目录
【1】用队列实现栈
思路分析
易错总结
Queue.c&Queue.h手撕队列
声明栈MyStack
创建&初始化栈myStackCreate
压栈myStackPush
出栈&返回栈顶元素myStackPop
返回栈顶元素myStackTop
判断栈空否myStackEmpty
释放空间myStackFree
MyStack总代码
【2】用栈实现队列
思路分析
易错总结
Stack.h&Stack.c手撕栈
声明队列MyQueue
创建&初始化队列myQueueCreate
入队列myQueuePush
返回队头元素myQueuePeek
出队列&返回队头元素myQueuePop
判断队列空否myQueueEmpty
释放空间myQueueFree
MyQueue总代码
昨天导游考试考完啦!!希望明年是导游小唐!!🙂当然,代码我们不能忘敲代码!!
【1】用队列实现栈
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(
push、top、pop和empty)。实现
MyStack类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 压入栈顶。int pop()移除并返回栈顶元素。int top()返回栈顶元素。boolean empty()如果栈是空的,返回true;否则,返回false。

思路分析 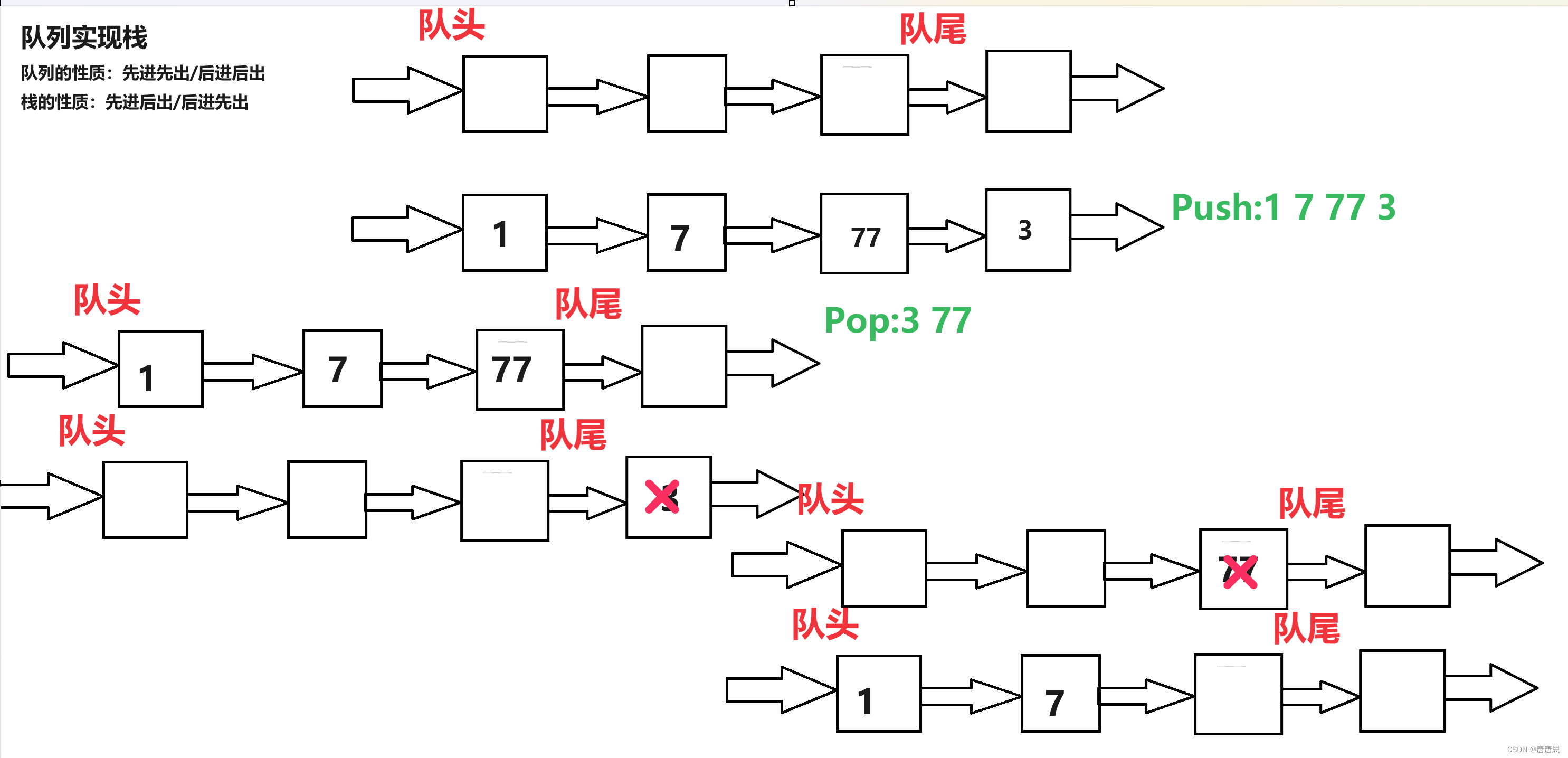
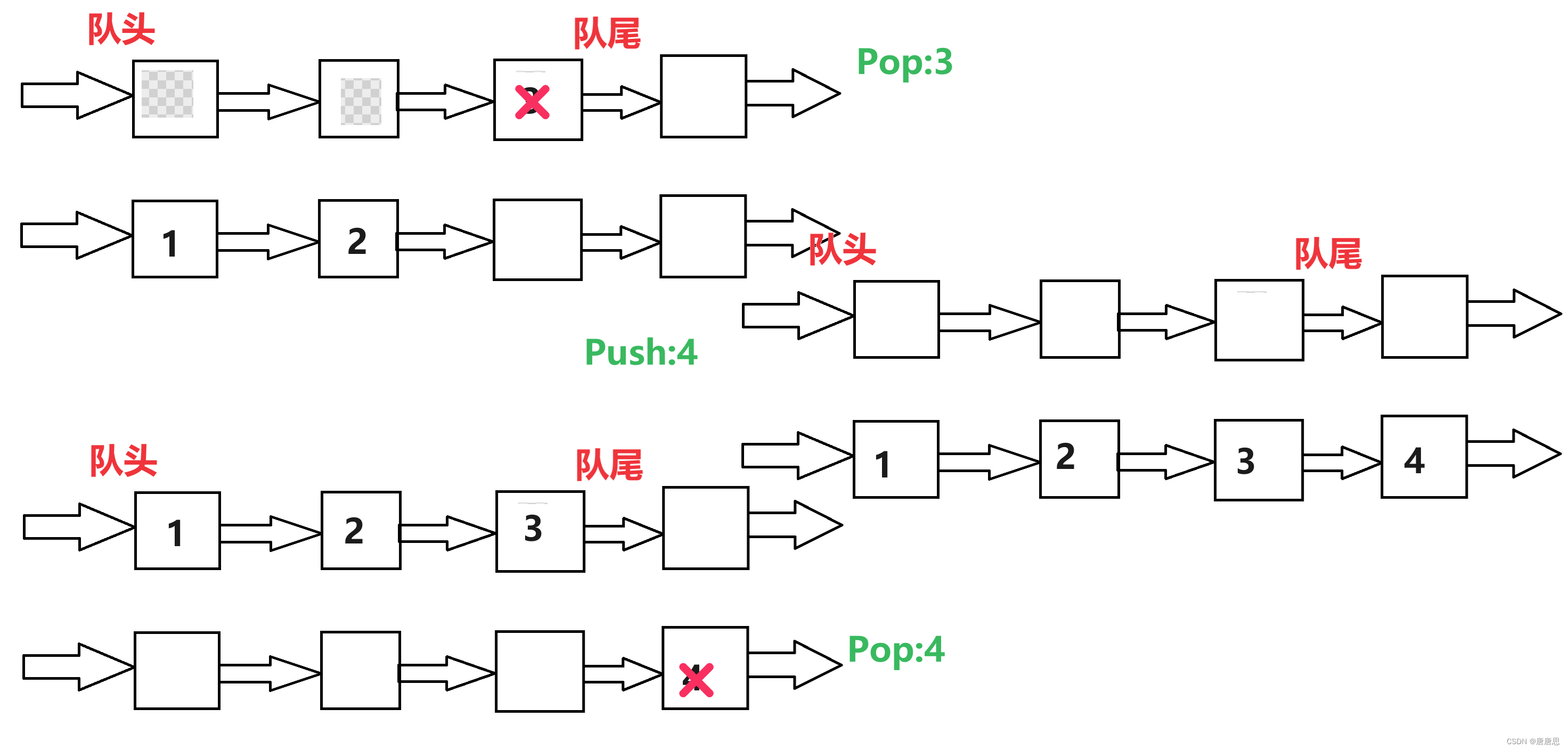
- 压栈:把元素放到不为空的队列里面。(两者若都为空随便放一个)
- 出栈:把不为空的队列里面元素>1,全部导入另外一个为空队列里面,Pop最后元素。
易错总结
- 创建的临时变量出了作用域就销毁了,所以需要malloc才可。
- 类型匹配的问题
- 假设法的使用
- 销毁的时候要先销毁队列开辟的空间,不然会造成野指针。
- 匿名结构体
- 耦合性
- -> 优先级高于&
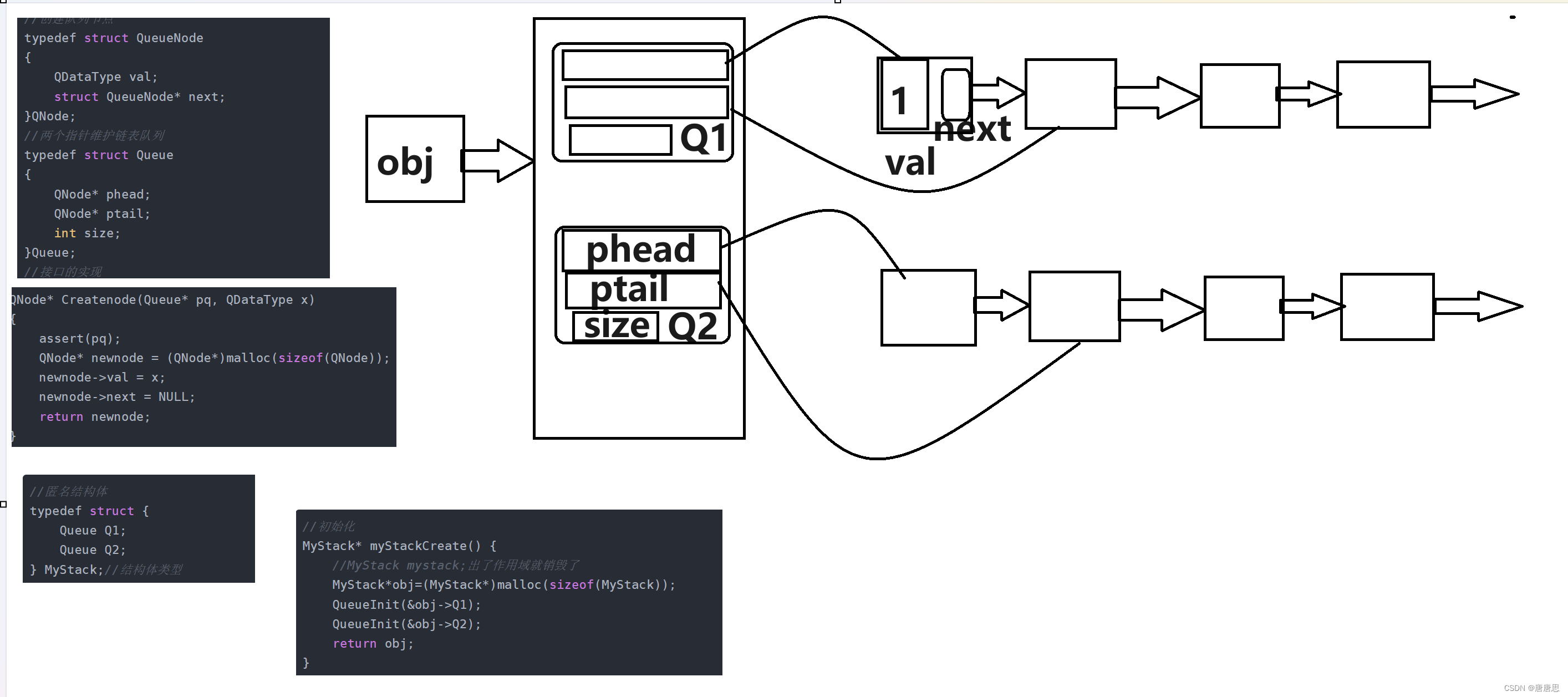
Queue.c&Queue.h手撕队列
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>typedef int QDataType;
//创建队列节点
typedef struct QueueNode
{QDataType val;struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
//两个指针维护链表队列
typedef struct Queue
{QNode* phead;QNode* ptail;int size;
}Queue;
//接口的实现
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);//初始化
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);//空间释放
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);//放元素到队列尾
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//出元素到队头
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);//队列头的元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);//队列尾的元素
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//判断队列是否是否为NULL
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);//队列里面的元素个数
//不需要头节点,初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
QNode* Createnode(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));newnode->val = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}
//Push元素
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);//创建节点QNode* newnode = Createnode(pq,x);if (pq->phead == NULL){pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;}else{pq->ptail->next = newnode;pq->ptail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}
//Pop元素
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->phead);//为NULL的判断QNode* cur = pq->phead;pq->phead = pq->phead->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;//为一个节点的判断if (pq->phead == NULL){pq->ptail = NULL;}pq->size--;
}
//队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->phead);return pq->phead->val;
}
//队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->ptail);return pq->ptail->val;
}
//判断是否为NULL
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->phead == NULL;//return pq->size == 0
}
//队员元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}
//空间释放
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);while (pq->phead){QNode* cur = pq->phead;pq->phead = pq->phead->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;}pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}在之前的博文里面,我们详细的阐述了单链表实现【队列】的实现。这里就不在过多解释了。这里我们来用【两个队列】实现一个【栈】🆗!
声明栈MyStack
//匿名结构体
typedef struct {Queue Q1;Queue Q2;
} MyStack;//结构体类型
//一级指针修改结构体变量
struct {Queue Q1;Queue Q2;
} MyStack;//结构体变量创建&初始化栈myStackCreate
//初始化
MyStack* myStackCreate() {//MyStack mystack;出了作用域就销毁了MyStack*obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));QueueInit(&obj->Q1);QueueInit(&obj->Q2);return obj;
}压栈myStackPush
//放元素
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {assert(obj);//找不为NULL的队列依次插入if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1))//!=0{QueuePush(&obj->Q1, x);//尾插}else//== 0{QueuePush(&obj->Q2, x);}//两个==0 随便进一个
}出栈&返回栈顶元素myStackPop
//出元素
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {assert(obj);//判断为空/非空------假设法Queue*nonempty=&obj->Q1;Queue*empty=&obj->Q2;if(QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1))//==0true与上面逻辑相反//出了作用域就销毁了姐姐❌{nonempty=&obj->Q2;empty=&obj->Q1;//创建}while(QueueSize(nonempty)>1)//队列里面的元素个数 > 1{int x = QueueFront(nonempty);//队列头的元素QueuePush(empty, x);//放元素到队列尾QueuePop(nonempty);//出元素到队头}int Back=QueueFront(nonempty);//队列尾的元素QueuePop(nonempty);return Back;
}返回栈顶元素myStackTop
//栈顶元素
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1)) {return QueueBack(&obj->Q1);}else{return QueueBack(&obj->Q2);}
}判断栈空否myStackEmpty
//判空
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {return QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->Q2);//&&
}释放空间myStackFree
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {QueueDestroy(&obj->Q1);QueueDestroy(&obj->Q2);free(obj);obj=NULL;
}MyStack总代码
typedef struct {Queue Q1;Queue Q2;
} MyStack;
//一级指针修改结构体变量//初始化
MyStack* myStackCreate() {//MyStack mystack;出了作用域就销毁了MyStack*obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));QueueInit(&obj->Q1);QueueInit(&obj->Q2);return obj;
}//放元素
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {assert(obj);//找不为NULL的队列依次插入if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1))//!=0{QueuePush(&obj->Q1, x);//尾插}else//== 0{QueuePush(&obj->Q2, x);}//两个==0 随便进一个
}//出元素
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {assert(obj);//判断为空/非空------假设法Queue*nonempty=&obj->Q1;Queue*empty=&obj->Q2;if(QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1){nonempty=&obj->Q2;empty=&obj->Q1;//创建}while(QueueSize(nonempty)>1)//队列里面的元素个数 > 1{int x = QueueFront(nonempty);//队列头的元素QueuePush(empty, x);//放元素到队列尾QueuePop(nonempty);//出元素到队头}int Back=QueueFront(nonempty);//队列尾的元素QueuePop(nonempty);return Back;
}//栈顶元素
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1)) {return QueueBack(&obj->Q1);}else{return QueueBack(&obj->Q2);}
}//判空
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {return QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->Q2);//&&
}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {QueueDestroy(&obj->Q1);QueueDestroy(&obj->Q2);free(obj);obj=NULL;
}【2】用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(
push、pop、peek、empty):实现
MyQueue类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 推到队列的末尾int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek()返回队列开头的元素boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回true;否则,返回false

思路分析

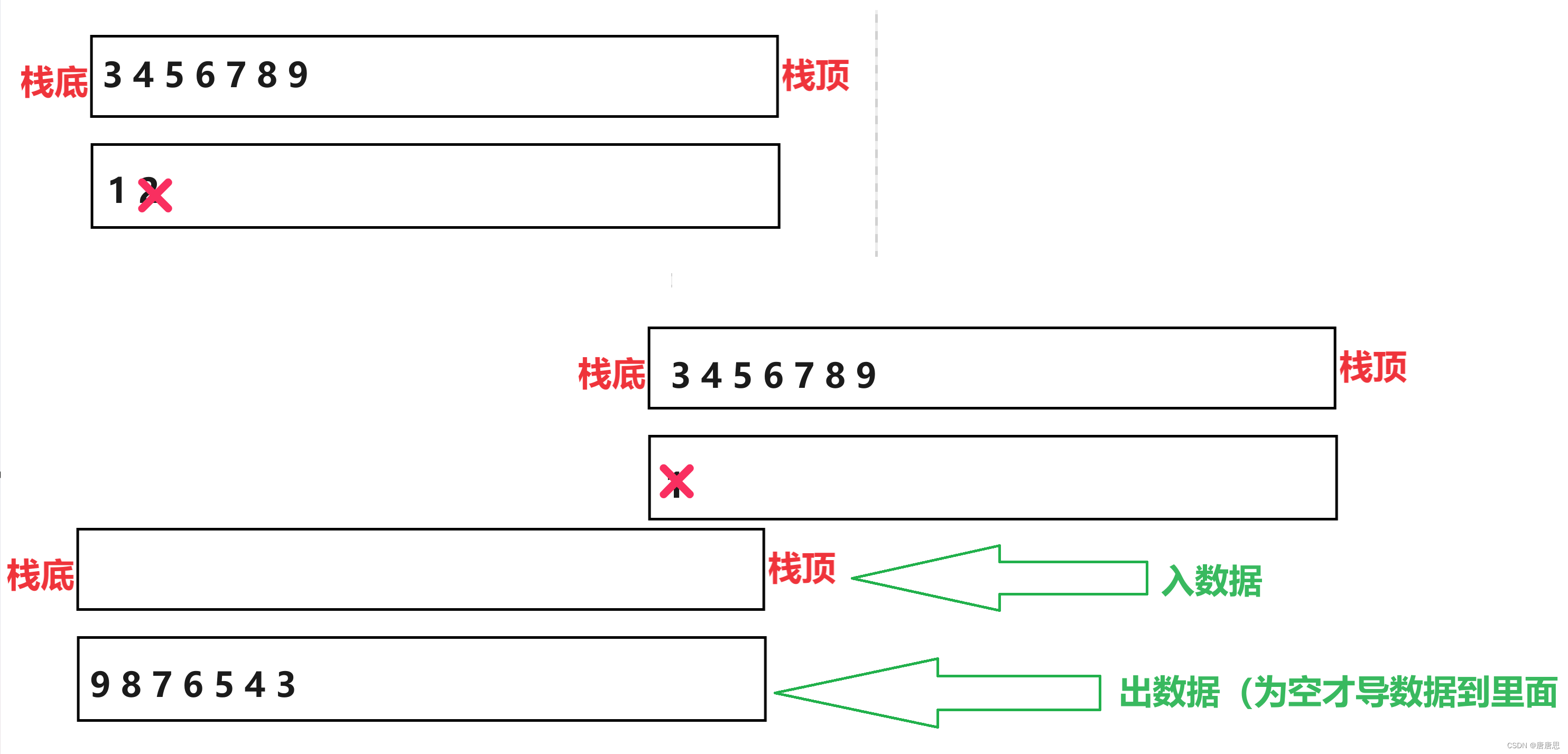
- 一个栈S1用来专门入数据Push
- 另外一个栈S2用来专门出数据Pop(S2为空的时候才能把S1的数据导入S2 直到S1为空)
- S2不为空的时候直接出数据即可
- 队列出数据的顺序性质 == 栈导入另外一个栈出数据的顺序
易错总结
- 创建的临时变量出了作用域就销毁了,所以需要malloc才可。
- 类型匹配的问题
- 销毁的时候要先销毁队列开辟的空间,不然会造成野指针。
- 匿名结构体
- 耦合性
- -> 优先级高于&
- !STempty(&obj->stackpush))//!=0 flase---true开始导 直到==0 true
- 结构体和结构体指针
Stack.h&Stack.c手撕栈
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int STDatatype;
typedef struct Stack
{STDatatype* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);
void STPush(ST* pst, STDatatype x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
STDatatype STTop(ST* pst);
bool STempty(ST* pst);
int STSize(ST* pst);void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->a = 0;pst->top = 0;pst->capacity = 0;
}void Createcapacity(ST* pst)
{if (pst->top == pst->capacity){int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * pst->capacity;STDatatype* tmp = (STDatatype*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(ST) * newcapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->a = tmp;pst->capacity = newcapacity;}
}void STPush(ST* pst, STDatatype x)
{assert(pst);Createcapacity(pst);pst->a[pst->top] = x;pst->top++;
}void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;
}STDatatype STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top-1];
}bool STempty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top == 0;
}int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->top = 0;pst->capacity = 0;
}同样我们之前用数组实现了【栈】,这里我们在来用两个栈实现【队列】 。
声明队列MyQueue
typedef struct {ST stackpush;ST stackpop;
} MyQueue;创建&初始化队列myQueueCreate
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {MyQueue*obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));STInit(&obj->stackpush);STInit(&obj->stackpop);return obj;
}入队列myQueuePush
//入队列
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {STPush(&obj->stackpush, x);
}返回队头元素myQueuePeek
//取出队列的数据 --所以可以先实现这个
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {if(STempty(&obj->stackpop))//==0 true为空导数据{while(!STempty(&obj->stackpush))//!=0//!=0 flase---true开始导 直到==0 true ---false{int x=STTop(&obj->stackpush);STPush(&obj->stackpop,x);STPop(&obj->stackpush);}}return STTop(&obj->stackpop);
}出队列&返回队头元素myQueuePop
//出队列 为NULL就导数据/出队列 不为NULL出队列
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {int back=myQueuePeek(obj);STPop(&obj->stackpop);return back;
}
判断队列空否myQueueEmpty
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {return STempty(&obj->stackpush) && STempty(&obj->stackpop);
}释放空间myQueueFree
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {STDestroy(&obj->stackpush);STDestroy(&obj->stackpop);free(obj);obj=NULL;
}MyQueue总代码
typedef struct {ST stackpush;ST stackpop;
} MyQueue;MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {MyQueue*obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));STInit(&obj->stackpush);STInit(&obj->stackpop);return obj;
}
//入队列
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {STPush(&obj->stackpush, x);
}//取出队列的数据 --所以可以先实现这个
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {if(STempty(&obj->stackpop))//==0 true为空导数据{while(!STempty(&obj->stackpush))//!=0//!=0 flase---true开始导 直到==0 true ---false{int x=STTop(&obj->stackpush);STPush(&obj->stackpop,x);STPop(&obj->stackpush);}}return STTop(&obj->stackpop);
}//出队列 为NULL就导数据/出队列 不为NULL出队列
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {int back=myQueuePeek(obj);STPop(&obj->stackpop);return back;
}//
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {return STempty(&obj->stackpush) && STempty(&obj->stackpop);
}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {STDestroy(&obj->stackpush);STDestroy(&obj->stackpop);free(obj);obj=NULL;
}- 不要对比代码!怎么想怎么写!
- 调试很重要!调式:按照自己预期的去走读代码(最后上编译器)
- 编译出错:运行的问题
- 执行错误:逻辑的问题
✔✔✔✔✔最后,感谢大家的阅读,若有错误和不足,欢迎指正!
【数组栈】实现-CSDN博客
单链表实现【队列】-CSDN博客









)







![[递归,动态规划] 和为定值的子集合](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[递归,动态规划] 和为定值的子集合)

