大家好,小编来为大家解答以下问题,笨办法学python 3电子书下载,笨办法学python3pdf完整版,今天让我们一起来看看吧!
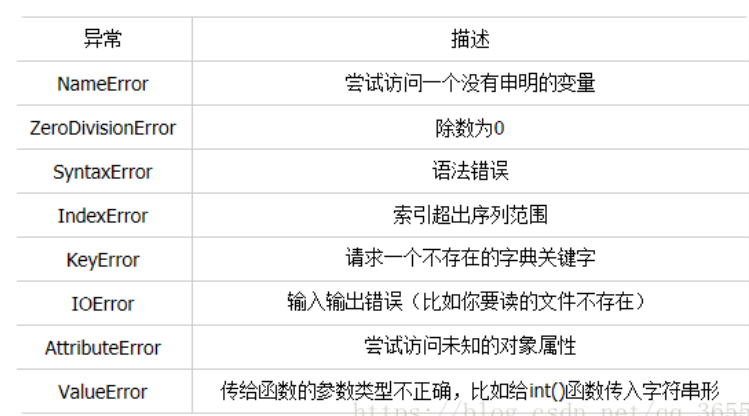
1、笨方法学python习题43
按照你说的
Map是一个类,scene_map是一老胡镇个类实例
scene_map.opening_scene()是调用scene_map类实例做悉的opening_scene方法
_不是特定格式,看具体你起的变量名以及方法侍粗名,其中的.是特定格式。
2、新手求教,笨方法学python的习题35问题
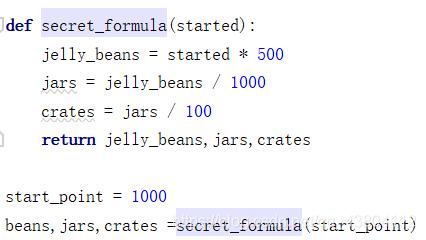
按照你说的
Map是一个类,scene_map是一老胡镇个类实例
scene_map.opening_scene()是调用scene_map类实例做悉的opening_scene方法
_不是特定格式,看具体你起的变量名以及方法侍粗名,其中的.是特定格式。
#!usr/bin/python
# -*-coding:utf-8-*- from sys import exit def gold_room(): print("This room is full of gold. How much do you take?") next = input("> ") if "0" in next or "1" in next: how_much = int(next) else: dead("Man, learn to type a number.") if how_much < 50: print("Nice, you're not greedy, you win!") exit(0) else: dead("You greedy bastard!") def bear_room(): print ("There is a bear here.") print ("The bear has a bunch of honey.") print ("The fat bear is in front of another door.") print ("How are you going to move the bear?") bear_moved = False while True: next = input("> ") if next == "take honey": dead("The bear looks at you then slaps your face off.") elif next == "taunt bear" and not bear_moved: print("The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now.") bear_moved = True elif next == "taunt bear" and 族稿bear_moved: dead("The bear gets pissed off and chews your leg off.") elif next == "open door" and bear_moved: gold_room() 喊穗氏 else: print("I got no idea what that means.") def cthulhu_room(): print ("Here you see the great evil Cthulhu.") print ("He, it, whatever stares at you and you go insane.") print ("Do you flee for your life or eat your head?") next = input("> ") if "flee" in next: start() elif "head" in next: dead("Well that was tasty!") else: cthulhu_room() def dead(why): print(why,"Good job") exit(0) def start(): print ("You are in a dark room.") print ("There is a door to your right and left.") print ("Which one do you take?") next = input("> ") if next == "left": bear_room() elif next == "right": cthulhu_room() else: dead("You stumble around the 郑散room until you starve.") start()
运行结果如下:
You are in a dark room. There is a door to your right and left. Which one do you take? > left There is a bear here. The bear has a bunch of honey. The fat bear is in front of another door. How are you going to move the bear? > taunt bear The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now. > open door This room is full of gold. How much do you take? > asf Man, learn to type a number. Good job!
3、笨方法学习python3的习题35中程序“def dead(why): print(why,"Good job!")”不太理解!请教!
按照你说的
Map是一个类,scene_map是一老胡镇个类实例
scene_map.opening_scene()是调用scene_map类实例做悉的opening_scene方法
_不是特定格式,看具体你起的变量名以及方法侍粗名,其中的.是特定格式。
#!usr/bin/python
# -*-coding:utf-8-*- from sys import exit def gold_room(): print("This room is full of gold. How much do you take?") next = input("> ") if "0" in next or "1" in next: how_much = int(next) else: dead("Man, learn to type a number.") if how_much < 50: print("Nice, you're not greedy, you win!") exit(0) else: dead("You greedy bastard!") def bear_room(): print ("There is a bear here.") print ("The bear has a bunch of honey.") print ("The fat bear is in front of another door.") print ("How are you going to move the bear?") bear_moved = False while True: next = input("> ") if next == "take honey": dead("The bear looks at you then slaps your face off.") elif next == "taunt bear" and not bear_moved: print("The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now.") bear_moved = True elif next == "taunt bear" and 族稿bear_moved: dead("The bear gets pissed off and chews your leg off.") elif next == "open door" and bear_moved: gold_room() 喊穗氏 else: print("I got no idea what that means.") def cthulhu_room(): print ("Here you see the great evil Cthulhu.") print ("He, it, whatever stares at you and you go insane.") print ("Do you flee for your life or eat your head?") next = input("> ") if "flee" in next: start() elif "head" in next: dead("Well that was tasty!") else: cthulhu_room() def dead(why): print(why,"Good job") exit(0) def start(): print ("You are in a dark room.") print ("There is a door to your right and left.") print ("Which one do you take?") next = input("> ") if next == "left": bear_room() elif next == "right": cthulhu_room() else: dead("You stumble around the 郑散room until you starve.") start()
运行结果如下:
You are in a dark room. There is a door to your right and left. Which one do you take? > left There is a bear here. The bear has a bunch of honey. The fat bear is in front of another door. How are you going to move the bear? > taunt bear The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now. > open door This room is full of gold. How much do you take? > asf Man, learn to type a number. Good job!
1、你要在exit前,打印信息,如果不打印这些信息,是可以不定义dead函数。
2、第一问已经回答了,就是用exit函数退出的。
3、why不是变量,是函数的参数,调用函数是传入的。
比如dead("You stumble around the room until you starve.")
why = "You stumble around the room until you starve."
print(why,"good job!")删除或注释没有关系的,你可能是把exit也给注释了
4、程序是从上而下执行的,但是函数的调用,对象的创建,都会有代码的跳转,所以不能只看输出的
比如
a=5
print(‘A’)
你的程序,前面都是函数的定义,就和我举例的,声明变量a=5是一个意思,它们执行了,只是没有输出而已
也只是打印的“A”,第一行没有任何输出的,你不能说程序就是从第2行开始的。
4、《笨办法学python》练习13
按照你说的
Map是一个类,scene_map是一老胡镇个类实例
scene_map.opening_scene()是调用scene_map类实例做悉的opening_scene方法
_不是特定格式,看具体你起的变量名以及方法侍粗名,其中的.是特定格式。
#!usr/bin/python
# -*-coding:utf-8-*- from sys import exit def gold_room(): print("This room is full of gold. How much do you take?") next = input("> ") if "0" in next or "1" in next: how_much = int(next) else: dead("Man, learn to type a number.") if how_much < 50: print("Nice, you're not greedy, you win!") exit(0) else: dead("You greedy bastard!") def bear_room(): print ("There is a bear here.") print ("The bear has a bunch of honey.") print ("The fat bear is in front of another door.") print ("How are you going to move the bear?") bear_moved = False while True: next = input("> ") if next == "take honey": dead("The bear looks at you then slaps your face off.") elif next == "taunt bear" and not bear_moved: print("The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now.") bear_moved = True elif next == "taunt bear" and 族稿bear_moved: dead("The bear gets pissed off and chews your leg off.") elif next == "open door" and bear_moved: gold_room() 喊穗氏 else: print("I got no idea what that means.") def cthulhu_room(): print ("Here you see the great evil Cthulhu.") print ("He, it, whatever stares at you and you go insane.") print ("Do you flee for your life or eat your head?") next = input("> ") if "flee" in next: start() elif "head" in next: dead("Well that was tasty!") else: cthulhu_room() def dead(why): print(why,"Good job") exit(0) def start(): print ("You are in a dark room.") print ("There is a door to your right and left.") print ("Which one do you take?") next = input("> ") if next == "left": bear_room() elif next == "right": cthulhu_room() else: dead("You stumble around the 郑散room until you starve.") start()
运行结果如下:
You are in a dark room. There is a door to your right and left. Which one do you take? > left There is a bear here. The bear has a bunch of honey. The fat bear is in front of another door. How are you going to move the bear? > taunt bear The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now. > open door This room is full of gold. How much do you take? > asf Man, learn to type a number. Good job!
1、你要在exit前,打印信息,如果不打印这些信息,是可以不定义dead函数。
2、第一问已经回答了,就是用exit函数退出的。
3、why不是变量,是函数的参数,调用函数是传入的。
比如dead("You stumble around the room until you starve.")
why = "You stumble around the room until you starve."
print(why,"good job!")删除或注释没有关系的,你可能是把exit也给注释了
4、程序是从上而下执行的,但是函数的调用,对象的创建,都会有代码的跳转,所以不能只看输出的
比如
a=5
print(‘A’)
你的程序,前面都是函数的定义,就和我举例的,声明变量a=5是一个意思,它们执行了,只是没有输出而已
也只是打印的“A”,第一行没有任何输出的,你不能说程序就是从第2行开始的。
首先,我没有看到你的row_input()函数在哪里定义的,这是一个疑问;但是根据报错,说明你的函数没问题,问题只是在命令行参数。
从第13行开始解释:衡橡
A, B, C, D = argv
那么argv这个笑拆list中就要有4个元素对应等号前面的变量。
通用的做法是:
A = argv[0] #argv[0]保存的是脚本名 B = argv[1] #argv[1]保存的是第一个参数 C = argv[2] #argv[2]保存的是第二个参数
依次类推。
你的报错原因应该是没有输入命令行参数或者参数不够,可以按照下面方法测试:
HOME:\work>python 你的脚本.py 参数1 参数2 参数3 参数4
一般的,如果使用命令行参数,必须要判断参数是否足够和类型是否正确,例如:
import sys'''
一些函数
'''if __name__ == '__main__':# 假如有4个参数
if len() < 5:print("缺少参数,提示参数类型和数量。")exit()
else:碰拦枣 [A, B, C, D] = [1:5]# 判断每个参数类型,此处省略# 执行函数体
5、笨办法学python习题17中我的exists函数是无效的,怎么办呢?
按照你说的
Map是一个类,scene_map是一老胡镇个类实例
scene_map.opening_scene()是调用scene_map类实例做悉的opening_scene方法
_不是特定格式,看具体你起的变量名以及方法侍粗名,其中的.是特定格式。
#!usr/bin/python
# -*-coding:utf-8-*- from sys import exit def gold_room(): print("This room is full of gold. How much do you take?") next = input("> ") if "0" in next or "1" in next: how_much = int(next) else: dead("Man, learn to type a number.") if how_much < 50: print("Nice, you're not greedy, you win!") exit(0) else: dead("You greedy bastard!") def bear_room(): print ("There is a bear here.") print ("The bear has a bunch of honey.") print ("The fat bear is in front of another door.") print ("How are you going to move the bear?") bear_moved = False while True: next = input("> ") if next == "take honey": dead("The bear looks at you then slaps your face off.") elif next == "taunt bear" and not bear_moved: print("The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now.") bear_moved = True elif next == "taunt bear" and 族稿bear_moved: dead("The bear gets pissed off and chews your leg off.") elif next == "open door" and bear_moved: gold_room() 喊穗氏 else: print("I got no idea what that means.") def cthulhu_room(): print ("Here you see the great evil Cthulhu.") print ("He, it, whatever stares at you and you go insane.") print ("Do you flee for your life or eat your head?") next = input("> ") if "flee" in next: start() elif "head" in next: dead("Well that was tasty!") else: cthulhu_room() def dead(why): print(why,"Good job") exit(0) def start(): print ("You are in a dark room.") print ("There is a door to your right and left.") print ("Which one do you take?") next = input("> ") if next == "left": bear_room() elif next == "right": cthulhu_room() else: dead("You stumble around the 郑散room until you starve.") start()
运行结果如下:
You are in a dark room. There is a door to your right and left. Which one do you take? > left There is a bear here. The bear has a bunch of honey. The fat bear is in front of another door. How are you going to move the bear? > taunt bear The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now. > open door This room is full of gold. How much do you take? > asf Man, learn to type a number. Good job!
1、你要在exit前,打印信息,如果不打印这些信息,是可以不定义dead函数。
2、第一问已经回答了,就是用exit函数退出的。
3、why不是变量,是函数的参数,调用函数是传入的。
比如dead("You stumble around the room until you starve.")
why = "You stumble around the room until you starve."
print(why,"good job!")删除或注释没有关系的,你可能是把exit也给注释了
4、程序是从上而下执行的,但是函数的调用,对象的创建,都会有代码的跳转,所以不能只看输出的
比如
a=5
print(‘A’)
你的程序,前面都是函数的定义,就和我举例的,声明变量a=5是一个意思,它们执行了,只是没有输出而已
也只是打印的“A”,第一行没有任何输出的,你不能说程序就是从第2行开始的。
首先,我没有看到你的row_input()函数在哪里定义的,这是一个疑问;但是根据报错,说明你的函数没问题,问题只是在命令行参数。
从第13行开始解释:衡橡
A, B, C, D = argv
那么argv这个笑拆list中就要有4个元素对应等号前面的变量。
通用的做法是:
A = argv[0] #argv[0]保存的是脚本名 B = argv[1] #argv[1]保存的是第一个参数 C = argv[2] #argv[2]保存的是第二个参数
依次类推。
你的报错原因应该是没有输入命令行参数或者参数不够,可以按照下面方法测试:
HOME:\work>python 你的脚本.py 参数1 参数2 参数3 参数4
一般的,如果使用命令行参数,必须要判断参数是否足够和类型是否正确,例如:
import sys'''
一些函数
'''if __name__ == '__main__':# 假如有4个参数
if len() < 5:print("缺少参数,提示参数类型和数量。")exit()
else:碰拦枣 [A, B, C, D] = [1:5]# 判断每个参数类型,此处省略# 执行函数体
严格的说,象你这么用是绝对伍孙属于没有定义的。不过有时候又可以是因为,如果你在程序开头函腊橘枯数前面定义一些变量,原则上它会自动变成global的。除非你另外启线程,或者是有可能有与它重名的变量,否则可以直接在函数体内使用,当然也可以在后面的语句中使用。函数式编程要记着IPO这个准则。就是每个函数最好都是有输入input有输出output。函数体就是处理process。尽量不要使用全局变量,轮洞也不要使用默认值。一个正规的做法是这样:defexample(a):a=0returnaa=1printexample(a)这是一个标准用法,你就不用为global变量头痛了。
6、你好! 我想请教有关笨办法学python习题48的问题
按照你说的
Map是一个类,scene_map是一老胡镇个类实例
scene_map.opening_scene()是调用scene_map类实例做悉的opening_scene方法
_不是特定格式,看具体你起的变量名以及方法侍粗名,其中的.是特定格式。
#!usr/bin/python
# -*-coding:utf-8-*- from sys import exit def gold_room(): print("This room is full of gold. How much do you take?") next = input("> ") if "0" in next or "1" in next: how_much = int(next) else: dead("Man, learn to type a number.") if how_much < 50: print("Nice, you're not greedy, you win!") exit(0) else: dead("You greedy bastard!") def bear_room(): print ("There is a bear here.") print ("The bear has a bunch of honey.") print ("The fat bear is in front of another door.") print ("How are you going to move the bear?") bear_moved = False while True: next = input("> ") if next == "take honey": dead("The bear looks at you then slaps your face off.") elif next == "taunt bear" and not bear_moved: print("The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now.") bear_moved = True elif next == "taunt bear" and 族稿bear_moved: dead("The bear gets pissed off and chews your leg off.") elif next == "open door" and bear_moved: gold_room() 喊穗氏 else: print("I got no idea what that means.") def cthulhu_room(): print ("Here you see the great evil Cthulhu.") print ("He, it, whatever stares at you and you go insane.") print ("Do you flee for your life or eat your head?") next = input("> ") if "flee" in next: start() elif "head" in next: dead("Well that was tasty!") else: cthulhu_room() def dead(why): print(why,"Good job") exit(0) def start(): print ("You are in a dark room.") print ("There is a door to your right and left.") print ("Which one do you take?") next = input("> ") if next == "left": bear_room() elif next == "right": cthulhu_room() else: dead("You stumble around the 郑散room until you starve.") start()
运行结果如下:
You are in a dark room. There is a door to your right and left. Which one do you take? > left There is a bear here. The bear has a bunch of honey. The fat bear is in front of another door. How are you going to move the bear? > taunt bear The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now. > open door This room is full of gold. How much do you take? > asf Man, learn to type a number. Good job!
1、你要在exit前,打印信息,如果不打印这些信息,是可以不定义dead函数。
2、第一问已经回答了,就是用exit函数退出的。
3、why不是变量,是函数的参数,调用函数是传入的。
比如dead("You stumble around the room until you starve.")
why = "You stumble around the room until you starve."
print(why,"good job!")删除或注释没有关系的,你可能是把exit也给注释了
4、程序是从上而下执行的,但是函数的调用,对象的创建,都会有代码的跳转,所以不能只看输出的
比如
a=5
print(‘A’)
你的程序,前面都是函数的定义,就和我举例的,声明变量a=5是一个意思,它们执行了,只是没有输出而已
也只是打印的“A”,第一行没有任何输出的,你不能说程序就是从第2行开始的。
首先,我没有看到你的row_input()函数在哪里定义的,这是一个疑问;但是根据报错,说明你的函数没问题,问题只是在命令行参数。
从第13行开始解释:衡橡
A, B, C, D = argv
那么argv这个笑拆list中就要有4个元素对应等号前面的变量。
通用的做法是:
A = argv[0] #argv[0]保存的是脚本名 B = argv[1] #argv[1]保存的是第一个参数 C = argv[2] #argv[2]保存的是第二个参数
依次类推。
你的报错原因应该是没有输入命令行参数或者参数不够,可以按照下面方法测试:
HOME:\work>python 你的脚本.py 参数1 参数2 参数3 参数4
一般的,如果使用命令行参数,必须要判断参数是否足够和类型是否正确,例如:
import sys'''
一些函数
'''if __name__ == '__main__':# 假如有4个参数
if len() < 5:print("缺少参数,提示参数类型和数量。")exit()
else:碰拦枣 [A, B, C, D] = [1:5]# 判断每个参数类型,此处省略# 执行函数体
严格的说,象你这么用是绝对伍孙属于没有定义的。不过有时候又可以是因为,如果你在程序开头函腊橘枯数前面定义一些变量,原则上它会自动变成global的。除非你另外启线程,或者是有可能有与它重名的变量,否则可以直接在函数体内使用,当然也可以在后面的语句中使用。函数式编程要记着IPO这个准则。就是每个函数最好都是有输入input有输出output。函数体就是处理process。尽量不要使用全局变量,轮洞也不要使用默认值。一个正规的做法是这样:defexample(a):a=0returnaa=1printexample(a)这是一个标准用法,你就不用为global变量头痛了。
受宠若惊,刚学习到单元测试,这边就可以回答了。我不知道你模块结构是怎样的,我这边先假设你的parse_subjuect()和parse_sentence()的方法是定义在配返parser模块里的,且该实例必须是时class A的实例,不能是其他的实例,例子如下。
import unittest import parserclass 伏卖散TestMethods(unittest.TestCase):def setUp(self):passdef test_parse_subject(self):subject = parser.parse_subjuect()#参数我不知道,我就假定不用传参数了#为了方便描述,我把异常的消息设置为中文了,运行的时候最好改成中文缺氏 self.assertTrue(isinstance(subject, A), msg="应该是A的实例,但是却是%s"%type(self._subject))def test_parse_sentence(self):sentence = parser.parse_sentence()#参数我不知道,我就假定不用传参数了self.assertTrue(callable(sentence), msg="应该是个可调用的函数对象,但是却不是")if __name__ == '__main__':()
这鱼就搞定了
7、笨方法学Python》中的习题25 出错
按照你说的
Map是一个类,scene_map是一老胡镇个类实例
scene_map.opening_scene()是调用scene_map类实例做悉的opening_scene方法
_不是特定格式,看具体你起的变量名以及方法侍粗名,其中的.是特定格式。
#!usr/bin/python
# -*-coding:utf-8-*- from sys import exit def gold_room(): print("This room is full of gold. How much do you take?") next = input("> ") if "0" in next or "1" in next: how_much = int(next) else: dead("Man, learn to type a number.") if how_much < 50: print("Nice, you're not greedy, you win!") exit(0) else: dead("You greedy bastard!") def bear_room(): print ("There is a bear here.") print ("The bear has a bunch of honey.") print ("The fat bear is in front of another door.") print ("How are you going to move the bear?") bear_moved = False while True: next = input("> ") if next == "take honey": dead("The bear looks at you then slaps your face off.") elif next == "taunt bear" and not bear_moved: print("The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now.") bear_moved = True elif next == "taunt bear" and 族稿bear_moved: dead("The bear gets pissed off and chews your leg off.") elif next == "open door" and bear_moved: gold_room() 喊穗氏 else: print("I got no idea what that means.") def cthulhu_room(): print ("Here you see the great evil Cthulhu.") print ("He, it, whatever stares at you and you go insane.") print ("Do you flee for your life or eat your head?") next = input("> ") if "flee" in next: start() elif "head" in next: dead("Well that was tasty!") else: cthulhu_room() def dead(why): print(why,"Good job") exit(0) def start(): print ("You are in a dark room.") print ("There is a door to your right and left.") print ("Which one do you take?") next = input("> ") if next == "left": bear_room() elif next == "right": cthulhu_room() else: dead("You stumble around the 郑散room until you starve.") start()
运行结果如下:
You are in a dark room. There is a door to your right and left. Which one do you take? > left There is a bear here. The bear has a bunch of honey. The fat bear is in front of another door. How are you going to move the bear? > taunt bear The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now. > open door This room is full of gold. How much do you take? > asf Man, learn to type a number. Good job!
1、你要在exit前,打印信息,如果不打印这些信息,是可以不定义dead函数。
2、第一问已经回答了,就是用exit函数退出的。
3、why不是变量,是函数的参数,调用函数是传入的。
比如dead("You stumble around the room until you starve.")
why = "You stumble around the room until you starve."
print(why,"good job!")删除或注释没有关系的,你可能是把exit也给注释了
4、程序是从上而下执行的,但是函数的调用,对象的创建,都会有代码的跳转,所以不能只看输出的
比如
a=5
print(‘A’)
你的程序,前面都是函数的定义,就和我举例的,声明变量a=5是一个意思,它们执行了,只是没有输出而已
也只是打印的“A”,第一行没有任何输出的,你不能说程序就是从第2行开始的。
首先,我没有看到你的row_input()函数在哪里定义的,这是一个疑问;但是根据报错,说明你的函数没问题,问题只是在命令行参数。
从第13行开始解释:衡橡
A, B, C, D = argv
那么argv这个笑拆list中就要有4个元素对应等号前面的变量。
通用的做法是:
A = argv[0] #argv[0]保存的是脚本名 B = argv[1] #argv[1]保存的是第一个参数 C = argv[2] #argv[2]保存的是第二个参数
依次类推。
你的报错原因应该是没有输入命令行参数或者参数不够,可以按照下面方法测试:
HOME:\work>python 你的脚本.py 参数1 参数2 参数3 参数4
一般的,如果使用命令行参数,必须要判断参数是否足够和类型是否正确,例如:
import sys'''
一些函数
'''if __name__ == '__main__':# 假如有4个参数
if len() < 5:print("缺少参数,提示参数类型和数量。")exit()
else:碰拦枣 [A, B, C, D] = [1:5]# 判断每个参数类型,此处省略# 执行函数体
严格的说,象你这么用是绝对伍孙属于没有定义的。不过有时候又可以是因为,如果你在程序开头函腊橘枯数前面定义一些变量,原则上它会自动变成global的。除非你另外启线程,或者是有可能有与它重名的变量,否则可以直接在函数体内使用,当然也可以在后面的语句中使用。函数式编程要记着IPO这个准则。就是每个函数最好都是有输入input有输出output。函数体就是处理process。尽量不要使用全局变量,轮洞也不要使用默认值。一个正规的做法是这样:defexample(a):a=0returnaa=1printexample(a)这是一个标准用法,你就不用为global变量头痛了。
受宠若惊,刚学习到单元测试,这边就可以回答了。我不知道你模块结构是怎样的,我这边先假设你的parse_subjuect()和parse_sentence()的方法是定义在配返parser模块里的,且该实例必须是时class A的实例,不能是其他的实例,例子如下。
import unittest import parserclass 伏卖散TestMethods(unittest.TestCase):def setUp(self):passdef test_parse_subject(self):subject = parser.parse_subjuect()#参数我不知道,我就假定不用传参数了#为了方便描述,我把异常的消息设置为中文了,运行的时候最好改成中文缺氏 self.assertTrue(isinstance(subject, A), msg="应该是A的实例,但是却是%s"%type(self._subject))def test_parse_sentence(self):sentence = parser.parse_sentence()#参数我不知道,我就假定不用传参数了self.assertTrue(callable(sentence), msg="应该是个可调用的函数对象,但是却不是")if __name__ == '__main__':()
这鱼就搞定了
>>> sorted_words=ex25.sort_sentence(sentence) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#4>", line 1, in <module> sorted_words=ex25.sort_sentence(sentence) File "E:\学好扮习\Python exercise\", line 23, in sort_sentence return (sort_works(words)) NameError: name 'sort_works' is not definedsorted_words=ex25.sort_sentence(sentence) # 调用ex25.sort_sentence(sentence) return (sort_works(words)) 型饥 # 返卜袜返回sort_works(words) # 错误原因sort_works函数没有被定义



)
 Qt事件系统(two))


 任务队列)
)


)



】实现简易相册)

的排序)

