标准流
标准流也叫文档流,指的是标签在页面中默认的派不规则,例如:块元素独占一行,行内元素可以一行显示多个。
但是很多的网页布局都是块元素在一行中显示的,这时候就需要浮动和 Flex 布局,浮动只需要了解即可
浮动
可以让块元素水平排列
给块元素加上 float属性可以使得块元素往左边或者往右边浮动,使得两个块元素可以出现在一行里面。
浮动后的格子会脱离标准流的控制,不再占用标准流的范围。
浮动-产品区域布局
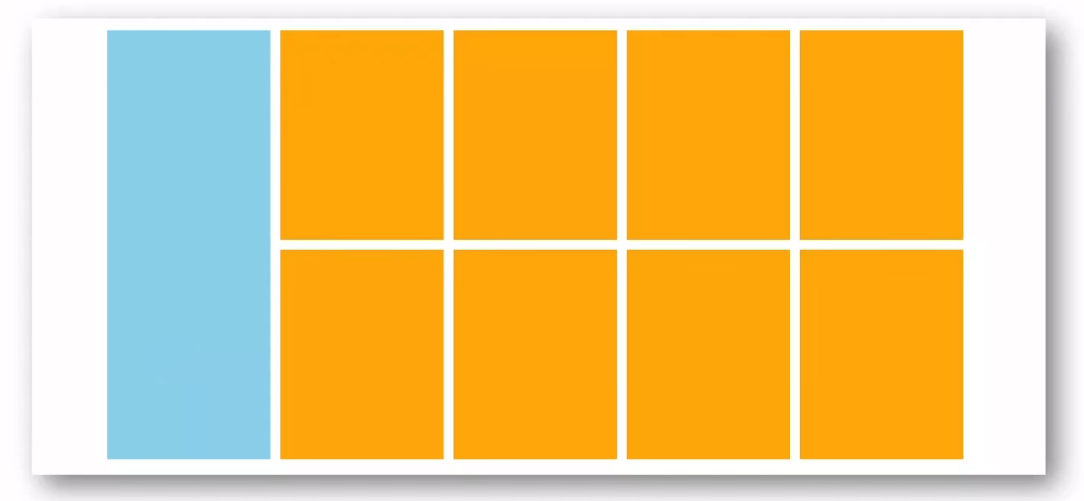
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>* {margin: 0;height: 0;}li {list-style: none;}.product {width: 1226px;height: 628px;background-color: greenyellow;margin: 50px auto;}.left {width: 234px;height: 628px;background-color: aqua;float: left;}.right {width: 978px;height: 628px;background-color: grey;float: right;}.right > li {width: 234px;height: 300px;margin-right: 14px;margin-bottom: 14px;background-color: orange;float: left;}.right > li:nth-child(4n) {margin-right: 0;}</style>
</head>
<body><div class="product"><div class="left"></div><div class="right"><li></li><li></li><li></li><li></li><li></li><li></li><li></li><li></li></div></div>
</body>
</html>
清除浮动
浮动元素脱标的情况,如果父级没有高度,子级无法撑开父级的高度(可能导致页面布局的错乱 )
方法一:额外标签法
- 在父元素内容的最后添加一个块级元素,设置 CSS 属性
clear:both
方法二:单伪元素法
.clearfix::after {content: "";display: block;clear: both;
}
方法三:双伪元素法
.clearfix::before,
.clearfix::after {content: "";display: table;
}
.clearfix::after {clear:both;
}
代码解释:
.clearfix::before 和 .clearfix::after:分别使用伪元素 ::before 和 ::after。
content: "";:添加了一个空内容,这样伪元素才能生效并占据空间。
display: table;:将伪元素的 display 属性设置为 table,使其表现得像一个表格元素。
.clearfix::after:在第二个伪元素后,应用了 clear: both;,使其清除浮动。
方法四:overflow
- 父元素添加属性:overflow:hidden
Flex 布局
Flex 布局又叫弹性布局,它使用 flexbox 使得容器有了弹性,更加适应设备的不同宽度,而不用再去依赖传统的块状布局和浮动定位,作为在 CSS3 中新增的规范,目前大部分的主流浏览器已经支持,是浏览器提倡的布局方式,
非常适合结构化布局,提供了空间分布和对其能力,它不会有浮动布局中的脱标、坍塌等现象,布局网页更简单更灵活。
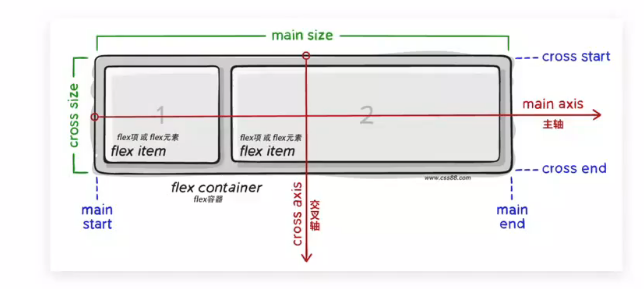
Flex - 组成
设置方式:给父元素设置 display:flex,子元素可以自动挤压或者拉伸
组成部分:
- 弹性容器:父级容器
- 弹性盒子:当父级容器设置为
display:flex的时候,子级自动变为flexbox(弹性盒子)。- 主轴:默认在水平方向,是子级弹性盒子排列的轴,所以一开始设置的时候弹性盒子默认是水平排列的。
- 侧轴 / 交叉轴:默在垂直方向,后面可以根据需要改变主轴和侧轴。
示意图:
Flex - 布局属性
这里展示一些 flex 布局有关的属性,后面会进行详细的讲解
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
display: flex | 创建 flex 容器 |
justify-content | 主轴对齐方式 |
align-items | 侧轴对齐方式 |
align-self | 修改某个盒子的侧轴对齐方式 |
flex-direction | 修改主轴方向 |
flex | 弹性伸缩比 |
flex-wrap | 弹性盒子换行 |
align-content | 行对齐方式 |
主轴对齐方式(justify-content)
属性名:justify-content
可以改变主轴上的对齐方式
| 属性值 | 效果 |
|---|---|
flex-start | 默认值,弹性盒子从起点依次排列 |
flex-end | 盒子从终点开始依次排列 |
center | 弹性盒子从主轴居中排列 |
space-between | 弹性盒子沿主轴均匀排列,空白间距在盒子中间 |
space-around | 弹性盒子沿主轴均匀排列,空白间距在盒子两侧 |
space-evenly | 弹性盒子演主轴均匀排列,弹性盒子与容器之间间距相等 |
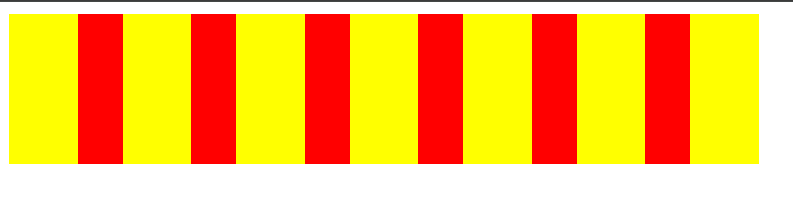
需要重点关注的是后面的几个,这里先来演示一下 space-around 和 space-evenly 的区别:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>div {/* 设置 flex 布局 */display: flex;width: 500px;background-color: yellow;// justify-content: space-evenly;justify-content: space-around;}li {list-style: none;width: 30px;height: 100px;background-color: red;}</style>
</head>
<body><div><li></li><li></li><li></li><li></li><li></li><li></li></div>
</body>
</html>
around

evenly
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title>
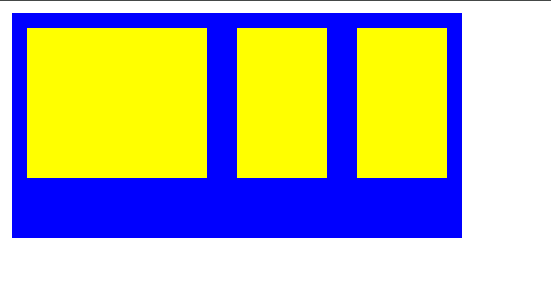
</head>
<style>.box {display: flex;/* justify-content: center;justify-content: space-around;justify-content: space-between; */justify-content: space-evenly;height: 300px;border: solid 2px black;}.box div {width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: yellow;}
</style>
<body><div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div></div>
</body>
</html>
侧轴对齐方式(align-items / align-self)
属性名
align-items:当前弹性容器内所有盒子的侧轴对齐方式
align-self:单独控制某个弹性盒子的侧轴对齐方式
这两个属性值是相同的,只不过 align-self 属性是设置在子级的
| 属性值 | 效果 |
|---|---|
stretch | 盒子沿侧轴被拉伸到铺满整个容器,如果没有设置盒子在侧轴方向尺寸则会默认拉伸 |
center | 弹性盒子沿侧轴居中排列 |
flex-start | 弹性盒子从起点开始依次排列 |
flex-end | 弹性盒子从终点开始依次排列 |
这里就不具体演示了,效果和描述的一样
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>.box {display: flex;justify-content: space-evenly;height: 300px;align-items: flex-end;}.box div {width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: yellow;}</style>
</head>
<body><div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div></div>
</body>
</html>
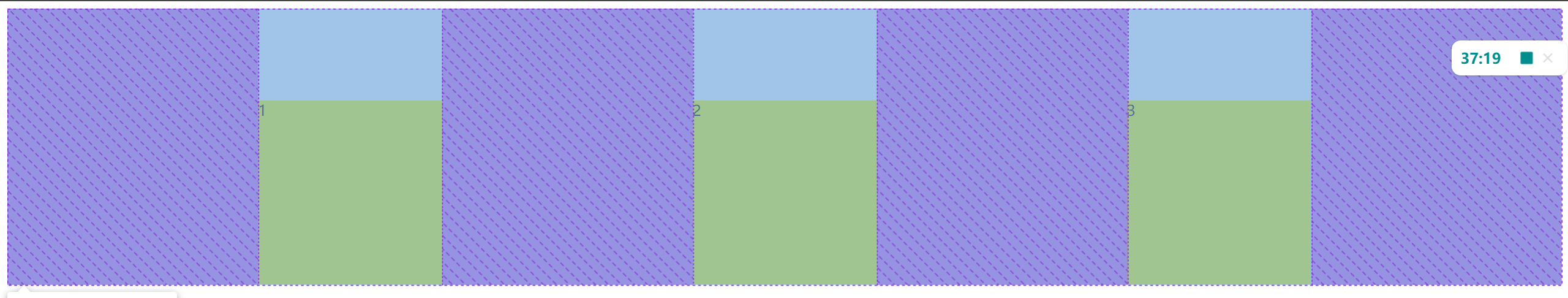
可以清晰的看到是从底部开始排列的
修改主轴方向(flex-direction)
主轴就是弹性盒子排列的轴,我们可以通过设置主轴方向来做到水平排列和数值排列
属性名:flex-direction
| 属性值 | 效果 |
|---|---|
row | 水平方向,从左到右 |
column | 竖直方向,从上到下 |
row-reverse | 水平方向,从右到左 |
column-reverse | 垂直方向,从下到上 |
只需要记忆垂直方向从上向下的 column 即可,这时候主轴的方向就变为垂直了
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>div {display: flex;width: 300px;height: 600px;background-color: blue;}div li {list-style: none;width: 90px;height: 100px;background-color: yellow;}</style>
</head>
<body><div><li></li><li></li><li></li></div>
</body>
</html>
看这段代码主轴是横轴,页面效果是这样的:

这时候我们加上 flex-direction:column 属性:
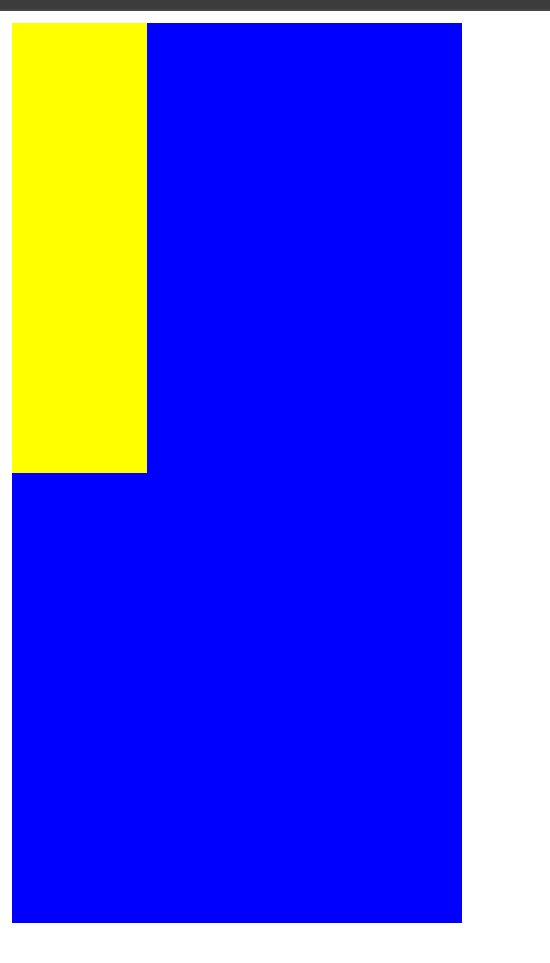 主轴就变为竖直方向了。
主轴就变为竖直方向了。
弹性伸缩比
可以用来控制弹性盒子在主轴方向的尺寸,比如主轴为水平方向控制的就是这个盒子的宽度。
属性名:flex
属性值:整数数字,表示占用父级剩余尺寸的份数
默认的情况下每一个盒子是占一份的,剩余尺寸是原本的尺寸减去
内容宽度和高度: Flex 项目的内容决定了其在主轴上的大小。比如,文字、图像或者内部元素的宽度和高度。
盒子模型属性: padding、border、margin 等属性也会影响 Flex 项目在主轴方向上的实际大小。
设置的宽度和高度属性: 如果明确设置了 Flex 项目的宽度和高度属性,那么这些属性值也会决定项目在主轴上的尺寸。
比如下面这段代码我们给不同的盒子设置不同的值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>div {display: flex;width: 300px;height: 150px;background-color: blue;justify-content: space-between;}div li:nth-child(1) {flex: 2;margin: 10px;list-style: none;width: 90px;height: 100px;background-color: yellow;}div li:nth-child(2) {flex: 1;margin: 10px;list-style: none;width: 90px;height: 100px;background-color: yellow;}div li:nth-child(3) {flex: 1;margin: 10px;list-style: none;width: 90px;height: 100px;background-color: yellow;}</style>
</head>
<body><div><li></li><li></li><li></li></div>
</body>
</html>
弹性换行
弹性盒子会自动挤压和拉伸,默认情况下,所有的盒子都在一行显示,如果盒子的宽度过大会被挤压到适合的大小
属性名:flex-wrap
| 属性值 | 效果 |
|---|---|
wrap | 换行 |
nowarp | 不换行(默认情况) |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>.flex-container {display: flex;flex-wrap: wrap; /* 设置项目换行 */width: 300px; /* 设置容器宽度 */border: 2px solid #ccc;}.flex-item {width: 80px;height: 80px;background-color: #f0f0f0;margin: 5px;display: flex;justify-content: center;align-items: center;}</style>
</head>
<body><div class="flex-container"><div class="flex-item">1</div><div class="flex-item">2</div><div class="flex-item">3</div><div class="flex-item">4</div><div class="flex-item">5</div><div class="flex-item">6</div></div></body>
</html>
显示效果:

行对齐方式
可以控制每行之间的对齐方式,需要设施flex-wrap: wrap
属性名:align-content
| 属性值 | 效果 |
|---|---|
flex-start | 默认值,弹性盒子从起点依次排列 |
flex-end | 盒子从终点开始依次排列 |
center | 弹性盒子从主轴居中排列 |
space-between | 弹性盒子沿主轴均匀排列,空白间距在盒子中间 |
space-around | 弹性盒子沿主轴均匀排列,空白间距在盒子两侧 |
space-evenly | 弹性盒子演主轴均匀排列,弹性盒子与容器之间间距相等 |
和主轴的对齐方式相同
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>.flex-container {display: flex;flex-wrap: wrap;height: 300px; /* 设置容器高度 */width: 300px;align-content: space-between; /* 设置轴线分布方式 */border: 2px solid #ccc;}.flex-item {width: 80px;height: 80px;background-color: #f0f0f0;margin: 5px;display: flex;justify-content: center;align-items: center;}</style>
</head>
<body><div class="flex-container"><div class="flex-item">1</div><div class="flex-item">2</div><div class="flex-item">3</div><div class="flex-item">4</div><div class="flex-item">5</div><div class="flex-item">6</div></div>
</body>
</html>


















