学习完单链表,习题就成了最好的巩固方式
目录
- 1.链表分割:
- 思路:
- 代码实现:
- 2.随机链表的复制:
- 思路1:
- 代码实现:
- 思路2:
- 代码实现:
- 3.环形链表:
- 3.1环形链表1:
- 思路:
- 代码实现:
- 3.2环形链表2:
- 思路:
- 代码实现:
1.链表分割:
链表分割,链接奉上
思路:
我们可以创建两个newhead,
将比x小的尾插放到newhead1中
比x大的放在newhead2中
再将两个链表进行链接
注意:
-
在进行创建新的链表时,最好使用带有哨兵位的链表,在进行链接时会比较容易,
因为没有哨兵位的链表需要判断是否两个链表是否为空,并分别做出处理措施 -
在尾插时,有可能出现如下图的情况
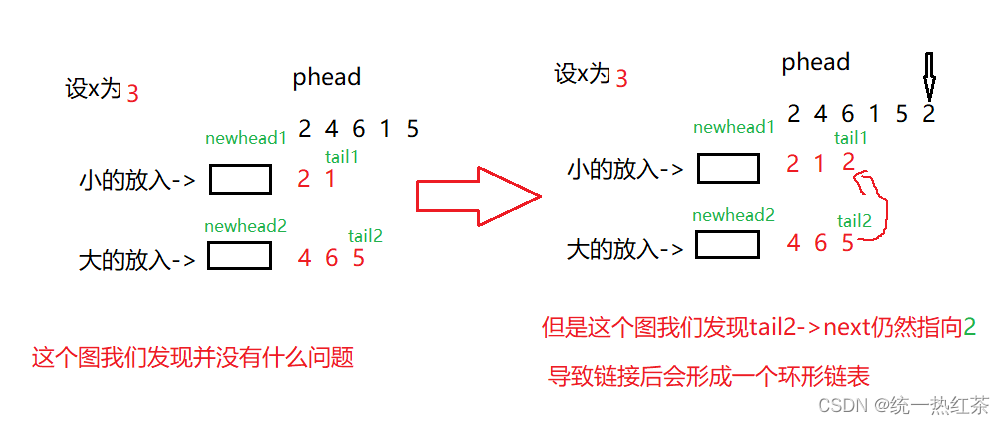
故我们需要将tail2->next = NULL
代码实现:
class Partition {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int val) {//两个哨兵位的创建struct ListNode* newhead1 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* newhead2 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* tail1 = newhead1;struct ListNode* tail2 = newhead2;tail1->next = newhead1->next = NULL;tail2->next = newhead2->next = NULL;while(pHead){if(pHead->val < val){tail1->next = pHead;tail1 = tail1->next;}else{tail2->next = pHead;tail2 = tail2->next;}pHead = pHead->next;}tail1->next = newhead2->next;tail2->next = NULL;return newhead1->next;}
};
2.随机链表的复制:
链接奉上
思路1:
先复制一份没有进行random处理的copy链表
我们可以根据random的指向的位置与原位置,
通过计算得出他们之间的距离,
再根据距离进行确定copy链表中random的位置
这样实现,时间复杂度是O(N^2)
代码实现:
理论存在,实践开始
/*** Definition for a Node.* struct Node {* int val;* struct Node *next;* struct Node *random;* };*/
struct Node* creat(int x)
{struct Node* newnode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));newnode->val = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{struct Node* cur = head;struct Node* newhead = NULL;struct Node* tail = NULL;while(cur){if(newhead == NULL){newhead = creat(cur->val);tail = newhead;}else{tail->next = creat(cur->val);tail = tail->next;}cur = cur->next;}int count = 0;cur = head;struct Node* subcur = newhead;while(cur){count = 0;struct Node* tmp1 = head;while(cur->random != tmp1){count++;tmp1 = tmp1->next;}struct Node* tmp = newhead;while(count--){tmp = tmp->next;}subcur->random = tmp;cur = cur->next;subcur = subcur->next;}return newhead;
}
思路2:
在原链表的每一个元素后边插入一个一样元素的copy节点
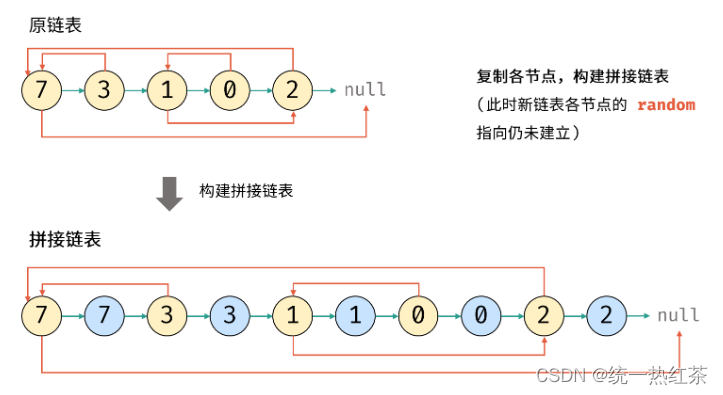
之后,我们发现当前节点后的copy节点的random指向当前节点的random的next,仔细咀嚼(可以自己画图感受一下),这句话也是整个代码的核心
最后再将整个链表进行拆解,返回新的结点
代码实现:
/*** Definition for a Node.* struct Node {* int val;* struct Node *next;* struct Node *random;* };*/struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{struct Node* cur = head;//添加copy节点while(cur){struct Node* copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));struct Node* next = cur->next;copy->val = cur->val;copy->next = next;cur->next = copy;cur = next;}cur = head;//random的复制while(cur){if(cur->random == NULL){cur->next->random = NULL;}else{cur->next->random = cur->random->next;}cur = cur->next->next;}//解开节点struct Node* newhead = NULL;struct Node* tail = NULL;cur = head;while(cur){struct Node* next = cur->next->next;if(newhead == NULL){newhead = tail = cur->next;}else{tail->next = cur->next;tail = tail->next;}cur = next;}return newhead;
}
3.环形链表:
3.1环形链表1:
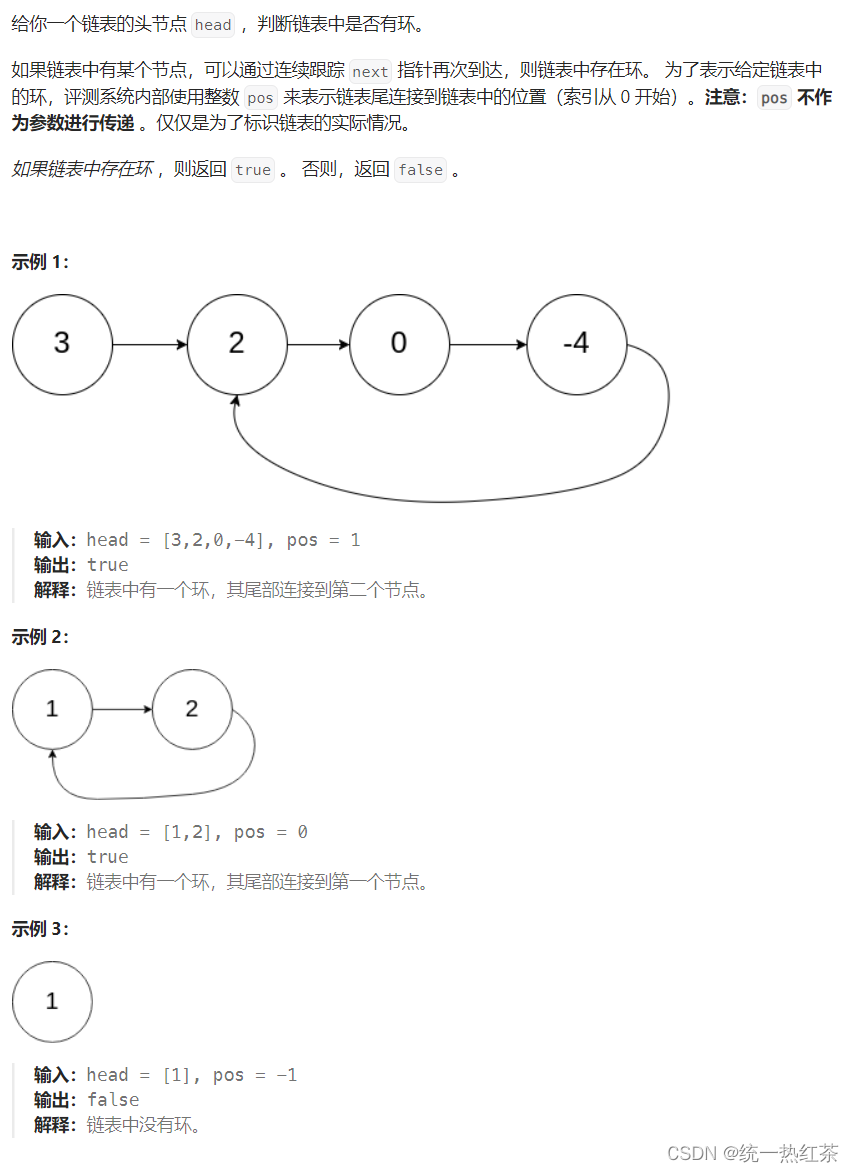
链接奉上
思路:
利用快慢指针,这是解决此问题的最可行办法,
一个走一步,一个走两步,
当有环时,两者都进入环,因为两者固定减少1步,故必然可以相遇,
当没有环时,fast == NULL,或者fast指针->next == NULL
代码实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if(slow == fast)return true;} return false;
}
3.2环形链表2:
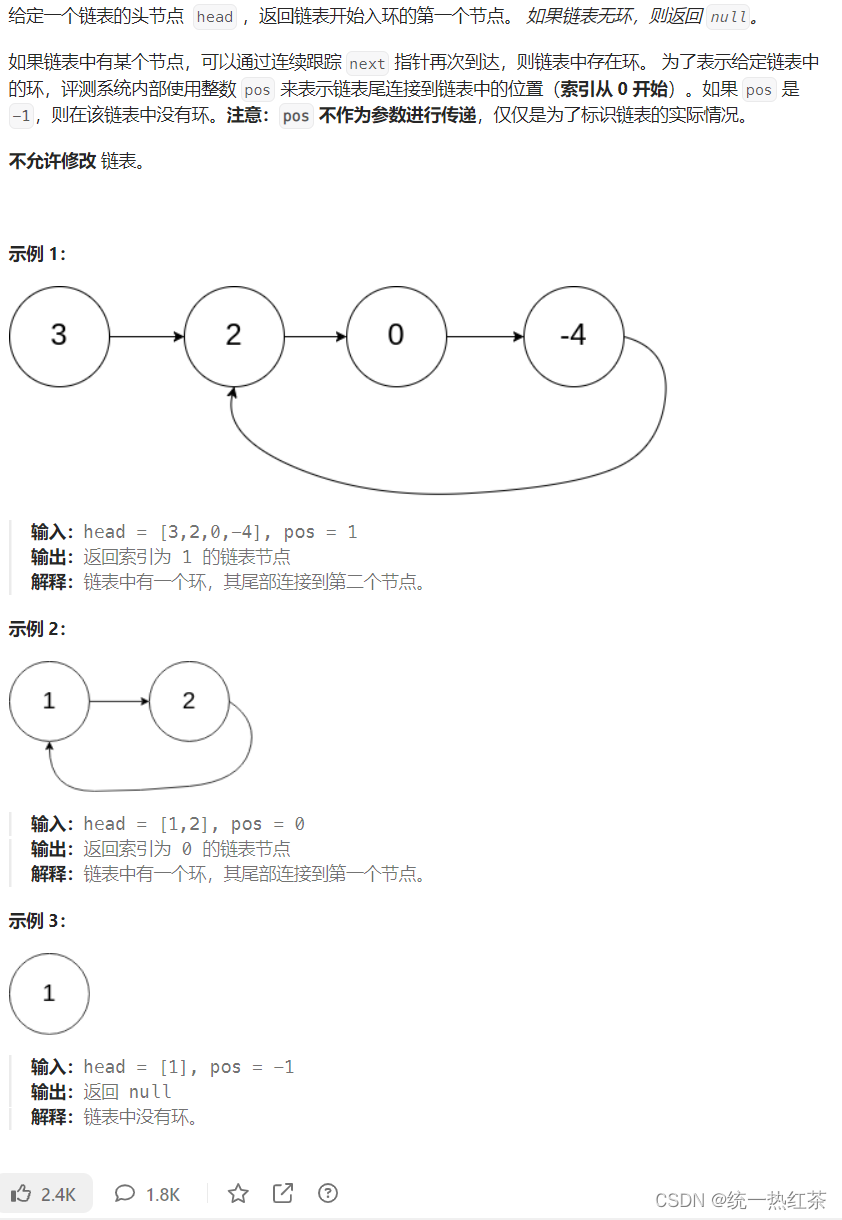
链接奉上
思路:
先输出一个结论:
找到快慢指针相遇的点,设置两个指针,一个从头开始走,一个从相遇点开始走,一次一步,相遇点就是环的开始点,我们返回此指针

代码实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;struct ListNode* cur = head;while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if(slow == fast){struct ListNode* meet = slow;while(1){if(cur == meet){return meet;}cur = cur->next;meet = meet->next;}}}return NULL;
}
若有问题可以及时询问博主





)













