一 配置文件
1 作用–解决硬编码的问题
在实际开发中,有时将变量的值直接定义在.java源文件中;如果维护人员想要修改数据,无法完成(因为没有修改权限),这种操作称之为硬编码
2 执行原理:
将经常需要改变的数据定义在指定类型的文件中,通过java代码对指定的类型的文件进行操作
核心技术:IO流 – 输入字节流 – InputStream对象
3 分类
① .properties : 文件类型:对应ava中定义好Properties类,他是一个集合类;是Map集合的一个具体实现类;以K-V键值对形式存储,呈现一一对应的映射关系;其中KEY和VALUE只支持String类型
② .xml:文件类型;可扩展标记(标签)语言;以标签的形式进行存储;与HTML一样
二 .properties文件
1 编写指定的.properties文件 – 首先在项目下创建一个resource文件夹(固定名称,与src同级)
2 将该文件夹通过Mark Directory as中的Resources Root设置为资源文件夹
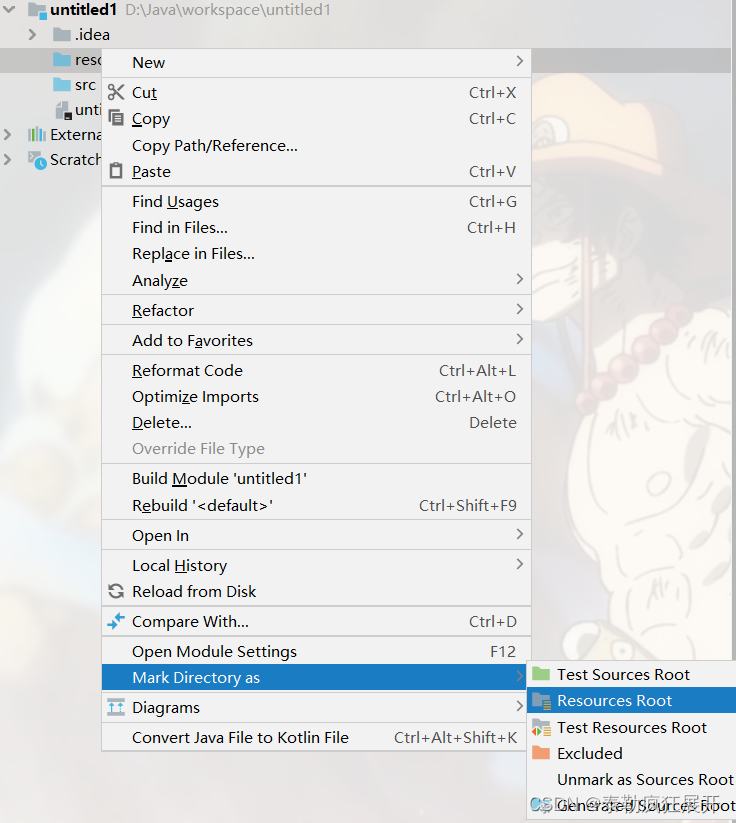
3 于该文件夹中创建.properties文件(文件需符合小驼峰命名法,且文件后缀也要写)
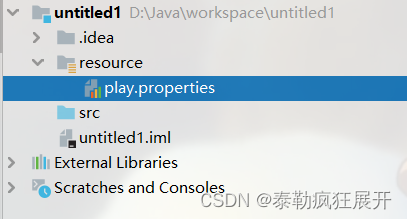
4 获取配置文件中的数据
配置文件
# 只支持String类型,故不需定义数据类型,"",注意不要多出空格
water=water
fire=fire
Test类
//方式1:将配置文件加载到InputStream对象中,需写绝对路径
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {InputStream is=null;try {is=new FileInputStream("D:\\Java\\workspace\\untitled1\\resource\\play.properties");// 定义properties集合Properties p=new Properties();// 通过集合对象的方法,将流中的数据加载到集合中p.load(is);// public String getProperty(String key) 通过key获取value// public Object get(String key) 通过key获取valueSystem.err.println(p.getProperty("water"));System.err.println(p.getProperty("fire"));} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}// 方式2:通过类加载器 ClassLoader对象(JVM提供)
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 反射机制 ClassLoader cl=类名.class.getClassLoader();// 通过当前执行线程对象获取 ClassLoader cl=Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();ClassLoader cl=Test.class.getClassLoader();// 通过类加载器对象调用方法,将指定的配置文件加载到InputStream对象中InputStream is=cl.getResourceAsStream("play.properties");// 定义集合Properties p=new Properties();try {p.load(is);System.out.println(p.getProperty("water"));System.out.println(p.getProperty("fire"));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if(is!=null){try {is.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}
三 .xml文件应用
1 概述:可扩展标记(标签)语言;由W3C组织编写,定义定规范;支持自定义标签(支持中文标签),创建方式与.properties相同(后缀改为.xml)
2 格式:
<标签名></标签名> – 没有特殊要求都是双标签
<标签名/> – 单标签,当且仅当标签之间没有编写文本内容,可以使用单标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--xml文件第一行是文档说明 version是xml的版本号 encoding是xml的字符编码集-->
<!--一个xml只有一个根标签:体现该xml的作用,可通过tab快捷键生成标签-->
<Water><!--区分大小写,类似Java的类--><water><name>大黄</name><kg>24</kg></water><water><name>大白</name><kg>30</kg></water>
</Water>
3 DOM方式–解析标签类型文件(.xml文件或.html文件)
概述:Document Object Model文档对象模型,将指定的配置文件(Document)通过对象(Object)的方式,按照指定规则(Model)进行操作
它将整个页面抽象为一棵树(读取XML或HTML文档,将其转换为一个DOM树,解析DOM树,将其转换为一个内存中的树形结构),开发者可以通过操作树上的节点来改变页面的内容、结构和样式,并将修改后的DOM树重新渲染到页面上。DOM树的根节点是document对象,它代表整个文档。每个节点都有自己的属性和方法,可以通过这些属性和方法来操作节点。
主要操作标签与文本内容,前提是操作语言必须支持面向对象编程方式,文件必须是标记(标签)类型的文件(主干-根标签,枝干-子标签,叶子-标签中的文本内容)
// 通过DOM对指定的xml文件进行crud操作// 获取并打印二号小动物的名字
public class DemoTest {@Testpublic void getName() throws Exception {// 获取配置文件对象// 获取文件构建工厂对象DocumentBuilderFactory dbf=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();// 根据工厂对象获取文件构建对象DocumentBuilder db=dbf.newDocumentBuilder();// 根据文件构建对象获取文件对象Document doc=db.parse("resource/play.xml");// 根据文件对象获取根标签Element root=doc.getDocumentElement();// 通过根标签获取指定位置上的元素 Node 父节点 Element 子元素NodeList animals=root.getElementsByTagName("animal");// 自0计算Element a2= (Element) animals.item(1);// 根据指定学生标签获取指定的name标签Element name= (Element) a2.getElementsByTagName("name").item(0);// 根据name标签获取文本内容System.err.println("name="+name.getTextContent());}
}// 增加一个小动物
public class DemoTest {@Testpublic void addAnimal() throws Exception {// 获取文件对象DocumentBuilderFactory dbf=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();DocumentBuilder db=dbf.newDocumentBuilder();Document doc=db.parse("resource/play.xml");// 通过文档对象创建Animal对应的标签Element animal=doc.createElement("animal");Element name=doc.createElement("name");Element kg=doc.createElement("kg");// 给标签设置对应的文本内容name.setTextContent("小花");kg.setTextContent("11");// 将子标签name,kg追加到animal的尾部animal.appendChild(name);animal.appendChild(kg);// 通过文档对象获取根标签并将animal标签追加到根标签尾部Element animals=doc.getDocumentElement();animals.appendChild(animal);// 此时后端操作完成,需通过回写刷新xml// 获取回写工厂对象TransformerFactory tff=TransformerFactory.newInstance();// 通过工厂对象获取回写对象Transformer tf=tff.newTransformer();// 通过回写对象调用Document对象中的内容完成回写xml// Source xmlSource 后端操作 Result outputTarget 写入xml中tf.transform(new DOMSource(doc),new StreamResult(new File("resource/play.xml")));System.out.println("OK");}
}// 修改2号小动物的体重
public class DemoTest {@Testpublic void replaceKg() throws Exception {// 获取文件对象DocumentBuilderFactory dbf=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();DocumentBuilder db=dbf.newDocumentBuilder();Document doc=db.parse("resource/play.xml");// 根标签Element animals=doc.getDocumentElement();// 通过根标签获取所有动物子标签查询指定动物Element a2= (Element) animals.getElementsByTagName("animal").item(1);// animal标签中的kg标签只有一个故item为0Element kg= (Element) a2.getElementsByTagName("kg").item(0);kg.setTextContent("20");// 获取回写对象TransformerFactory tff=TransformerFactory.newInstance();Transformer tf=tff.newTransformer();tf.transform(new DOMSource(doc),new StreamResult(new File("resource/play.xml")));System.out.println("OK");}
}// 删除2号小动物
public class DemoTest {@Testpublic void removeAnimal() throws Exception {// 获取文件对象DocumentBuilderFactory dbf=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();DocumentBuilder db=dbf.newDocumentBuilder();Document doc=db.parse("resource/play.xml");// 根标签Element animals=doc.getDocumentElement();// 获取子标签Element a2= (Element) animals.getElementsByTagName("animal").item(1);// 根标签调用方法删除子标签 父一级删除子一级animals.removeChild(a2);// 获取回写对象TransformerFactory tff=TransformerFactory.newInstance();Transformer tf=tff.newTransformer();tf.transform(new DOMSource(doc),new StreamResult(new File("resource/play.xml")));System.out.println("OK");}
}
4 xml中约束
约束:规范指定编程语言或文件的编写格式
xml约束:由w3c组织规定,规定xml语言格式
xml约束分类 – 一般是下载网络上编写好的约束文件①.dtd ②.schema
四 封装工具类
1 作用
重复操作(获取文档对象+回写文件)会导致配置文件加载次数过多,此时需要通过 jar包(需要大量API)或者工具类 (针对某个操作)简化代码
2 工具类定义
① 将指定配置文件加载定义到static代码块中(只加载一次,优先加载)
② 提供获取文档对象的方法和回写xml文档的方法
封装工具类
① 编写.properties文件,配置指定的xml文件的路径
# xml的路径 xmlPath.properties
path=resource/play.xml
② 编写工具类
public abstract class DOMUtils {private static String path;private static Document doc; //导入w3c包的doc// 指定配置文件只需优先加载一次static{ClassLoader cl=DOMUtils.class.getClassLoader();InputStream is=cl.getResourceAsStream("xmlPath.properties");Properties p=new Properties();try {p.load(is);path=p.getProperty("path");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if(is!=null){try {is.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}// 根据路径获取xml对应的Document对象public static Document getDoc() throws Exception{DocumentBuilderFactory dbf=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();DocumentBuilder db=dbf.newDocumentBuilder();doc=db.parse(new File(path));return doc;}// 回写xml方法public static void writeForXml() throws Exception{TransformerFactory tff=TransformerFactory.newInstance();Transformer tf=tff.newTransformer();tf.transform(new DOMSource(doc),new StreamResult(new File(path)));}
}
② 测试
public class DemoTest {@Testpublic void playUtils() throws Exception {// 获取文档对象Document doc= DOMUtils.getDoc();// 通过文档对象创建子标签Element animal=doc.createElement("animal");Element name=doc.createElement("name");Element kg=doc.createElement("kg");// 为子标签设置内容name.setTextContent("煤球");kg.setTextContent("16");// 子标签追加animal.appendChild(name);animal.appendChild(kg);// 跟标签追加Element animals=doc.getDocumentElement();animals.appendChild(animal);// 回写xmlDOMUtils.writeForXml();System.out.println("OK");}
}

》)







:auto_ptr, unique_ptr, shared_ptr,weak_ptr)


)


 C++入门篇概述)
)


