先看仓库:soedinglab/MMseqs2: MMseqs2: ultra fast and sensitive search and clustering suite (github.com)
无论哪个工具软件,无论你是否熟悉,都推荐你看一下作者原文,这样后面的步骤以及怎么使用头脑里会更清晰。
Fast and sensitive taxonomic assignment to metagenomic contigs | Bioinformatics | Oxford AcademicMMseqs2 desktop and local web server app for fast, interactive sequence searches | Bioinformatics | Oxford Academic
Clustering huge protein sequence sets in linear time | Nature Communications
MMseqs2 enables sensitive protein sequence searching for the analysis of massive data sets | Nature Biotechnology
MMseqs是一种快速和有效的蛋白质序列比对工具。以下是使用MMseqs的详细方法:
官网用户说明在这里:Home · soedinglab/MMseqs2 Wiki (github.com)
1. 安装MMseqs软件
在MMseqs官方网站(https://mmseqs.com/)上下载并安装MMseqs软件。
# install by brew 一般是mac系统默认的,当然mac就是linux系统,所以其他linux系统也可以自己安装配置brew工具
brew install mmseqs2# install via conda,这个大家都能用,估计做生信的都有了,直接命令安装
conda install -c conda-forge -c bioconda mmseqs2# install docker,会容器管理的建议这个,导入导出方便,随处可移,运行完自动释放
docker pull ghcr.io/soedinglab/mmseqs2###下面的就做参考吧,大家可能没有运维经验的会不熟悉
# static build with AVX2 (fastest)
wget https://mmseqs.com/latest/mmseqs-linux-avx2.tar.gz; tar xvfz mmseqs-linux-avx2.tar.gz; export PATH=$(pwd)/mmseqs/bin/:$PATH
# static build with SSE4.1
wget https://mmseqs.com/latest/mmseqs-linux-sse41.tar.gz; tar xvfz mmseqs-linux-sse41.tar.gz; export PATH=$(pwd)/mmseqs/bin/:$PATH
# static build with SSE2 (slowest, for very old systems)
wget https://mmseqs.com/latest/mmseqs-linux-sse2.tar.gz; tar xvfz mmseqs-linux-sse2.tar.gz; ###linux环境下就这样不用写注册表,将生成的二进制程序文件加入到系统环境中就好了。
export PATH=$(pwd)/mmseqs/bin/:$PATH###克隆git仓库,自行编译,需要有debug经验
git clone https://github.com/soedinglab/MMseqs2.git
cd MMseqs2
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=. ..
make
make install
export PATH=$(pwd)/bin/:$PATH全参数使用帮助信息:
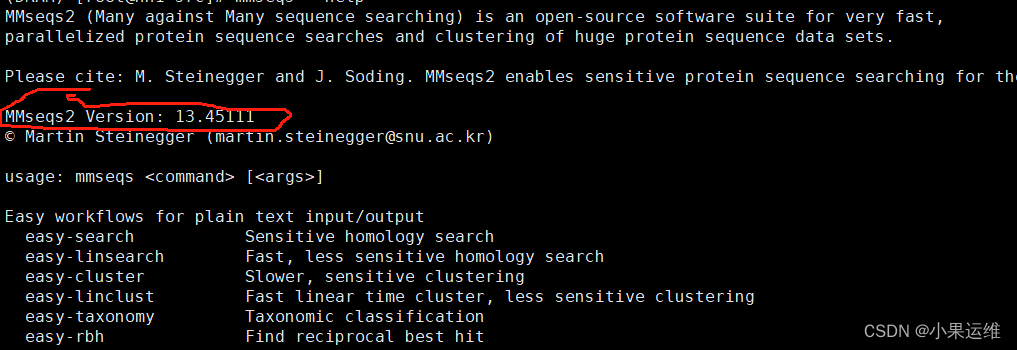
MMseqs2 Version: 13.45111
© Martin Steinegger (martin.steinegger@snu.ac.kr)usage: mmseqs <command> [<args>]Easy workflows for plain text input/outputeasy-search Sensitive homology searcheasy-linsearch Fast, less sensitive homology searcheasy-cluster Slower, sensitive clusteringeasy-linclust Fast linear time cluster, less sensitive clusteringeasy-taxonomy Taxonomic classificationeasy-rbh Find reciprocal best hitMain workflows for database input/outputsearch Sensitive homology searchlinsearch Fast, less sensitive homology searchmap Map nearly identical sequencesrbh Reciprocal best hit searchlinclust Fast, less sensitive clusteringcluster Slower, sensitive clusteringclusterupdate Update previous clustering with new sequencestaxonomy Taxonomic classificationInput database creationdatabases List and download databasescreatedb Convert FASTA/Q file(s) to a sequence DBcreateindex Store precomputed index on disk to reduce search overheadcreatelinindex Create linsearch indexconvertmsa Convert Stockholm/PFAM MSA file to a MSA DBtsv2db Convert a TSV file to any DBtar2db Convert content of tar archives to any DBmsa2profile Convert a MSA DB to a profile DBHandle databases on storage and memorycompress Compress DB entriesdecompress Decompress DB entriesrmdb Remove a DBmvdb Move a DBcpdb Copy a DBlndb Symlink a DBunpackdb Unpack a DB into separate filestouchdb Preload DB into memory (page cache)Unite and intersect databasescreatesubdb Create a subset of a DB from list of DB keysconcatdbs Concatenate two DBs, giving new IDs to entries from 2nd DBsplitdb Split DB into subsetsmergedbs Merge entries from multiple DBssubtractdbs Remove all entries from first DB occurring in second DB by keyFormat conversion for downstream processingconvertalis Convert alignment DB to BLAST-tab, SAM or custom formatcreatetsv Convert result DB to tab-separated flat fileconvert2fasta Convert sequence DB to FASTA formatresult2flat Create flat file by adding FASTA headers to DB entriescreateseqfiledb Create a DB of unaligned FASTA entriestaxonomyreport Create a taxonomy report in Kraken or Krona formatSequence manipulation/transformationextractorfs Six-frame extraction of open reading framesextractframes Extract frames from a nucleotide sequence DBorftocontig Write ORF locations in alignment formatreverseseq Reverse (without complement) sequencestranslatenucs Translate nucleotides to proteinstranslateaa Translate proteins to lexicographically lowest codonssplitsequence Split sequences by lengthmasksequence Soft mask sequence DB using tantanextractalignedregion Extract aligned sequence region from queryResult manipulation swapresults Transpose prefilter/alignment DBresult2rbh Filter a merged result DB to retain only reciprocal best hitsresult2msa Compute MSA DB from a result DBresult2dnamsa Compute MSA DB with out insertions in the query for DNA sequencesresult2stats Compute statistics for each entry in a DBfilterresult Pairwise alignment result filteroffsetalignment Offset alignment by ORF start positionproteinaln2nucl Transform protein alignments to nucleotide alignmentsresult2repseq Get representative sequences from result DBsortresult Sort a result DB in the same order as the prefilter or align modulesummarizealis Summarize alignment result to one row (uniq. cov., cov., avg. seq. id.)summarizeresult Extract annotations from alignment DBTaxonomy assignment createtaxdb Add taxonomic labels to sequence DBcreatebintaxonomy Create binary taxonomy from NCBI inputaddtaxonomy Add taxonomic labels to result DBtaxonomyreport Create a taxonomy report in Kraken or Krona formatfiltertaxdb Filter taxonomy result databasefiltertaxseqdb Filter taxonomy sequence databaseaggregatetax Aggregate multiple taxon labels to a single labelaggregatetaxweights Aggregate multiple taxon labels to a single labellcaalign Efficient gapped alignment for lca computationlca Compute the lowest common ancestormajoritylca Compute the lowest common ancestor using majority votingMulti-hit search multihitdb Create sequence DB for multi hit searchesmultihitsearch Search with a grouped set of sequences against another grouped setbesthitperset For each set of sequences compute the best element and update p-valuecombinepvalperset For each set compute the combined p-valuemergeresultsbyset Merge results from multiple ORFs back to their respective contigPrefiltering prefilter Double consecutive diagonal k-mer searchungappedprefilter Optimal diagonal score searchkmermatcher Find bottom-m-hashed k-mer matches within sequence DBkmersearch Find bottom-m-hashed k-mer matches between target and query DBAlignment align Optimal gapped local alignmentalignall Within-result all-vs-all gapped local alignmenttransitivealign Transfer alignments via transitivityrescorediagonal Compute sequence identity for diagonalalignbykmer Heuristic gapped local k-mer based alignmentClustering clust Cluster result by Set-Cover/Connected-Component/Greedy-Incrementalclusthash Hash-based clustering of equal length sequencesmergeclusters Merge multiple cascaded clustering stepsProfile databases result2profile Compute profile DB from a result DBmsa2result Convert a MSA DB to a profile DBmsa2profile Convert a MSA DB to a profile DBprofile2pssm Convert a profile DB to a tab-separated PSSM fileprofile2consensus Extract consensus sequence DB from a profile DBprofile2repseq Extract representative sequence DB from a profile DBconvertprofiledb Convert a HH-suite HHM DB to a profile DBProfile-profile databasesenrich Boost diversity of search resultresult2pp Merge two profile DBs by shared hitsprofile2cs Convert a profile DB into a column state sequence DBconvertca3m Convert a cA3M DB to a result DBexpandaln Expand an alignment result based on anotherexpand2profile Expand an alignment result based on another and create a profileUtility modules to manipulate DBsview Print DB entries given in --id-list to stdoutapply Execute given program on each DB entryfilterdb DB filtering by given conditionsswapdb Transpose DB with integer values in first columnprefixid For each entry in a DB prepend the entry key to the entry itselfsuffixid For each entry in a DB append the entry key to the entry itselfrenamedbkeys Create a new DB with original keys renamedSpecial-purpose utilitiesdiffseqdbs Compute diff of two sequence DBssummarizetabs Extract annotations from HHblits BLAST-tab-formatted resultsgff2db Extract regions from a sequence database based on a GFF3 filemaskbygff Mask out sequence regions in a sequence DB by features selected from a GFF3 fileconvertkb Convert UniProtKB data to a DBsummarizeheaders Summarize FASTA headers of result DBnrtotaxmapping Create taxonomy mapping for NR databaseextractdomains Extract highest scoring alignment regions for each sequence from BLAST-tab filecountkmer Count k-mers
光看帮助会有点懵了,但总体还是清晰的,下面大家可以在逐步使用中熟悉这些参数的使用方法。
这里说一下主要工作流程模块:
###帮助文件最上面是关于主要工作流程模块的介绍。
easy-search Sensitive homology search,高敏感度同源基因搜索
easy-linsearch Fast, less sensitive homology search,较低敏感度同源基因搜索
easy-cluster Slower, sensitive clustering,较慢的较高敏感度聚类
easy-linclust Fast linear time cluster, less sensitive clustering,快速线性时间聚类,低灵敏度聚类
easy-taxonomy Taxonomic classification,物种注释
easy-rbh Find reciprocal best hit,查找最佳命中#####使用时很简单,分别查看帮助文件
mmseqs easy-search --help
mmseqs easy-linsearch --help
mmseqs easy-cluster --help
mmseqs easy-linclust --help
mmseqs easy-taxonomy --help
mmseqs easy-rbh --help2. 下载数据库Downloading databases
#先查看有些什么数据库,可以直接使用下面的帮助信息查看mmseqs databasesUsage: mmseqs databases <name> <o:sequenceDB> <tmpDir> [options]Name Type Taxonomy Url
- UniRef100 Aminoacid yes https://www.uniprot.org/help/uniref
- UniRef90 Aminoacid yes https://www.uniprot.org/help/uniref
- UniRef50 Aminoacid yes https://www.uniprot.org/help/uniref
- UniProtKB Aminoacid yes https://www.uniprot.org/help/uniprotkb
- UniProtKB/TrEMBL Aminoacid yes https://www.uniprot.org/help/uniprotkb
- UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot Aminoacid yes https://uniprot.org
- NR Aminoacid yes https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/db/FASTA
- NT Nucleotide - https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/db/FASTA
- GTDB Aminoacid yes https://gtdb.ecogenomic.org
- PDB Aminoacid - https://www.rcsb.org
- PDB70 Profile - https://github.com/soedinglab/hh-suite
- Pfam-A.full Profile - https://pfam.xfam.org
- Pfam-A.seed Profile - https://pfam.xfam.org
- Pfam-B Profile - https://xfam.wordpress.com/2020/06/30/a-new-pfam-b-is-released
- CDD Profile - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cdd.shtml
- eggNOG Profile - http://eggnog5.embl.de
- VOGDB Profile - https://vogdb.org
- dbCAN2 Profile - http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2
- SILVA Nucleotide yes https://www.arb-silva.de
- Resfinder Nucleotide - https://cge.cbs.dtu.dk/services/ResFinder
- Kalamari Nucleotide yes https://github.com/lskatz/Kalamari下载指定数据库
#下载swissprot数据库
mmseqs databases UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot outpath/swissprot tmp下载完的数据库就在指定路径下,不含swissprot名, 也就是自己指定的/outpath路径,使用的时候指定数据库路径/outpath/swissprot
当然可以自己下载fasta文件手动配置数据库
3. 创建数据库
使用MMseqs创建一个数据库,该数据库将包含您要使用的蛋白质序列数据。要创建数据库,请执行以下命令:
#先将参考库fasta文件生成mmseqs对应数据库文件
mmseqs createdb <sequences.fasta> <database_name>## 其中,`<sequences.fasta>`是您的蛋白质序列文件名,`<database_name>`是您要为数据库指定的名称。#######################################################################################
mmseqs createdb examples/QUERY.fasta queryDB
mmseqs createdb examples/DB.fasta targetDB4. 训练数据库
为了提高比对质量,可以训练数据库。要训练数据库,请执行以下命令:
#建立索引,加速比对
mmseqs createindex <database_name> <index_prefix># 其中,`<database_name>`是您之前创建的数据库名称,`<index_prefix>`是用于索引的前缀。5. 进行比对
现在,您可以使用MMseqs比对您的蛋白质序列了。要进行比对,请执行以下命令:
mmseqs search <query.fasta> <database_name> <result_file> <tmp_dir>#其中,`<query.fasta>`是您要比对的蛋白质序列文件名,`<database_name>`是您之前创建的数据库名称,`<result_file>`是将保存结果的文件名,`<tmp_dir>`是用于临时文件的目录。#### 例如,这里直接用easy-search模块基于swissprot数据库进行QUERY.fasta输入文件的比对
#### 比对结果放入alnRes.m8
#### 个人建议输入文件,数据库文件还有输出文件和tmp目录统一都使用绝对路径
mmseqs easy-search examples/QUERY.fasta swissprot alnRes.m8 tmp###结果是不是很熟悉:
k141_759496_length_1110_cov_3.0000_1 A8BQB4 0.258 337 187 0 117 369 1084 1420 2.200E-12 73
k141_759496_length_1110_cov_3.0000_1 Q2PQH8 0.258 337 187 0 117 369 1084 1420 3.903E-12 72
k141_759496_length_1110_cov_3.0000_1 P35574 0.252 337 188 0 117 369 1106 1442 6.921E-12 72
k141_759496_length_1110_cov_3.0000_1 P35573 0.244 337 191 0 117 369 1083 1419 1.205E-10 68
k141_759496_length_1110_cov_3.0000_1 Q06625 0.345 83 51 0 117 195 1067 1149 8.270E-08 59
k141_399534_length_2355_cov_6.0000_2 Q8ZL58 0.680 372 119 0 3 374 24 395 4.669E-169 533
k141_399534_length_2355_cov_6.0000_2 Q9RKF7 0.349 352 226 0 6 357 1 348 1.247E-56 207
k141_399534_length_2355_cov_6.0000_2 H2IFX0 0.317 353 237 0 7 359 5 352 7.486E-51 190
k141_399534_length_2355_cov_6.0000_2 Q97U96 0.339 344 222 0 25 361 20 363 6.501E-50 187
k141_399534_length_2355_cov_6.0000_2 P11444 0.303 357 242 0 6 362 5 352 1.706E-43 168### 同样使用其他模块也可以使用相同格式
mmseqs search queryDB targetDB resultDB tmp简单工作流程模块使用
mmseqs easy-search examples/QUERY.fasta examples/DB.fasta alnResult.m8 tmpmmseqs easy-cluster examples/DB.fasta clusterRes tmpmmseqs easy-linclust examples/DB.fasta clusterRes tmpmmseqs里的结果
mmseqs包含了近百个使用模块,这其中包括其结果格式转换,例如将比对结果转换为BLAST的几种格式:
mmseqs convertalis queryDB targetDB alnRes alnRes.tab##默认情况下会 以 --format-mode 0 方式转换,
##用户可自定义自己想要的格式比如 --format-mode 4mmseqs convertalis queryDB targetDB alnRes alnRes.tab --format-mode 4By default (--format-mode 0), alnRes.tab will contain alignment result in a BLAST tabular result (comparable to -m 8 -outfmt 6) with 12 columns: (1,2) identifiers for query and target sequences/profiles, (3) sequence identity, (4) alignment length, (5) number of mismatches, (6) number of gap openings, (7-8, 9-10) domain start and end-position in query and in target, (11) E-value, and (12) bit score.
The option --format-output defines a custom output format. For example, the format string --format-output "query,target,evalue,qaln,taln" prints the query and target identifiers, e-value of the alignment and the alignments.
Column headers can be added to the output with --format-mode 4. This mode also supports chosing a custom output format.
The following field are supported
- query Query sequence identifier
- target Target sequence identifier
- evalue E-value
- gapopen Number of gap open events (note: this is NOT the number of gap characters)
- pident Percentage of identical matches
- fident Fraction of identical matches
- nident Number of identical matches
- qstart 1-indexed alignment start position in query sequence
- qend 1-indexed alignment end position in query sequence
- qlen Query sequence length
- tstart 1-indexed alignment start position in target sequence
- tend 1-indexed alignment end position in target sequence
- tlen Target sequence length
- alnlen Alignment length (number of aligned columns)
- raw Raw alignment score
- bits Bit score
- cigar Alignment as string. Each position contains either M (match), D (deletion, gap in query), or I (Insertion, gap in target)
- qseq Query sequence
- tseq Target sequence
- qaln Aligned query sequence with gaps
- taln Aligned target sequence with gaps
- qheader Header of Query sequence
- theader Header of Target sequence
- qframe Query frame (-3 to +3)
- tframe Target frame (-3 to +3)
- mismatch Number of mismatches
- qcov Fraction of query sequence covered by alignment
- tcov Fraction of target sequence covered by alignment
- empty Dash column '-'
- taxid Taxonomical identifier (needs mmseqs tax db)
- taxname Taxon Name (needs mmseqs tax db)
- taxlineage Taxonomical lineage (needs mmseqs tax db)
- qset Query filename of FASTA/Q (useful if multiple files were passed to createdb)
- qsetid Numeric identifier for query filename
- tset Target filename of FASTA/Q (useful if multiple files were passed to createdb)
- tsetid Numeric identifier for target filename
We support output in SAM format using --format-mode 1: the AS tag contains the raw score, NM is the mismatch count.
--format-mode 3 will return an interactive HTML document to visualize search results. The input alignment result needs to contain backtraces (i.e. the search must have been run with the -a parameter).
6、在多节点MPI并行计算上使用MMseqs
要使用MMseqs2在多节点上做并行计算不能使用预编译的版本不能用于MPI计算,需要使用cmake在手动编译时加入“-DHAVE_MPI=1”参数。所以很明显,这里需要集群管理员做维护了,因为这里集群环境编译会有很多依赖需要安装和debug。
Warning: Make sure that MMseqs2 was compiled with MPI support by using the -DHAVE_MPI=1 flag during the cmake invocation. The precompiled versions of MMseqs2 cannot use MPI (including Conda, Brew, Apt, etc.):
mkdir build-mpi && cd build-mpi
cmake -DHAVE_MPI=1 -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release ..#使用 -DHAVE_MPI=1 编译的mmseqs会有一个 “-MPI” 的后缀
#If MMseqs2 was compiled correctly with MPI support you should see a -MPI suffix when you call mmseqs version.#########################################################
## 编译示例:
git clone https://github.com/soedinglab/MMseqs2.git
cd MMseqs2
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE -DHAVE_MPI=1 -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/nfs/sopt/mmseqs2 ..
未使用MPI编译的mmseqs帮助头:
使用MPI参数编译的mmseqs帮助头信息: 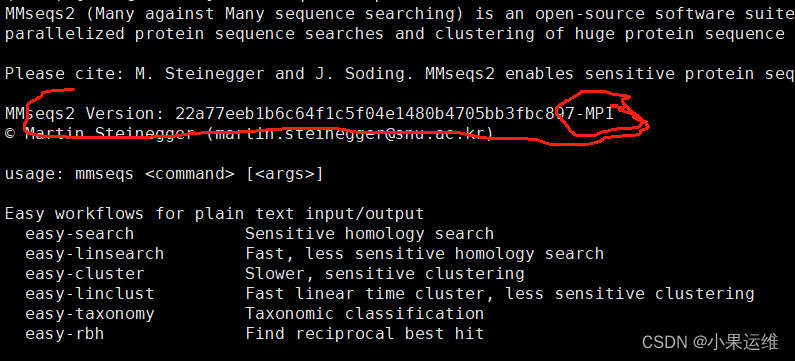
运行使用方法:
### 使用跨节点并行计算的格式
RUNNER="mpirun -pernode -np 42" mmseqs search queryDB targetDB resultDB tmp### TMP文件夹必须在各计算节点之间共享,一般使用NFS
### For clustering just call the clustering. The TMP folder has to be shared between all nodes (e.g. NFS)RUNNER="mpirun -pernode -np 42" mmseqs cluster DB clu tmp#Write temporary files to local disk when running with MPI
As part of its computation, MMseqs2 writes temporary files corresponding to each of the database splits. The number of the database splits is determined by the number of servers and number of cores in each server. By default, temporary files are written to the shared disk.#In case the number of database splits is large, it would mean a high burden of I/O operations on the same disk. To avoid slowdowns due to this issue, an additional parameter can be passed to search in MPI mode:RUNNER="mpirun -np 42" mmseqs search queryDB targetDB resultDB tmp --local-tmp /local/hdd/
#Passing this parameter will write the temporary files of each server (created by its cores) on the indicated path (local disk) and reduce the number of temporary files handled on the shared disk.#How to run MMseqs2 on multiple servers using batch systems
#MMseqs2 comes with tools to split database to distribute jobs in batch systems (like sge, slurm, moab, lsf, ...). However, the MPI solution is preferred if available since it optimizes the distribution of computing load. Splitting the query database can be used to distribute the load, MMseqs2 has a module called splitdb that splits the database in --split N chunks. Each can be submitted separate to the grid system.# script to splits the database in 3 parts and submit them to the grid# split query dbSPLITS=3QUERYFASTA=queryDB.fastaQUERYDB=queryDBmmseqs createdb "${QUERYFASTA}" "${QUERYDB}" mmseqs splitdb "${QUERYDB}" "${QUERYDB}_split" --split $SPLITS# create header database to support full mmseqs functionality# this step can be used if queryDB is used in downstream stepsfor file in $(ls "${QUERYDB}_split"_*_$SPLITS); dommseqs createsubdb "${file}.index" "${QUERYDB}_h" "${file}_h"done# submit job split=0for file in $(ls "${QUERYDB}_split"_*_$SPLITS); dobsub mmseqs search "${file}" targetDB aln_${split} tmp((split++))done




:基于本地知识库的检索增强生成RAG)
)





)


)




)