目录
一、什么是链表?
1.链表的定义
2.链表的实现
2.1链表的定义
2.2创建一个链表
二、链表的各个接口
1.创建节点
2.头插(将新创建的节点作为头插入到链表中)
3.打印链表
4.尾插(将新创建的节点插入到链表的末端)
5.头删
6.尾删
7.查找
8.删除指定节点位置之后
9.删除指定位置节点
10.在指定位置节点之后插入
11.在指定位置节点之前插入
三、全部代码
1.接口头文件
2.接口实现
3.测试
一、什么是链表?
1.链表的定义
链表是是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。比较通俗易懂的说法就是,在计算机内存中开辟了一个个空间,然后通过地址的方式将它们链接在一起,并通过地址的方式进行访问。
2.链表的实现
只知道了链表的定义,估计大家还是云里雾里的,不知道什么才算是链表,接下来笔者就手动创建一个很挫的链表给大家,不通过函数的形式实现,主要是让大家先感受一下。
2.1链表的定义
在手动创建链表之前,我们要先对链表进行定义,对链表的定义,接口函数的引用和头文件的引用最好放在一个头文件中 这样在要使用创建的接口时便只需要引用一个头文件即可,而接口函数的实现你也可以放在一个.c文件中,最后在另一个.c文件中引用函数测试即可,如图:
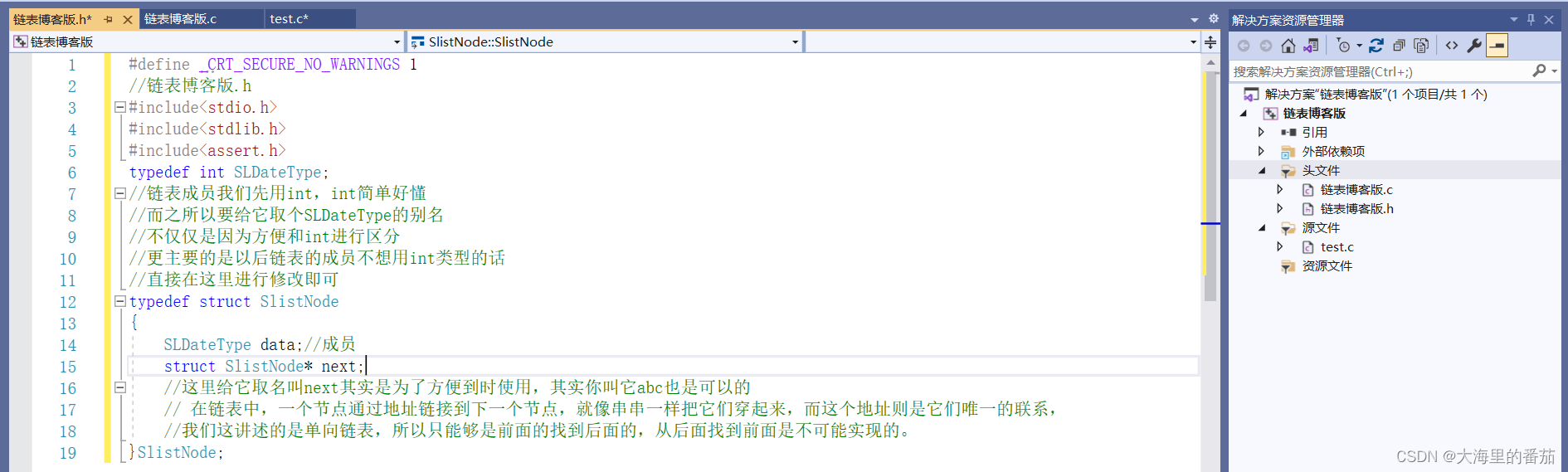
//链表博客版.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLDateType;
//链表成员我们先用int,int简单好懂
//而之所以要给它取个SLDateType的别名
//不仅仅是因为方便和int进行区分
//更主要的是以后链表的成员不想用int类型的话
//直接在这里进行修改即可
typedef struct SlistNode
{SLDateType data;//成员struct SlistNode* next;//这里给它取名叫next其实是为了方便到时使用,其实你叫它abc也是可以的// 在链表中,一个节点通过地址链接到下一个节点,就像串串一样把它们穿起来,而这个地址则是它们唯一的联系,//我们这讲述的是单向链表,所以只能够是前面的找到后面的,从后面找到前面是不可能实现的。
}SlistNode;2.2创建一个链表
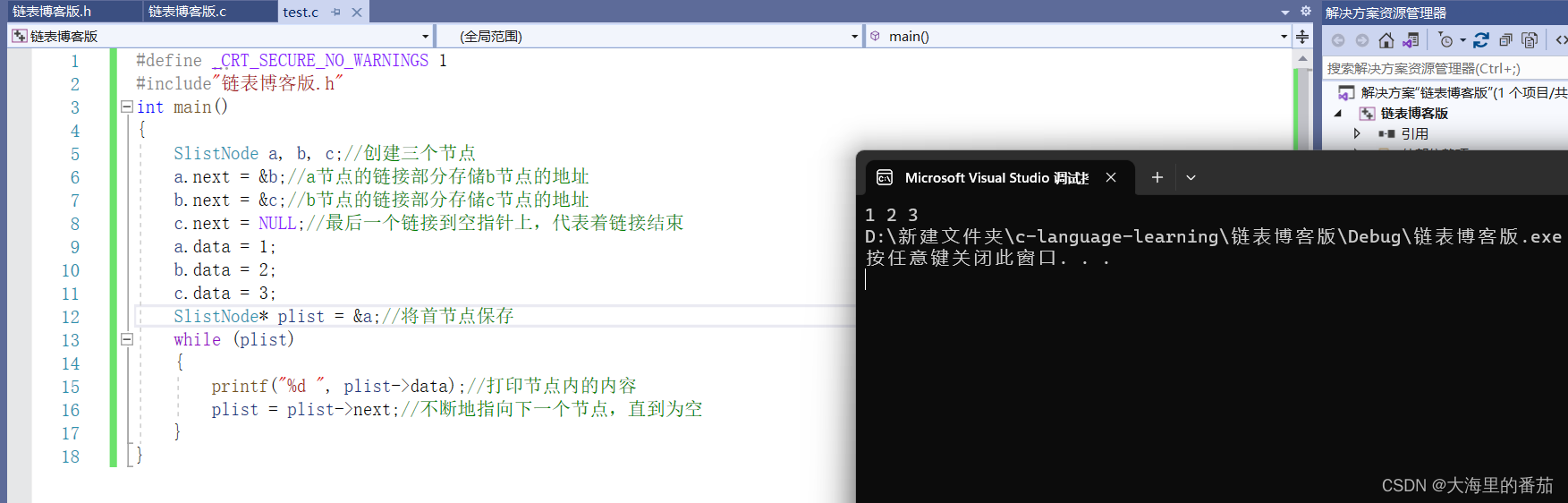
链表,其实也没什么高大上的,就是通过地址找到下一个节点然后进行对应的访问,核心在于地址上 只要我们能够将首节点的地址链接到下一个节点,将下一个节点的地址链接到下下个节点的地址.....直到链接完成就停止即可,这里我们就先不链接那么多个节点,我们就简单的链接个节点数为3的链表
#include"链表博客版.h"
int main()
{SlistNode a, b, c;//创建三个节点a.next=&b;//a节点的链接部分存储b节点的地址b.next = &c;//b节点的链接部分存储c节点的地址c.next = NULL;//最后一个链接到空指针上,代表着链接结束a.data = 1;b.data = 2;c.data = 3;SlistNode* plist = &a;//将首节点保存while (plist){printf("%d ", plist->data);//打印节点内的内容plist = plist->next;//不断地指向下一个节点,直到为空}
}
二、链表的各个接口
1.创建节点
创建节点是一个很重要的函数,在插入函数中需要使用。在函数中创建节点,我们就不能够像之前一样直接创建了,众所周知,在函数上创建节点出了函数就会自动销毁,为了避免节点被自动销毁,这里采用malloc的方式创建节点,别忘了在头文件中引用函数
#include"链表博客版.h"
SlistNode* buy_slistnode(SLDateType x)
//使用节点指针作为返回类型,来拿到创建好的新节点
{SlistNode* newnode = (SlistNode*)malloc(sizeof(SlistNode));//使用malloc创建一个新节点if (newnode == NULL){perror("buy_slistnode");exit(-1);//创建失败直接中止程序}newnode->data = x;//将节点内容修改成需要的值newnode->next = NULL;//将链接对象置为空,因为不知道要链接谁return newnode;
}2.头插(将新创建的节点作为头插入到链表中)
为什么先将头插节点呢?无他,相比尾插它简单很多
void slist_pushfront(SlistNode** phead, SLDateType x)
//采用二级指针的原因是,当没有节点的时候,我们要对首节点的地址进行修改
{//先创建一个新的节点SlistNode* newnode = buy_slistnode(x);//我们要头插是吧,也就是说新创建的节点是新的头//那么我们是不是应该把我们自己原来的头更新一下//然后再将之前的节点,也就是之前的头链接到新的头后面/* *phead = newnode;newnode->next = *phead;*///但这是错误的,原因很简单,你的头更新了,那么你就找不到之前的节点了//换一下顺序即可newnode->next = *phead;*phead = newnode;
}3.打印链表
插入完节点之后,也不知道自己到底有没有插入,因此我们来设计一个打印链表的函数
void print_slist(SlistNode* phead)
{while (phead)//phead不为空意味着还有节点没被访问完{printf("%d->", phead->data);phead=phead->next;//指向下一个节点}printf("NULL\n");//访问完了打印空,提示已经访问完了
}测试效果:
#include"链表博客版.h"
void test1()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;//创建一个链表头slist_pushfront(&plist, 1);//依次将1,2,3头插进链表中slist_pushfront(&plist, 2);//那么链表最后应该是3为头,1为尾slist_pushfront(&plist, 3);print_slist(plist);
}
int main()
{test1();
}
4.尾插(将新创建的节点插入到链表的末端)
尾插要在链表的末端进行插入,那么找到链表的末端是一件必须要做的事
void slist_pushback(SlistNode** phead, SLDateType x)
{SlistNode* tmp = *phead;//创建一个首节点的拷贝,避免影响到首节点的指向SlistNode* newnode = buy_slistnode(x);//创建一个新节点while(tmp->next)//当成员的next为空的时候意味着已经找到目标了// 跳出循环//接下来就是把这个成员的指向改变{tmp = tmp->next;}tmp->next = newnode;
}很多小伙伴,写到这里的时候就以为已经完成了,但你想一想,如果此时链表中没有节点呢,也就是*phead此时为NULL的时候,你还能够指向next吗,你能对空指针进行解引用吗?显然不能,因此我们把这种情况单独处理。
void slist_pushback(SlistNode** phead, SLDateType x)
{SlistNode* tmp = *phead;//创建一个首节点的拷贝,避免影响到首节点的指向SlistNode* newnode = buy_slistnode(x);//创建一个新节点if (*phead==NULL)//当*phead==NULL时,意味着链表为空{*phead = newnode;//直接链接return;}while(tmp->next)//当成员的next为空的时候意味着已经找到目标了// 跳出循环//接下来就是把这个成员的指向改变{tmp = tmp->next;}tmp->next = newnode;
}测试代码:
void test2()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;slist_pushback(&plist, 10086);//依次尾插10086,666,555,111slist_pushback(&plist, 666);slist_pushback(&plist, 555);slist_pushback(&plist, 111);print_slist(plist);
}
int main()
{test2();
}
错误情况
程序直接就崩溃了,连print_slist即使是空也应该打印出来的NULL都没打印出来

正确情况
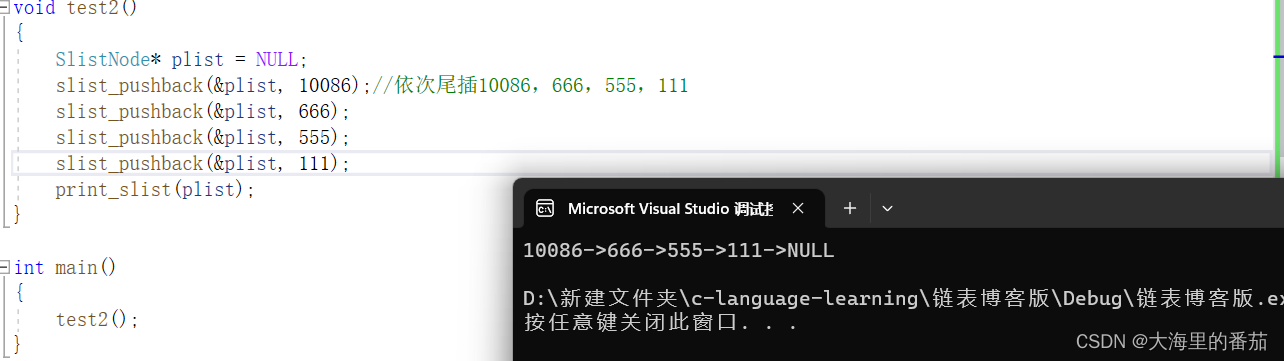
5.头删
void slist_popfront(SlistNode** phead)
{if (*phead==NULL)//空了就别删了{printf("链表为空,操作失败\n");return;}SlistNode* tmp = (*phead)->next;//储存头的下一个节点,避免找不到free(*phead);//直接释放头节点*phead =tmp;//头节点重新指向下一个节点
}效果测试:
void test3()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;slist_popfront(&plist);//直接删除,测试报错slist_pushback(&plist, 10086);//依次尾插10086,666,555,111slist_pushback(&plist, 666);slist_pushback(&plist, 555);slist_pushback(&plist, 111);print_slist(plist);slist_popfront(&plist);//删除10086print_slist(plist);slist_popfront(&plist);//删除666print_slist(plist);slist_popfront(&plist);//删除555print_slist(plist);slist_popfront(&plist);//删除111print_slist(plist);
}int main()
{test3();
}
6.尾删
void slist_popback(SlistNode** phead)
{if (*phead == NULL){printf("链表为空,操作失败\n");return;}if ((*phead)->next == NULL)//如果只有一个节点,我们就不可能找到上一个节点,因此单独处理{free(*phead);//直接释放*phead = NULL;return;}SlistNode* tmp = *phead;SlistNode* prev = NULL;//用来存储目标的上一个节点while (tmp->next){prev = tmp;tmp=tmp->next;}prev->next = NULL;//改变上一个节点的指向free(tmp);
}测试代码:
void test4()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;slist_popback(&plist);//直接删除,测试报错slist_pushback(&plist, 10086);//依次尾插10086,666,555,111slist_pushback(&plist, 666);slist_pushback(&plist, 555);slist_pushback(&plist, 111);print_slist(plist);slist_popback(&plist);//删除111print_slist(plist);slist_popback(&plist);//删除555print_slist(plist);slist_popback(&plist);//删除666print_slist(plist);slist_popback(&plist);//删除10086print_slist(plist);slist_popback(&plist);//删除空链表print_slist(plist);
}int main()
{test4();
}
7.查找
在对指定位置操作之前,我们得先找到目标位置才行,找到目标位置是比较简单的,简单地遍历一遍链表,找的到就返回对应的地址,找不到就返回空指针
SlistNode* slist_find(SlistNode* phead,SLDateType x)
{while (phead){if (phead->data == x){return phead;}phead=phead->next;}return NULL;
}8.删除指定节点位置之后
之所以先讲指定位置之后删除,是因为这个相比指定位置删除简单很多
void slist_erase_after(SlistNode* pos)
{if (pos == NULL ||pos->next==NULL )//如果为空则删除失败,如果下一个节点为空也不能删除{printf("该位置无效,操作失败\n");return;}SlistNode* tmp = pos->next;pos->next = pos->next->next;free(tmp);
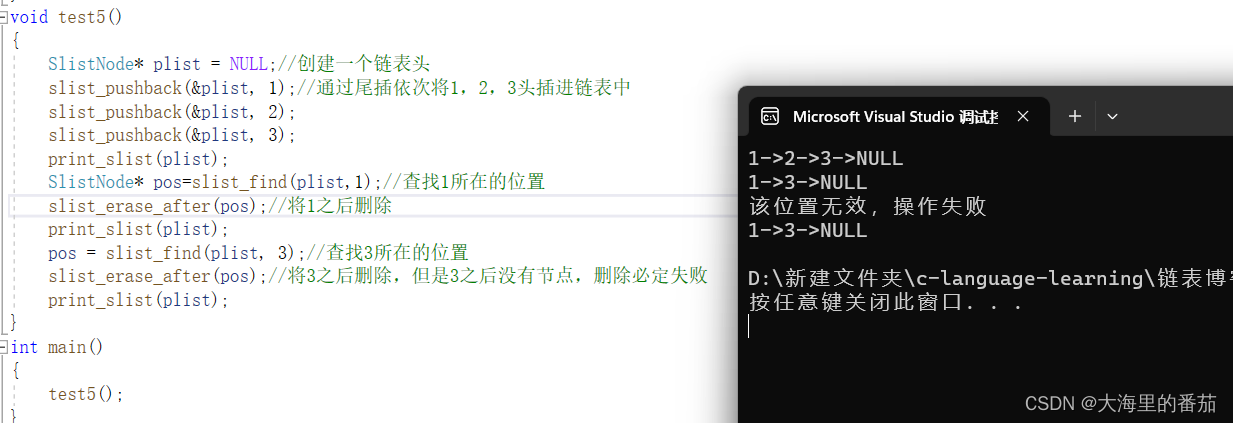
}测试代码
void test5()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;//创建一个链表头slist_pushback(&plist, 1);//通过尾插依次将1,2,3头插进链表中slist_pushback(&plist, 2);slist_pushback(&plist, 3);print_slist(plist); SlistNode* pos=slist_find(plist,1);//查找1所在的位置slist_erase_after(pos);//将1之后删除print_slist(plist);pos = slist_find(plist, 3);//查找3所在的位置slist_erase_after(pos);//将3之后删除,但是3之后没有节点,删除必定失败print_slist(plist);
}
int main()
{test5();
}
9.删除指定位置节点
void slist_erase(SlistNode* pos,SlistNode**phead)
{if (pos == NULL)//为空就别删了{printf("该位置无效,操作失败\n");return;}if(*phead==pos)//当只有一个节点时,操作不到两个节点,单独处理{SlistNode*tmp=(*phead)->next;free(*phead);*phead = tmp;return;}SlistNode* cur = *phead;while (cur->next){if (cur->next == pos){break;}cur=cur->next;}//此时phead的next就是目标节点SlistNode* tmp = cur->next;cur->next = cur->next->next;//将目标节点的上一个节点链接到目标节点的下一个地址free(tmp);
}测试代码:
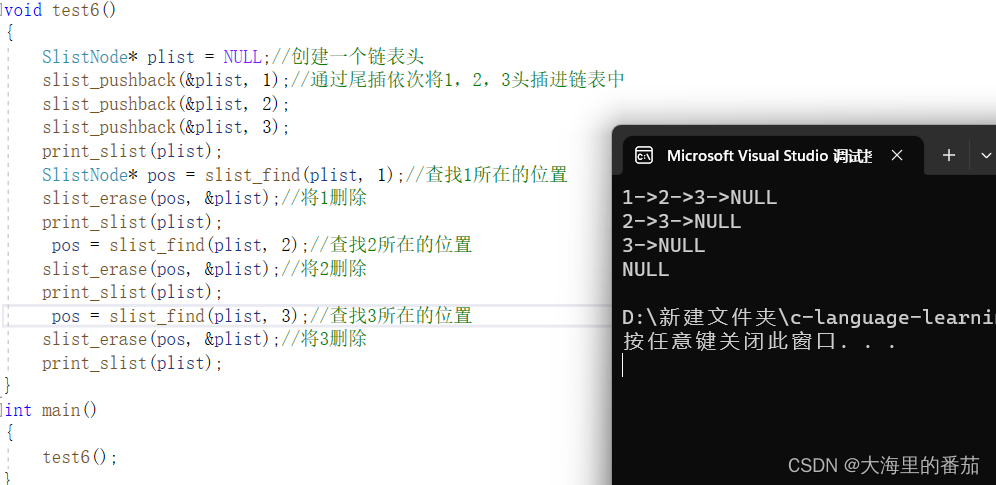
void test6()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;//创建一个链表头slist_pushback(&plist, 1);//通过尾插依次将1,2,3头插进链表中slist_pushback(&plist, 2);slist_pushback(&plist, 3);print_slist(plist);SlistNode* pos = slist_find(plist, 1);//查找1所在的位置slist_erase(pos, &plist);//将1删除print_slist(plist); pos = slist_find(plist, 2);//查找2所在的位置slist_erase(pos, &plist);//将2删除print_slist(plist);pos = slist_find(plist, 3);//查找3所在的位置slist_erase(pos, &plist);//将3删除print_slist(plist);
}
int main()
{test6();
}
10.在指定位置节点之后插入
void slist_insert_after(SlistNode* pos, SLDateType x)
{if (pos == NULL){printf("目标不存在,操作失败\n");return;}SlistNode* newnode = buy_slistnode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}测试代码:
void test7()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;//创建一个链表头slist_pushback(&plist, 1);//通过尾插依次将1,2,3头插进链表中slist_pushback(&plist, 2);slist_pushback(&plist, 3);SlistNode* pos = slist_find(plist, 1);//查找1所在的位置slist_insert_after(pos, 10086);//在1之后进行插入print_slist(plist);pos = slist_find(plist, 3);//查找3所在的位置slist_insert_after(pos, 520);//在3之后进行插入print_slist(plist);pos = slist_find(plist, 10086);//查找10086所在的位置slist_insert_after(pos,9 );//在10086之后进行插入print_slist(plist);
}
int main()
{test7();
}
11.在指定位置节点之前插入
void slist_insert_before(SlistNode* pos, SLDateType x,SlistNode**phead)
{if (pos == NULL){printf("目标不存在,操作失败\n");return;} SlistNode* newnode = buy_slistnode(x);if (*phead==pos)//在第一个节点前插入,没有上一个节点,单独处理{newnode->next = pos;*phead = newnode;return;}SlistNode* cur = *phead;while (cur)//为空意味着找不到{if (cur->next == pos)//找到上一个节点了{break;}cur = cur->next;}if (cur == NULL){printf("目标不存在,操作失败\n");return;}cur->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;
}测试代码
void test8()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;//创建一个链表头slist_pushback(&plist, 1);//通过尾插依次将1,2,3头插进链表中print_slist(plist);SlistNode* pos = slist_find(plist, 1);//查找1所在的位置slist_insert_before(pos, 10086,&plist);//在1之前插入666print_slist(plist);slist_pushback(&plist, 2);slist_pushback(&plist, 3);pos = slist_find(plist, 10086);//查找10086所在的位置slist_insert_before(pos, 666, &plist);//在10086之前插入666print_slist(plist);pos = slist_find(plist, 3);//查找3所在的位置slist_insert_before(pos, 999, &plist);//在3之前插入999print_slist(plist);}
int main()
{test8();
}
三、全部代码
1.接口头文件
//链表博客版.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLDateType;
//链表成员我们先用int,int简单好懂
//而之所以要给它取个SLDateType的别名
//不仅仅是因为方便和int进行区分
//更主要的是以后链表的成员不想用int类型的话
//直接在这里进行修改即可
typedef struct SlistNode
{SLDateType data;//成员struct SlistNode* next;//这里给它取名叫next其实是为了方便到时使用,其实你叫它abc也是可以的// 在链表中,一个节点通过地址链接到下一个节点,就像串串一样把它们穿起来,而这个地址则是它们唯一的联系,//我们这讲述的是单向链表,所以只能够是前面的找到后面的,从后面找到前面是不可能实现的。
}SlistNode;
SlistNode* buy_slistnode(SLDateType x);
//头插
void slist_pushfront(SlistNode**phead,SLDateType x);
//打印链表
void print_slist(SlistNode* phead);
//尾插
void slist_pushback(SlistNode** phead, SLDateType x);
//头删
void slist_popfront(SlistNode** phead);
//尾删
void slist_popback(SlistNode**phead);
//查找
SlistNode* slist_find(SlistNode*phead,SLDateType x);
//删除指定位置之后
void slist_erase_after(SlistNode*pos);
//删除指定位置
void slist_erase(SlistNode* pos,SlistNode**phead);
//在指定位置之后插入
void slist_insert_after(SlistNode* pos, SLDateType x);
//在指定位置之前插入
void slist_insert_before(SlistNode* pos, SLDateType x, SlistNode** phead);2.接口实现
#include"链表博客版.h"
SlistNode* buy_slistnode(SLDateType x)
//使用节点指针作为返回类型,来拿到创建好的新节点
{SlistNode* newnode = (SlistNode*)malloc(sizeof(SlistNode));//使用malloc创建一个新节点if (newnode == NULL){perror("buy_slistnode");exit(-1);//创建失败直接中止程序}newnode->data = x;//将节点内容修改成需要的值newnode->next = NULL;//将链接对象置为空,因为不知道要链接谁return newnode;
}
void slist_pushfront(SlistNode** phead, SLDateType x)
//采用二级指针的原因是,当没有节点的时候,我们要对首节点的地址进行修改
{//先创建一个新的节点SlistNode* newnode = buy_slistnode(x);//我们要头插是吧,也就是说新创建的节点是新的头//那么我们是不是应该把我们自己原来的头更新一下//然后再将之前的节点,也就是之前的头链接到新的头后面/* *phead = newnode;newnode->next = *phead;*///但这是错误的,原因很简单,你的头更新了,那么你就找不到之前的节点了//换一下顺序即可newnode->next = *phead;*phead = newnode;
}
void print_slist(SlistNode* phead)
{while (phead)//phead不为空意味着还有节点没被访问完{printf("%d->", phead->data);phead=phead->next;//指向下一个节点}printf("NULL\n");//访问完了打印空,提示已经访问完了
}
void slist_pushback(SlistNode** phead, SLDateType x)
{SlistNode* tmp = *phead;//创建一个首节点的拷贝,避免影响到首节点的指向SlistNode* newnode = buy_slistnode(x);//创建一个新节点if (*phead==NULL)//当*phead==NULL时,意味着链表为空{*phead = newnode;//直接链接return;}while(tmp->next)//当成员的next为空的时候意味着已经找到目标了// 跳出循环//接下来就是把这个成员的指向改变{tmp = tmp->next;}tmp->next = newnode;
}
void slist_popfront(SlistNode** phead)
{if (*phead==NULL)//空了就别删了{printf("链表为空,操作失败\n");return;}SlistNode* tmp = (*phead)->next;//储存头的下一个节点,避免找不到free(*phead);//直接释放头节点*phead =tmp;//头节点重新指向下一个节点
}
void slist_popback(SlistNode** phead)
{if (*phead == NULL){printf("链表为空,操作失败\n");return;}if ((*phead)->next == NULL)//如果只有一个节点,我们就不可能找到上一个节点,因此单独处理{free(*phead);//直接释放*phead = NULL;return;}SlistNode* tmp = *phead;SlistNode* prev = NULL;//用来存储目标的上一个节点while (tmp->next){prev = tmp;tmp=tmp->next;}prev->next = NULL;//改变上一个节点的指向free(tmp);
}
SlistNode* slist_find(SlistNode* phead,SLDateType x)
{while (phead){if (phead->data == x){return phead;}phead=phead->next;}return NULL;
}
void slist_erase_after(SlistNode* pos)
{if (pos == NULL ||pos->next==NULL )//如果为空则删除失败,如果下一个节点为空也不能删除{printf("该位置无效,操作失败\n");return;}SlistNode* tmp = pos->next;pos->next = pos->next->next;free(tmp);
}
void slist_erase(SlistNode* pos,SlistNode**phead)
{if (pos == NULL)//为空就别删了{printf("该位置无效,操作失败\n");return;}if(*phead==pos)//当只有一个节点时,操作不到两个节点,单独处理{SlistNode*tmp=(*phead)->next;free(*phead);*phead = tmp;return;}SlistNode* cur = *phead;while (cur->next){if (cur->next == pos){break;}cur=cur->next;}//此时phead的next就是目标节点SlistNode* tmp = cur->next;cur->next = cur->next->next;//将目标节点的上一个节点链接到目标节点的下一个地址free(tmp);
}
void slist_insert_after(SlistNode* pos, SLDateType x)
{if (pos == NULL){printf("目标不存在,操作失败\n");return;}SlistNode* newnode = buy_slistnode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}
void slist_insert_before(SlistNode* pos, SLDateType x,SlistNode**phead)
{if (pos == NULL){printf("目标不存在,操作失败\n");return;} SlistNode* newnode = buy_slistnode(x);if (*phead==pos)//在第一个节点前插入,没有上一个节点,单独处理{newnode->next = pos;*phead = newnode;return;}SlistNode* cur = *phead;while (cur)//为空意味着找不到{if (cur->next == pos)//找到上一个节点了{break;}cur = cur->next;}if (cur == NULL){printf("目标不存在,操作失败\n");return;}cur->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;
}3.测试
#include"链表博客版.h"
void test1()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;//创建一个链表头slist_pushfront(&plist, 1);//依次将1,2,3头插进链表中slist_pushfront(&plist, 2);//那么链表最后应该是3为头,1为尾slist_pushfront(&plist, 3);print_slist(plist);
}
void test2()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;slist_pushback(&plist, 10086);//依次尾插10086,666,555,111slist_pushback(&plist, 666);slist_pushback(&plist, 555);slist_pushback(&plist, 111);print_slist(plist);
}
void test3()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;slist_popfront(&plist);//直接删除,测试报错slist_pushback(&plist, 10086);//依次尾插10086,666,555,111slist_pushback(&plist, 666);slist_pushback(&plist, 555);slist_pushback(&plist, 111);print_slist(plist);slist_popfront(&plist);//删除10086print_slist(plist);slist_popfront(&plist);//删除666print_slist(plist);slist_popfront(&plist);//删除555print_slist(plist);slist_popfront(&plist);//删除111print_slist(plist);
}
void test4()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;slist_popback(&plist);//直接删除,测试报错slist_pushback(&plist, 10086);//依次尾插10086,666,555,111slist_pushback(&plist, 666);slist_pushback(&plist, 555);slist_pushback(&plist, 111);print_slist(plist);slist_popback(&plist);//删除111print_slist(plist);slist_popback(&plist);//删除555print_slist(plist);slist_popback(&plist);//删除666print_slist(plist);slist_popback(&plist);//删除10086print_slist(plist);slist_popback(&plist);//删除空链表print_slist(plist);
}
void test5()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;//创建一个链表头slist_pushback(&plist, 1);//通过尾插依次将1,2,3头插进链表中slist_pushback(&plist, 2);slist_pushback(&plist, 3);print_slist(plist); SlistNode* pos=slist_find(plist,1);//查找1所在的位置slist_erase_after(pos);//将1之后删除print_slist(plist);pos = slist_find(plist, 3);//查找3所在的位置slist_erase_after(pos);//将3之后删除,但是3之后没有节点,删除必定失败print_slist(plist);
}
void test6()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;//创建一个链表头slist_pushback(&plist, 1);//通过尾插依次将1,2,3头插进链表中slist_pushback(&plist, 2);slist_pushback(&plist, 3);print_slist(plist);SlistNode* pos = slist_find(plist, 1);//查找1所在的位置slist_erase(pos, &plist);//将1删除print_slist(plist); pos = slist_find(plist, 2);//查找2所在的位置slist_erase(pos, &plist);//将2删除print_slist(plist);pos = slist_find(plist, 3);//查找3所在的位置slist_erase(pos, &plist);//将3删除print_slist(plist);
}
void test7()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;//创建一个链表头slist_pushback(&plist, 1);//通过尾插依次将1,2,3头插进链表中slist_pushback(&plist, 2);slist_pushback(&plist, 3);SlistNode* pos = slist_find(plist, 1);//查找1所在的位置slist_insert_after(pos, 10086);//在1之后进行插入print_slist(plist);pos = slist_find(plist, 3);//查找3所在的位置slist_insert_after(pos, 520);//在3之后进行插入print_slist(plist);pos = slist_find(plist, 10086);//查找10086所在的位置slist_insert_after(pos,9 );//在10086之后进行插入print_slist(plist);
}
void test8()
{SlistNode* plist = NULL;//创建一个链表头slist_pushback(&plist, 1);//通过尾插依次将1,2,3头插进链表中print_slist(plist);SlistNode* pos = slist_find(plist, 1);//查找1所在的位置slist_insert_before(pos, 10086,&plist);//在1之前插入666print_slist(plist);slist_pushback(&plist, 2);slist_pushback(&plist, 3);pos = slist_find(plist, 10086);//查找10086所在的位置slist_insert_before(pos, 666, &plist);//在10086之前插入666print_slist(plist);pos = slist_find(plist, 3);//查找3所在的位置slist_insert_before(pos, 999, &plist);//在3之前插入999print_slist(plist);}
int main()
{test8();
}今天的分享到这里就结束了,更新各位友友的来访,祝各位友友前程似锦O(∩_∩)O

)
题解)







)






)

![[Spring]Spring声明式事务总结](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Spring]Spring声明式事务总结)