原型模式是从一个对象再创建另一个可定制的对象,而且不需要知道任何创建的细节。拷贝分浅拷贝和深拷贝。浅拷贝无法拷贝引用对象。在面试的时候,我们会投多家公司,根据岗位的不同我们会适当调整。使用原型模式可以快速达到需求,下面通过这个案例说明。

注意WorkExperience要实现Serializable接口。
package Prototype;import java.io.Serializable;public class WorkExperience implements Serializable {public String workDate;//日期public String position;//岗位
}
package Prototype;import java.io.*;public class Resume implements Cloneable, Serializable {private String name;//姓名private int age;//年龄private WorkExperience we = new WorkExperience();//工作经验public Resume(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public void setWorkExperience(String workDate, String position) {we.workDate = workDate;we.position = position;}public Resume clone() {Resume resume = null;try {resume = (Resume)super.clone();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}return resume;}public Resume deepClone() {Resume resume = null;ByteArrayOutputStream bos = null;ObjectOutputStream oos = null;ByteArrayInputStream bis = null;ObjectInputStream ois = null;try {//序列化bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);oos.writeObject(this);//反序列化bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);resume = (Resume) ois.readObject();return resume;} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();return null;} finally {try {bos.close();oos.close();bis.close();ois.close();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Resume{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", we.workDate=" + we.workDate +",we.position=" + we.position +'}';}
}
package Prototype;public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {Resume a = new Resume("张三",20);a.setWorkExperience("2023-1","Java工程师");Resume b = a.clone();b.setWorkExperience("2015-10","前端工程师");Resume c = a.deepClone();c.setWorkExperience("2015-5","网络工程师");System.out.println(a.toString());System.out.println(b.toString());System.out.println(c.toString());}
}
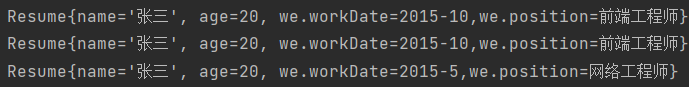
第一张简历是原型,第二张是第一张的浅拷贝并且修改了一定的信息,发现第一张与第二张有关工作经验的内容是一样的,因为这两张简历的工作经验指向的是同一个对象,而第三张是深拷贝,引用对象的信息被修改。





模为60的BCD码计数器_2023.11.22】)

)
)










