给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。(注意题意)
示例 1:
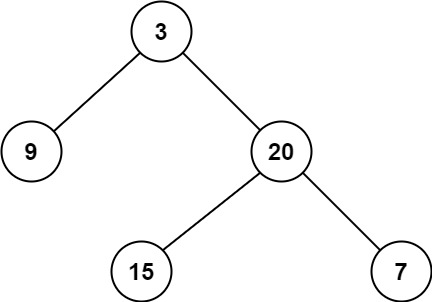
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
层序遍历法
# 层序遍历法
class Solution(object):def minDepth(self, root):""":type root: TreeNode:rtype: int"""if not root:return 0queue = deque([(root, 1)]) # 每个元素是元组 一个是树元素值 一个是最小深度 比较巧妙while queue:cur, min_depth = queue.popleft()if not cur.left and not cur.right:return min_depthif cur.left:queue.append((cur.left, min_depth+1))if cur.right:queue.append((cur.right, min_depth+1))return 0
时间复杂度:O(N) 因为每个结点会访问一次
空间复杂度:O(N)在层序遍历法中空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
递归法
注意这块和最大深度不一样,如下是错误代码:说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。(注意题意)

这个代码就犯了此图中的误区:说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。(注意题意)
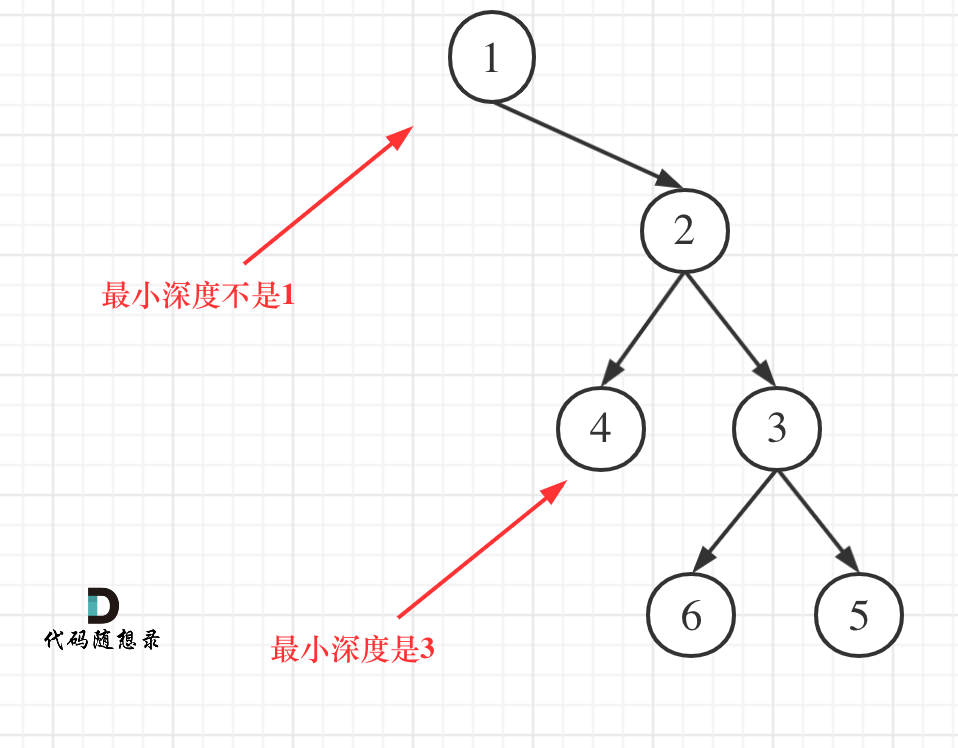
如果这么求的话,没有左孩子的分支会算为最短深度。
所以,如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。
反之,右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。 最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1 。

# 递归法
class Solution(object):def minDepth(self, root):""":type root: TreeNode:rtype: int"""return self.getDepth(root)def getDepth(self, node):if node is None:return 0leftDepth = self.getDepth(node.left) # 左rightDepth = self.getDepth(node.right) # 右# 中# 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点if node.left is None and node.right is not None:return 1 + rightDepth# 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点if node.left is not None and node.right is None:return 1 + leftDepthresult = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth)return result
时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
空间复杂度:O(N)/O(H) 其中 H 是树的高度。空间复杂度主要取决于递归时栈空间的开销,最坏情况下,树呈现链状,空间复杂度为 O(N)。平均情况下树的高度与节点数的对数正相关,空间复杂度为 O(logN)
参考:
https://www.programmercarl.com/0111.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E5%B0%8F%E6%B7%B1%E5%BA%A6.html

】队列(2))

)










)




