钟折算为1.0元。
与此同时,出租车需要实现开始行程、停车等待、恢复行程和结束行程四个动作,因此控制出租车的状态需要设计三个按键,用来选择出租车的启动、暂停和终止,对应按键按下时将对应的电平从低电平翻转为高电平,并将此信号送往控制模块产生相应的响应动作。
(3)译码显示模块:
译码显示模块用于将出租车的实时里程数、价格费用和等待时间显示出来。
① 用2个数码管显示实时里程数;
② 用2个数码管显示等待时间;
③ 用4个数码管显示价格费用。
系统顶层框图如下:

三、系统实现
1、基本流程
(1)设计输入:运用VHDL硬件描述语言根据题目所要求实现的功能和自己设计的拓展部分进行电路设计(开发软件:Quartus Ⅱ 9.0);
(2)文件处理:对设计输入的文件进行编译检查、逻辑化简、改进优化等一系列步骤,最后生成对应的编程文件;
(3)仿真验证:对设计处理的编程文件进行仿真测试,以验证程序是否符合题目给出的要求和设计的功能是否可以实现;
(4)元器件编程:将对应的VHDL硬件描述语言的编程代码数据下载至具体的可编程元器件中;
(5)硬件测试:将编写好的系统程序载入到实验电路板上并按题目要求进行测试(硬件:EDA-I实验板,如下图)。

2、程序流程图

3、代码说明
(1)分频:根据题目要求首先设置秒计时,即先完成1s分频;再根据50米给出一个高脉冲,设置4.5s分频;对于精确到0.1元的计价,设计6s分频;对于精确到0.1km的里程,设计9s分频。
p1:process(rst, clk) -- 1s 分频begin if rst = '0' then if clk'event and clk = '1' then if count_1 = 99 then count_1 <= 0;clk1hz <= '1'; else count_1 <= count_1 + 1;clk1hz <= '0'; end if;end if; end if; end process; p2:process(rst, clk) -- 4.5s 分频begin if rst = '0' then if clk'event and clk = '1' then if count_2 = 449 then count_2 <= 0;clklhz_1 <= '1'; else count_2 <= count_2 + 1;clklhz_1 <= '0'; end if;end if; end if; end process; p3:process(rst, clk) -- 6s 分频begin if rst = '0' then if clk'event and clk = '1' then if count = 599 then count <= 0;clklhz_2 <= '1'; else count <= count + 1;clklhz_2 <= '0'; end if;end if; end if; end process; p4:process(rst, clk) -- 9s 分频begin if rst = '0' then if clk'event and clk = '1' then if count_3 = 899 then count_3 <= 0;clklhz_3 <= '1'; else count_3 <= count_3 + 1;clklhz_3 <= '0'; end if;end if; end if; end process;
(2)段选与片选:对需要显示在数码管上的信号量设计译码方案,并根据实际情况分出的不同情况进行不同的段选与片选。
p9:process(clk2)beginif clk2'event and clk2 = '1' thencase show iswhen "000" =>show <= "001";pianxuan <= "11111110";bt <= c0;flag <= 0;when "001" =>show <= "010";pianxuan <= "11111101";bt <= c1;flag <= 1;when "010" =>show <= "011";pianxuan <= "11111011";bt <= c2;flag <= 0;when "011" =>show <= "100";pianxuan <= "11110111";bt <= c3;flag <= 0;when "100" =>show <= "101";pianxuan <= "11101111";bt <= k0;flag <= 0;when "101" =>show <= "110";pianxuan <= "11011111";bt <= k1;flag <= 1;when "110" =>show <= "111";pianxuan <= "10111111";bt <= m0;flag <= 0;when "111" =>show <= "000";pianxuan <= "01111111";bt <= m1;flag <= 0;end case;end if;end process;p10:process(bt, flag)beginif flag = 1 thencase bt iswhen "0000" => duanxuan <= "11111110"; --0when "0001" => duanxuan <= "10110000";when "0010" => duanxuan <= "11101101";when "0011" => duanxuan <= "11111001";when "0100" => duanxuan <= "10110011";when "0101" => duanxuan <= "11011011";when "0110" => duanxuan <= "11011111";when "0111" => duanxuan <= "11110000";when "1000" => duanxuan <= "11111111";when "1001" => duanxuan <= "11111011"; --9when others => NULL;end case;elsif flag = 0 thencase bt iswhen "0000" => duanxuan <= "01111110"; --0when "0001" => duanxuan <= "00110000";when "0010" => duanxuan <= "01101101";when "0011" => duanxuan <= "01111001";when "0100" => duanxuan <= "00110011";when "0101" => duanxuan <= "01011011";when "0110" => duanxuan <= "01011111";when "0111" => duanxuan <= "01110000";when "1000" => duanxuan <= "01111111";when "1001" => duanxuan <= "01111011"; --9when others => NULL;end case; end if;end process;
end;
(3)里程计数:根据3km内和超出3km部分进行计价模式切换,并设计完成进位部分和重置部分。
p7:process(rst, start, mile_clk) --里程计数begin if rst = '1' then k0 <= "0000"; k1 <= "0000"; mode <= '0';elsif clklhz_3'event and clklhz_3 = '1' thenif wait_signal = '0' and start = '1' then if k1 & k0="00110000" then --超过3kmmode <= '1'; end if; if k0 = "1001" then k0 <= "0000"; if k1 = "1001" then k1 <= "0000"; else k1 <= k1 + '1'; end if; else k0 <= k0 + '1'; end if; end if;end if; end process;
(4)等待时间计数:此处为了方便观察实验结果,我将显示分钟改为了显示秒钟,但仍按分钟对应的秒数进行进位(0-59s)。
p5:process(rst, clk1hz, start, wait_signal) --等待时间计数begin if rst = '1' then --乘客离开m0 <= "0000";m1 <= "0000"; elsif start = '0' then --没开车wait_clk <= '0'; elsif clklhz_2'event and clklhz_2 = '1' then if wait_signal = '1' then --停车if sec = 9 thensec <= 0;if m0 = "1001" then m0 <= "0000"; if m1 = "0101" thenm1 <= "0000"; else m1 <= m1 + '1'; end if; else m0 <= m0 + '1'; end if;else wait_clk <= '0'; sec <= sec + 1;if m0 = "1001" then m0 <= "0000"; if m1 = "0101" thenm1 <= "0000"; else m1 <= m1 + '1'; end if; else m0 <= m0 + '1'; end if; end if; else wait_clk <= '0'; end if; end if; end process;
(5)计费:根据不同的行程状态对应不同的时钟信号cost_clk,按50m上升沿时钟频率更新计算费用,并完成进位部分和重置。
p6:process(rst, clklhz_1, clklhz_2) --检测mile上升沿beginif wait_clk = '1' or rst = '1' thenmile_clk <= '0';elsif rst = '0' and wait_clk = '0' thenmile_clk <= clklhz_1;end if; end process; cost_clk <= clklhz_2 when wait_signal = '1' else mile_clk when mode = '1' else '0'; p8:process(rst, start, cost_clk) --计费begin if rst = '1' then --计价结束c0 <= "0000";c1 <= "0000"; c2 <= "0000";c3 <= "0000"; elsif start = '1' and mode = '0' then --还在起步范围c0 <= "0000";c1 <= "1000"; --8.0元c2 <= "0000"; c3 <= "0000"; elsif cost_clk'event and cost_clk = '1' then --50m每个上升沿/中途停车等待if mode = '1' and start = '1' then if c0 = "1001" then c0 <= "0000"; if c1 = "1001" then c1 <= "0000"; if c2 = "1001" then c2 <= "0000";if c3 = "1001" thenc3 <= "0000";elsec3 <= c3 + '1';end if;else c2 <= c2 + '1'; end if; else c1 <= c1 + '1'; end if; else c0 <= c0 + '1'; end if; end if;end if; end process;
(6)消除抖动:通过延时计数的方法将不连续的输入脉冲信号调整为稳定的输出信号。
xiaodou:process(clk, start_in, wait_signal_in, rst_in)beginif clk'event and clk = '1' thenif count < 1 thencount <= count + 1;elsecount <= 0;if start_in = '1' thenstart <= '1';elsif wait_signal_in = '1' thenwait_signal <= '1';elsif rst_in = '1' thenrst <= '1';end if;end if;end if;end process;
4、完整代码
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
use ieee.std_logic_arith.all;
entity taxi is
port(clk:in std_logic; --时钟信号start:inout std_logic;wait_signal:inout std_logic;rst:inout std_logic;numViewOutputSg:out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);numViewOutputBt:out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);clk2: in std_logic --高频时钟);
end; architecture bhv of taxi is signal mile_clk,clk1hz,clklhz_1,clklhz_2,clklhz_3:std_logic; --clklhz:分频后的时钟信号signal count:integer range 0 to 599;signal count_1:integer range 0 to 99; signal count_2:integer range 0 to 449;signal count_3:integer range 0 to 899;signal sec:integer range 0 to 59 :=0; --秒数signal c0,c1,c2,c3:std_logic_vector(3 downto 0); --费用(从低到高)signal k0,k1,m0,m1:std_logic_vector(3 downto 0); --k指公里 m指时间signal en0:std_logic :='0'; signal wait_clk,cost_clk:std_logic; signal temp:std_logic;signal show:std_logic_vector(2 downto 0):="000";signal bt:std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);signal flag:integer range 0 to 1;--signal rst:std_logic; --判断是否停车--signal start:std_logic; --使能信号--signal wait_signal:std_logic; --停车信号
begin
--xiaodou:process(clk,start_in,wait_signal_in,rst_in)
-- begin
-- if clk'event and clk='1' then
-- if count<1 then
-- count<=count+1;
-- else
-- count<=0;
-- if start_in='1' then
-- start<='1';
-- elsif wait_signal_in='1' then
-- wait_signal<='1';
-- elsif rst_in='1' then
-- rst<='1';
-- end if;
-- end if;
-- end if;
-- end process;U1:process(rst,clk) -- 1s 分频begin if rst='0' then if clk'event and clk='1' then if count_1=99 then count_1<=0;clk1hz<='1'; else count_1<=count_1+1;clk1hz<='0'; end if;end if; end if; end process; U0:process(rst,clk) -- 4.5s 分频begin if rst='0' then if clk'event and clk='1' then if count_2=449 then count_2<=0;clklhz_1<='1'; else count_2<=count_2+1;clklhz_1<='0'; end if;end if; end if; end process; U6:process(rst,clk) -- 6sbegin if rst='0' then if clk'event and clk='1' then if count=599 then count<=0;clklhz_2<='1'; else count<=count+1;clklhz_2<='0'; end if;end if; end if; end process; U9:process(rst,clk) -- 9sbegin if rst='0' then if clk'event and clk='1' then if count_3=899 then count_3<=0;clklhz_3<='1'; else count_3<=count_3+1;clklhz_3<='0'; end if;end if; end if; end process; U2:process(rst,clk1hz,start,wait_signal) --等待时间计数begin if rst='1' then --乘客离开m0<="0000";m1<="0000"; elsif start='0' then --没开车wait_clk<='0'; elsif clk1hz'event and clk1hz='1' then if wait_signal='1' then --停车if sec=59 thensec<=0;elsif ((sec+1) mod 6)=0 thensec<=sec+1; if m0="1001" then m0<="0000"; if m1="0101" thenm1<="0000"; else m1<=m1+'1'; end if; else m0<=m0+'1'; end if;else wait_clk<='0'; sec<=sec+1;if m0="1001" then m0<="0000"; if m1="0101" thenm1<="0000"; else m1<=m1+'1'; end if; else m0<=m0+'1'; end if; end if; else wait_clk<='0'; end if; end if; end process; U3:process( rst,clklhz_1,clklhz_2) --检测mile上升沿beginif wait_clk='1' or rst='1' thenmile_clk<='0';elsif rst='0' and wait_clk='0' thenmile_clk<=clklhz_1;end if; end process; cost_clk<=clklhz_2 when wait_signal='1' else mile_clk when en0='1' else '0'; U4:process(rst,start,mile_clk) --里程计数begin if rst='1' then k0<="0000"; k1<="0000"; en0<='0';elsif clklhz_3'event and clklhz_3='1' thenif wait_signal='0' and start='1' then if k1 & k0="00000011" then --超过3kmen0<='1'; end if; if k0="1001" then k0<="0000"; if k1="1001" then k1<="0000"; else k1<=k1+'1'; end if; else k0<=k0+'1'; end if; end if;end if; end process; U5:process( rst,start,cost_clk) --计费begin if rst='1' then --计价结束c0<="0000";c1<="0000"; c2<="0000";c3<="0000"; elsif start='1' and en0='0' then --还在起步范围c0<="0000";c1<="1000"; --8.0元c2<="0000"; c3<="0000"; elsif cost_clk'event and cost_clk='1' then --50m每个上升沿/中途停车等待if en0='1' and start='1' then if c0="1001" then c0<="0000"; if c1="1001" then c1<="0000"; if c2="1001" then c2<="0000";if c3="1001" thenc3<="0000";elsec3<=c3+'1';end if;else c2<=c2+'1'; end if; else c1<=c1+'1'; end if; else c0<=c0+'1'; end if; end if;end if; end process;p4:process(clk2)beginif clk2'event and clk2='1' thencase show iswhen "000" =>show <= "001";numViewOutputSg <= "11111110";bt <= c0;flag <= 0;when "001" =>show <= "010";numViewOutputSg <= "11111101";bt <= c1;flag <= 1;when "010" =>show <= "011";numViewOutputSg <= "11111011";bt <= c2;flag <= 0;when "011" =>show <= "100";numViewOutputSg <= "11110111";bt <= c3;flag <= 0;when "100" =>show <= "101";numViewOutputSg <= "11101111";bt <= k0;flag <= 0;when "101" =>show <= "110";numViewOutputSg <= "11011111";bt <= k1;flag <= 1;when "110" =>show <= "111";numViewOutputSg <= "10111111";bt <= m0;flag <= 0;when "111" =>show <= "000";numViewOutputSg <= "01111111";bt <= m1;flag <= 0;end case;end if;end process p4;p5:process(bt, flag)beginif flag = 1 thencase bt iswhen "0000" => numViewOutputBt <= "11111110";--0when "0001" => numViewOutputBt <= "10110000";when "0010" => numViewOutputBt <= "11101101";when "0011" => numViewOutputBt <= "11111001";when "0100" => numViewOutputBt <= "10110011";when "0101" => numViewOutputBt <= "11011011";when "0110" => numViewOutputBt <= "11011111";when "0111" => numViewOutputBt <= "11110000";when "1000" => numViewOutputBt <= "11111111";when "1001" => numViewOutputBt <= "11111011";--9when others => NULL;end case;elsif flag = 0 thencase bt iswhen "0000" => numViewOutputBt <= "01111110";--0when "0001" => numViewOutputBt <= "00110000";when "0010" => numViewOutputBt <= "01101101";when "0011" => numViewOutputBt <= "01111001";when "0100" => numViewOutputBt <= "00110011";when "0101" => numViewOutputBt <= "01011011";when "0110" => numViewOutputBt <= "01011111";when "0111" => numViewOutputBt <= "01110000";when "1000" => numViewOutputBt <= "01111111";when "1001" => numViewOutputBt <= "01111011";--9when others => NULL;end case;end if;end process p5;
end;四、仿真
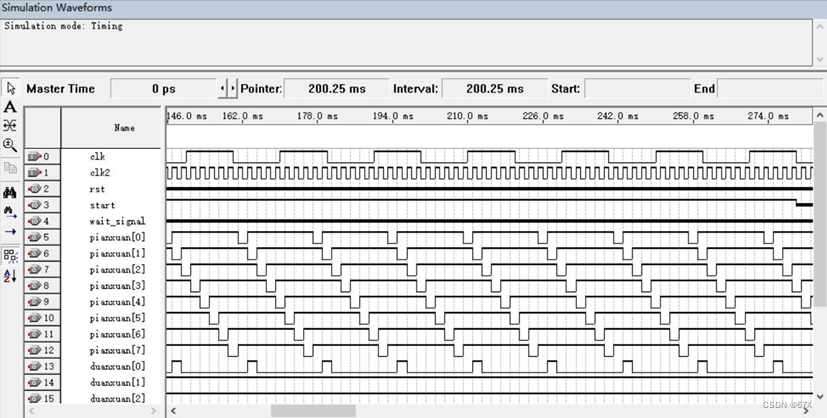
五、测试
1、初始状态(行程未开始)

2、行程开始,计价开始(3km内)

3、里程达到3km

4、里程超过3km(切换计价模式)
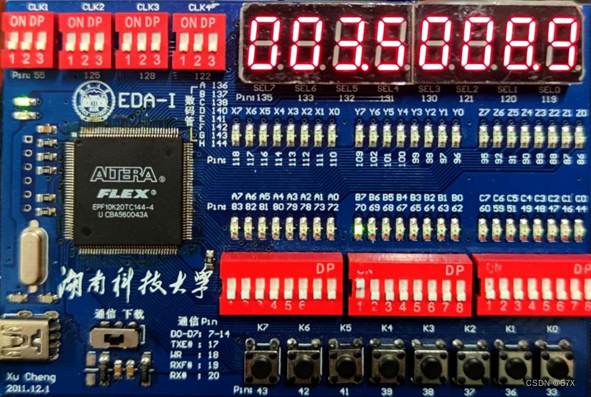
5、停车等待,开始按时计价

6、行程继续(切换计价模式)
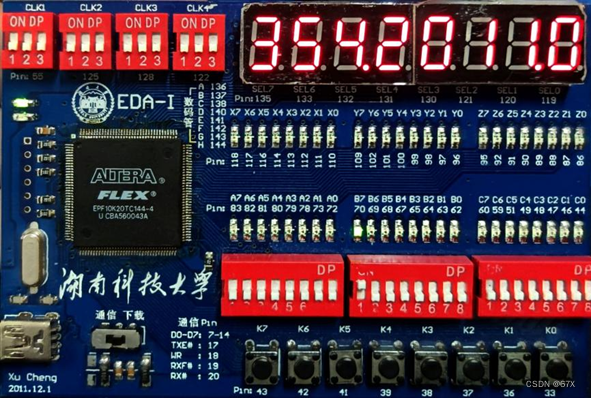
7、行程结束

8、演示视频
EDA出租车计价系统演示视频(2x)
六、课程学习或实验过程中出现的问题
1、对端口模式的理解不透彻,导致在分析教材部分例题和其他代码的过程中出现问题,尤其以双向端口(INOUT)最难学习与掌握;
2、使用EDA实验板时,对于设置好的按钮在进行按键操作的过程中,信号稳定的前后出现了多个不稳定的脉冲现象,而正常情况下一次按键操作理论上应只产生一个边沿信号脉冲(如下图所示);

3、本题中需要实现对价格费用、里程和等待时间的显示,而在VHDL硬件描述语言的编程设计过程中,在Pin Planner(引脚规划器)的设置中各个数字都出现了4个引脚选择,而EDA实验板上只有8个数码管而不够使用;

4、 实验过程中设置引脚后发现没有解决小数点的问题,在应该精确到0.1的地方没有显示小数点;
七、对各种问题的解决过程、方法和结果
(注:序号对应第六部分中的问题)
1、对于之前看过的一道程序中的以下部分源码(其中,程序中DataB为双向端口INOUT):
......
DataB <= Din when CE = '1' and Rd = '0' else
Others => 'Z';
Dout <= DataB when CE = '1' and Rd = '1' else
Others => '1';
......通过查阅相关书籍及在CSDN等平台上查找相关的资料,了解到教材上仅仅只提到了端口的双向模式允许信号双向传输(即既可以进入实体,也可以离开实体),可代替IN、OUT和BUFFER。但在实际编程时还必须要注意的细节是,当双向端口DataB作为输出且空闲时,必须将其设为高阻态挂起,即在上述程序的部分代码中需要有“Others => 'Z'”这一条语句,否则实现后会导致端口死锁;而当双向端口DataB作为有效输入时,DataB输出必须处于高阻态,即在上述程序的部分代码中需要有“CE = '1' and Rd = '1'”这一条语句,否则同样也会出现问题。
2、通过对实验电路板的结构分析以及在其他相关课程(如计算机组成原理)的学习中,了解到本次实验中使用的实验电路板的按键为机械式开关结构,由于机械式开关的核心部件为弹性金属簧片,因而在开关切换的瞬间会在接触点出现来回弹跳的现象,因此虽然看上去只是进行了一次按键,结果却可能是在按键的信号稳定的前后出现了多个不规则的脉冲,如果将这样的脉冲信号直接送给微处理器进行扫描采集的话,将可能把按键稳定前后出现的脉冲信号当作按键信号,这就会导致人为的一次按键但是微处理器以为是执行多次按键的现象。因此为了确保按键识别的准确性,应当使得在按键信号产生抖动的情况之下禁止进入状态输入,为此就必须对按键进行消抖处理,消除出现抖动时的不稳定的、随机的电压信号。测试过程中发现机械式按键的抖动次数、抖动时间、抖动波形都是随机的,而不同类型的按键其最长抖动时间也有差别,进一步查阅相关资料可知抖动时间的长短和按键的机械特性有关,一般为5-10ms,但是有些按键的抖动时间可达到20 ms,甚至更长。所以在具体设计过程中要具体分析,根据实际情况来调整设计。
3、分析代码后发现,在设置端口数据时将端口宽度设置为4(如下):
![]()
未对输出端口进行分组处理,因此会导致每个数字都按照四位二进制的形式有4个输出,因此可以将原先定义在结构体内的信号经译码后打包送到对应输出端口(一种可行的解决方案如下):
![]()



4、根据设置的信号量分析可知,应当在c1和k1处固定显示小数点,经过分析决定设置一个flag标记位,在片选模块中单独标记c1和k1两处(flag=1),其余部分不做标记(flag=0),最后在段选模块中根据flag的值进行输出,即flag=1时段选信号的第一位置“1”,即显示小数点,而flag=0时则相反。
八、总结
通过本次数字系统设计实验设计,首先我学到了很多关于数字逻辑和数字系统的知识,基本理解了一些系统的设计理念以及设计方案的制定和流程。同时通过对VHDL硬件描述语言的学习,我深刻的感受到了软硬件相结合的强大,基于软件设计硬件的方法十分高效,同时代码相对于电路更具备可读性,能更好的理解系统设计原理和方法。本次我选择的出租车计价器设计难度中等偏上,在我完成实验设计的过程中遇到了很多问题,比如对VHDL硬件描述语言的基本语法掌握得不够熟练,亦或者是对数字逻辑的相关知识和一些基础的实验元件的认识不足,因此设计过程举步维艰,对信号量的设计也有很多的不合理之处,比如输出信号量cost、kilogram和minute,最早设计的时候采取的方案是单独设置输出信号量out static_logic_vector(3 downto 0),输出对应的二进制数,但没有考虑到数码管的译码部分,从而导致无法正确选择合适的引脚进行数码显示。之后我意识到这个问题后决定将其包装一下,对四位BCD码进行译码后,再送入后续改进设计的段选模块和片选模块进行输出,从而解决了这一问题。在完成实验之后我也尝试思考一些实验过程中的问题,尝试去改进一些方法策略,后来发现了按键抖动的问题之后设计了消除抖动的模块,为了进行更好的演示将等待时间计时的分钟显示改为秒钟显示……通过不断的思考,我也渐渐掌握了一定的设计能力,培养了创新思想。但仅仅是对VHDL硬件描述语言的掌握是远远不够完成实验的,管脚的连接、实验板的操作或是软件的安装使用都出现过问题,而只是学习书本上的知识也是不够的,书本上的知识往往偏向理论,实际实验涉及到的范围往往更广,因此也应该要不断学习,自觉拓展知识面,开拓视野,一步一步的完成每一件学习任务,这样才能更好的掌握EDA这门课程。





)


Docker简介)
:扩展正则表达式)
-窗口函数等)






原理+图示+MATLAB调试)

