一、前言
日常工作中,我们用到mybatis的时候,都是写一个Mapper接口+xml文件/注解形式,然后就可以在业务层去调用我们在Mapper接口中定义的CRUD方法,很方便,但一直都没有去研究过执行逻辑,下面附一篇我自己研究的过程。
二、注入过程分析
平时我们在使用时,都是直接注解标在Mapper接口上,从而去注入一个实例,但我们是并没有实现过这个Mapper接口的,就很容易想到必然是有一个代理类(MapperProxy)来帮我们执行真正的过程,而且既然我们定义了接口,那大概率就是JDK动态代理了。
注入的过程也比较简单,在我们使用时会注明一个mapper扫描的包路径,然后在SqlSessionFactory初始化的过程中,会去解析每个mapper接口,并将其放在Configuration的MapperRegistry中,实际存放位置是在MapperRegistry中Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers。
接下来我们在使用mapper接口时,会从knownMappers中去获取到对应的MapperProxyFactory,从而去实例化真正的代理类,代码如下:
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {if (type.isInterface()) {if (hasMapper(type)) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");}boolean loadCompleted = false;try {knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);parser.parse();loadCompleted = true;} finally {if (!loadCompleted) {knownMappers.remove(type);}}}} public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");}try {//关键步骤,里面会使用JDK动态代理,创建一个MapperProxyreturn mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);} catch (Exception e) {throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);}}public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {private final Class<T> mapperInterface;private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;}public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {return mapperInterface;}public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {return methodCache;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);}public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);return newInstance(mapperProxy);}}三、执行过程分析
综上来看,其实我们真正的方法是由MapperProxy来实现的,接下来看看它的逻辑,我们主要分析查询类的执行流程:
/*** 执行入口*/@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args);} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);}} catch (Throwable t) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);}//缓存方法final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);//真正的执行逻辑return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);}
/**
* 根据sql类型,执行不同的分支
* convertArgsToSqlCommandParam会转换传入的参数
*/
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Object result;switch (command.getType()) {case INSERT: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));break;}case UPDATE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));break;}case DELETE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));break;}case SELECT://如果是void方法,并且自定义了ResultMap等映射,则执行此逻辑if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);result = null;} else if (method.returnsMany()) {//返参为集合类型result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsMap()) {//返参为Mapresult = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {//返参为游标result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);} else {//返参为单对象Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);}break;case FLUSH:result = sqlSession.flushStatements();break;default:throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());}if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");}return result;}上面的查询方法,都会走到下面这两行代码
//获取sql执行的映射过程对象,包含了参数、数据源、返参等
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//执行查询方法
executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);接着会走到执行器executor,主要有两类实现:
-
-
- org.apache.ibatis.executor.BaseExecutor(基本执行器)
- CachingExecutor(带缓存的执行器)
-
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {//获取BoundSql对象,包含了解析动态SQl生成的sql语句以及参数映射的封装BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);//生成缓存keyCacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);//查询return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);}public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {//调用sqlSource获取BoundSql,sqlSource默认为DynamicSqlSource类型(动态SQL)BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();//若参数映射为空,手动创建boundSqlif (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);}// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();if (rmId != null) {ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);if (rm != null) {hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();}}}return boundSql;} public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {//获取上下文对象,并将传入的入参对象及数据源标识放入bindingsDynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);//基于动态sql解析成的List<SqlNode> contents,遍历赋值参数rootSqlNode.apply(context);SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : context.getBindings().entrySet()) {boundSql.setAdditionalParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());}return boundSql;}
准备好BoundSql后,就该执行真正的查询了,主要链路如下
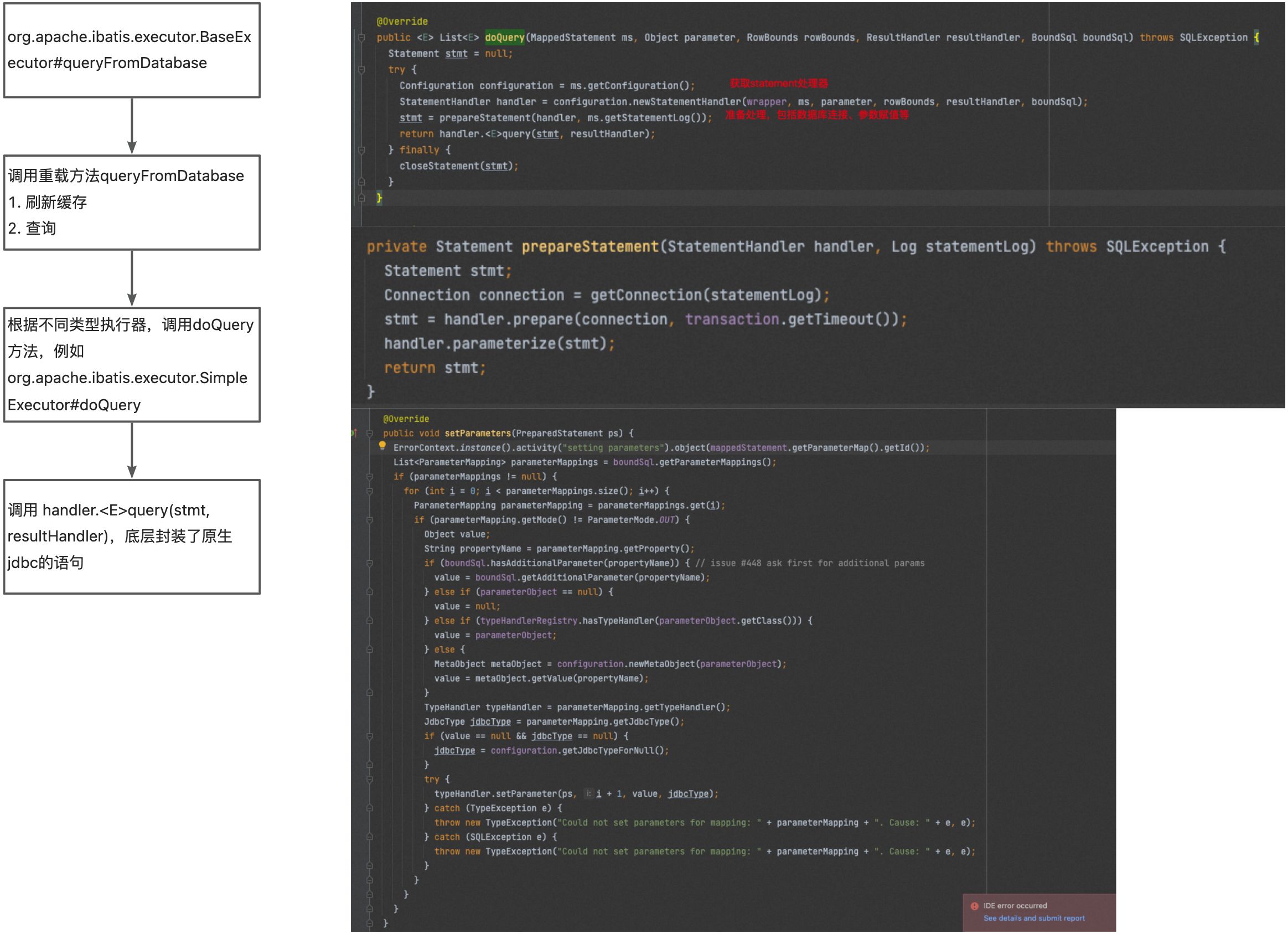
)

FP-V58-W(c))










之什么是清明梦)





