内容:将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构。组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。 角色: 抽象组建(component) 叶子组建(Leaf) 复合组建(Composite) 客户端 (Client) UML 图 举个例子
from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod
class Graphic ( metaclass= ABCMeta) : @abstractmethod def draw ( self) : pass
class Point ( Graphic) : def __init__ ( self, x, y) : self. x = xself. y = ydef __str__ ( self) : return "点(%s,%s)" % ( self. x, self. y) def draw ( self) : print ( str ( self) ) class Line ( Graphic) : def __init__ ( self, p1, p2) : self. p1 = p1self. p2 = p2def __str__ ( self) : return "线段[%s,%s]" % ( self. p1, self. p2) def draw ( self) : print ( str ( self) )
class Picture ( Graphic) : def __init__ ( self, iterable) : self. children = [ ] for g in iterable: self. add( g) def add ( self, graphic) : self. children. append( graphic) def draw ( self) : print ( "----------复合图形----------" ) for g in self. children: g. draw( ) print ( "----------复合图形----------" ) p1 = Point( 2 , 3 )
l1 = Line( Point( 3 , 4 ) , Point( 6 , 7 ) )
l2 = Line( Point( 1 , 5 ) , Point( 2 , 8 ) )
pic1 = Picture( [ p1, l1, l2] ) p2 = Point( 4 , 2 )
l3 = Line( Point( 1 , 4 ) , Point( 2 , 5 ) )
l4 = Line( Point( 3 , 5 ) , Point( 1 , 8 ) )
pic2 = Picture( [ p2, l3, l4] ) pic= Picture( [ pic1, pic2] )
pic. draw( )
适用场景: 表示对象的“部分-整体”层次结构(特别是结构是递归的) 希望用户忽略组合对对象与单个对象的不同,用户统一地使用组合结构中的所有对象 优点: 定义了包含基本对象和组合对象的类层次结构 简化客户端代码,即客户端可以一致地使用组合对象和单个对象 更容易增加新类型的组件 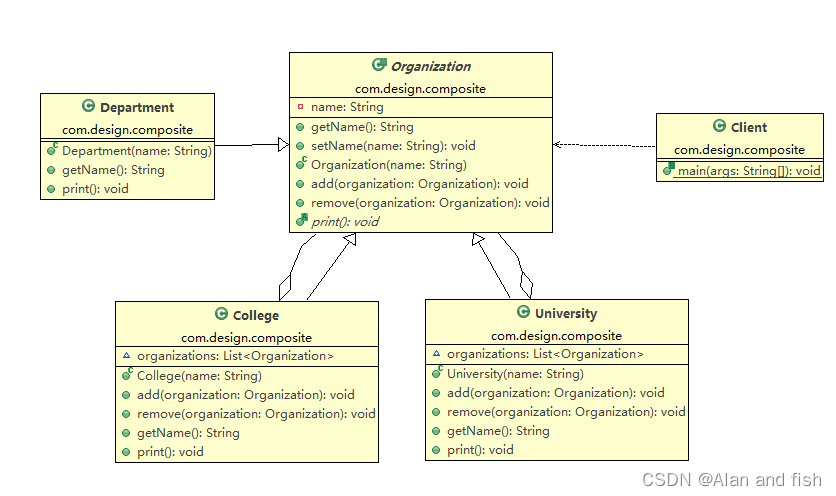



)



之 面向云原生环境的安全体系)


-- 算法导论6.5 6题)





多源广度优先搜索 JAVA)

)
