前言
如果你的前后端分离项目采用SpringBoot3+Vue3+Element Plus,且在没有OSS(对象存储)的情况下,使用mysql读写图片(可能不限于图片,待测试)。
耗时三天,在踩了无数雷后,终于完成本功能。为你呈上。
本文完成功能:
- 前端采用Element发起上传图片请求,后端接收并将其存储到mysql。
- 后端相应图片base64数据,前端接收并渲染到页面。
1.前端上传到数据库
1.1前端上传图片
<el-form-item label="宠物照片" prop="pictureId">
<el-upload v-model="form.pictureId" :auto-upload="false" :action="''" :show-file-list="true" :on-change="handleAvatarChangeIcon"><el-button type="primary">选取文件</el-button>
</el-upload>
</el-form-item>
参数:
:auto-upload 是否自动上传
:action 自动上传的请求路径
:show-file-list 显示已上传的图片列表
:on-change 选中文件触发的change事件
自动上传与否都不影响,这里主要是判断一下图片的大小、后缀名。如下:
const handleAvatarChangeIcon = (file) => {// 限制文件后缀名const isJPG = file.raw.type === 'image/jpeg'const isPNG = file.raw.type === 'image/png'// 限制上传文件的大小const isLt5M = file.raw.size / 1024 / 1024 < 5if (!isPNG && !isJPG) {ElMessage.error('图片只能是 JPG/PNG 格式')return false} else if (!isLt5M) {ElMessage.error('图片应在5MB以内')return false} else {// 发起请求let param = new FormData();// 文件为form data格式param.append("file", file.raw);post('/api/file/upload', param, (res) => {ElMessage.success('上传成功');// 返回值为图片idform.pictureId = res})}
}
1.2后端接收并保存数据库
controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/file")
public class FileController {@Resourceprivate FileService fileService;@PostMapping("/upload")public RestBean<String> upload(@RequestParam MultipartFile file) {Integer res = fileService.upload(file);return RestBean.success(String.valueOf(res));}
}
serviceImpl
@Service
public class FileServiceImpl implements FileService {@Resourceprivate FileMapper fileMapper;/*** 文件上传到数据库*/@Overridepublic Integer upload(MultipartFile file) throws IOException {// 获取文件原始名String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();// 获取文件后缀名String endName = "png";if (originalFilename != null) {endName = originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf("."));}// 拼接文件名String filename = UUID.randomUUID() + endName;Integer pictureId;// 创建图片对象byte[] fileBytes = file.getBytes();Picture picture = new Picture();picture.setName(filename);picture.setPicData(fileBytes);// 上传数据库fileMapper.upload(picture);pictureId = picture.getId();// 返回图片idreturn pictureId;}
}
mapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.ycb.mapper.FileMapper"><insert id="upload" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">insert into `pet-adoption`.picture(name, pic_data)value (#{name}, #{picData})</insert>
</mapper>
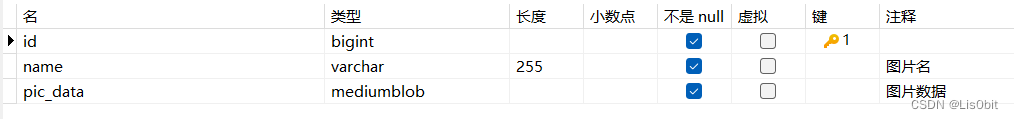
数据库设计
2.前端从数据库获取图片并渲染
2.1后端从数据库中获取
entity
public class PetAndBulVO {/*** 照片*/private byte[] picData;
}
controller
如果是一个图片数据直接封装到实体类,很多数据就封装成集合
@RequestMapping("/api/pet")
public class PetController {@Resourceprivate PetService petService;@GetMapping("/getAllPB")public RestBean<List<PetAndBulVO>> getAll() {List<PetAndBulVO> pets = petService.getAll();return RestBean.success(pets);}
}
serviceImpl
@Service
public class PetServiceImpl implements PetService {@Resourceprivate PetMapper petMapper;@Overridepublic List<PetAndBulVO> getAll() {return petMapper.getAll();}
}
mapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.ycb.mapper.PetMapper"><!-- 一定要映射结果集 --><resultMap type="com.ycb.entity.vo.response.PetAndBulVO" id="petAndBulVO"><id column="pic_data" property="picData" javaType="byte[]" jdbcType="BLOB" typeHandler="org.apache.ibatis.type.BlobTypeHandler"/></resultMap><select id="getAll" resultMap="petAndBulVO">select *from `pet-adoption`.pet petjoin `pet-adoption`.picture p on p.id = pet.picture_id</select>
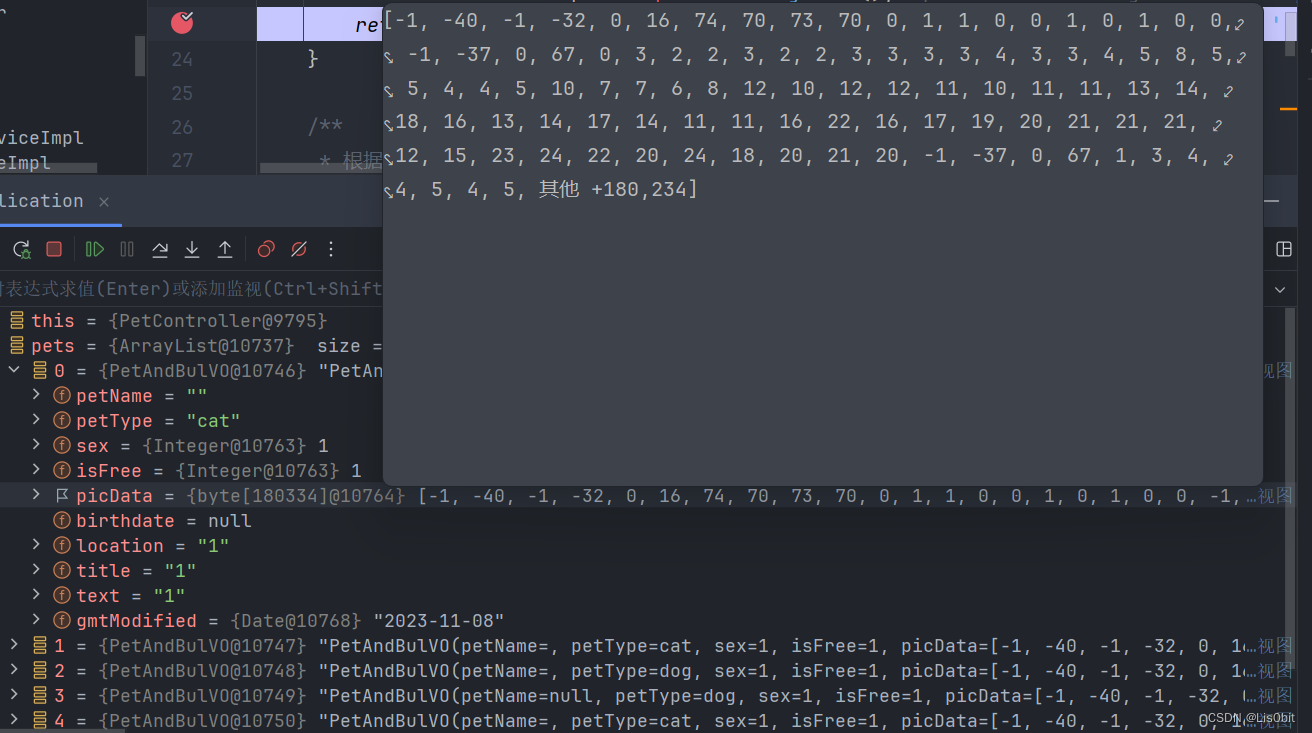
后端返回的图片数据如下:
2.2前端接收数据并渲染
后端传来的数据是 base64 形式的,需要解码
// 解码
const base64ToUrl = (base64) => {return 'data:image/png;base64,' + base64
}// 获取数据
get('/api/pet/getAllPB', (data) => {for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {data[i].picData = base64ToUrl(data[i].picData)}pBList.value = data
}, (err) => {ElMessage.error(err)
})
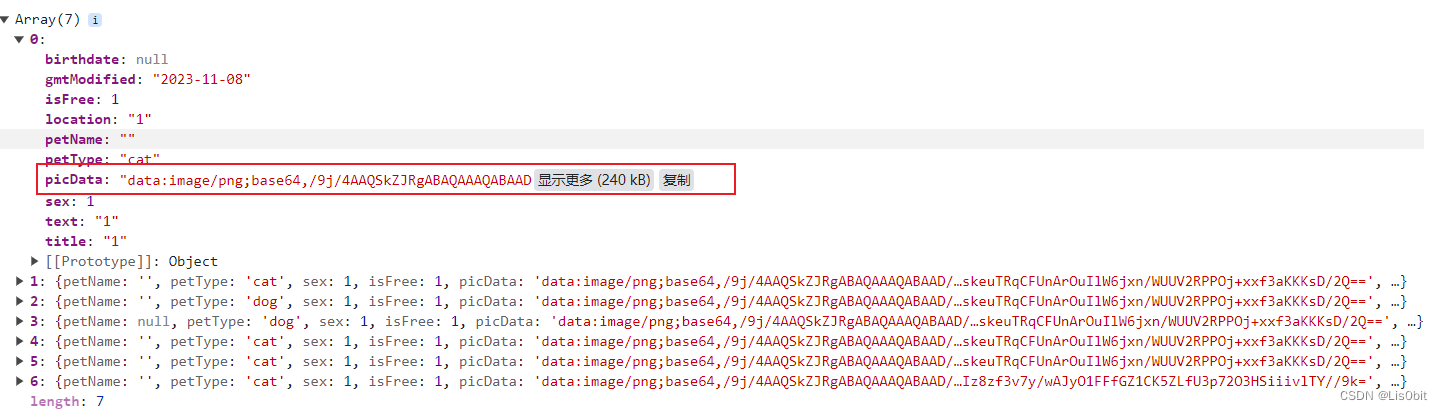
解码后的图片数据如下:
渲染是大坑!一定要 v-bind: 绑定 src
// v-for循环获取picData, v-for="(pb) in pBList"
<el-image v-bind:src="pb.picData"/>
《林克可爱图》
写在最后
虽然可以实现仅用mysql就能完成图片读写,但其性能堪忧。
很难,但贵在坚持。



















