上一章我们分析了Aspect中advice的排序为Around.class, Before.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class,然后advice真正的执行顺序是什么?多个Aspect之间的执行顺序又是什么?就是我们本章探讨的问题。
准备工作
既然需要知道advide的执行顺序,那么我们就得有Aspect。我们还是使用之前创建的那个ThamNotVeryUsefulAspect,代码内容如下:
@Component
@Aspect
public class ThamNotVeryUsefulAspect {@Pointcut("execution(* com.qhyu.cloud.aop.service.QhyuAspectService.*(..))") // the pointcut expressionprivate void thamAnyOldTransfer() {} // the pointcut signature@Before("thamAnyOldTransfer()")public void before(){System.out.println("tham Before 方法调用前");}@After("thamAnyOldTransfer()")public void after(){System.out.println("tham After 方法调用前");}@AfterReturning("thamAnyOldTransfer()")public void afterReturning(){System.out.println("tham afterReturning");}@AfterThrowing("thamAnyOldTransfer()")public void afterThrowing(){System.out.println("tham AfterThrowing");}@Around("thamAnyOldTransfer()")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{// start stopwatchSystem.out.println("tham around before");Object retVal = pjp.proceed();// stop stopwatchSystem.out.println("tham around after");return retVal;}
}
Pointcut(官网使用地址)指向的是执行QhyuAspectService接口定义的任意方法。
public interface QhyuAspectService {void test();
}@Component
public class QhyuAspectServiceImpl implements QhyuAspectService {@Overridepublic void test() {System.out.println("执行我的方法");}
}
然后就是启动类调用一下
public class QhyuApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext =new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AopConfig.class);//test(annotationConfigApplicationContext);aspectTest(annotationConfigApplicationContext);//eventTest(annotationConfigApplicationContext);//transactionTest(annotationConfigApplicationContext);}private static void aspectTest(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext) {QhyuAspectService bean1 = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(QhyuAspectService.class);bean1.test();}}
到此我们就准备就绪了,接下来就开发源码层面的分析。
JdkDynamicAopProxy
wrapIfNecessary的时候会为我们的类创建代理对象,这边没有强制使用cglib,@EnableAspectJAutoProxy中proxyTargetClass default false。
由于我的QhyuAspectServiceImpl实现了QhyuAspectService接口,所以我这里就是用JdkDynamicAopProxy来创建代理对象。所以QhyuAspectServiceImpl的test方法调用的时候会进入JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法。源码如下:
@Nullablepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {Object oldProxy = null;boolean setProxyContext = false;TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;Object target = null;try {if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.return equals(args[0]);}else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.return hashCode();}else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);}else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);}Object retVal;if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {// Make invocation available if necessary.oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);setProxyContext = true;}// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,// in case it comes from a pool.target = targetSource.getTarget();Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);// Get the interception chain for this method.List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.if (chain.isEmpty()) {// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);}else {// We need to create a method invocation...MethodInvocation invocation =new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.// 执行拦截器链retVal = invocation.proceed();}// Massage return value if necessary.Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets// a reference to itself in another returned object.retVal = proxy;}else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {throw new AopInvocationException("Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);}return retVal;}finally {if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {// Must have come from TargetSource.targetSource.releaseTarget(target);}if (setProxyContext) {// Restore old proxy.AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);}}}
this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass) 就是获取到我们之前排序的Aspect的advice,顺序就是之前排序的顺序。
ExposeInvocationInterceptor是Spring AOP框架中的一个拦截器(Interceptor),用于在方法调用期间将当前代理对象暴露给AopContext。
AopContext是Spring提供的一个工具类,用于获取当前代理对象。在使用AOP进行方法拦截时,Spring会为每个代理对象创建一个AopContext实例,并在方法调用前将当前代理对象设置到AopContext中。这样,在方法内部可以通过AopContext来获取当前代理对象,进而在方法内部调用代理的其他方法,实现方法间的相互调用。
ExposeInvocationInterceptor的作用就是在方法调用期间将当前代理对象设置到AopContext中。它是整个AOP拦截器链中的第一个拦截器,确保在后续的拦截器或切面中可以通过AopContext获取到当前代理对象。
为什么每个AOP都需要ExposeInvocationInterceptor呢?这是因为AOP框架需要保证在方法调用期间能够正确地处理代理对象。由于AOP是通过动态代理机制实现的,代理对象会被包装在一个拦截器链中,并在方法调用时依次通过这个链进行处理。为了能够正确地传递当前代理对象,需要借助ExposeInvocationInterceptor来在方法调用前将代理对象设置到AopContext中。
需要注意的是,ExposeInvocationInterceptor是Spring AOP框架特有的拦截器,在其他AOP框架中可能没有相应的实现。它的存在是为了支持Spring AOP中的AopContext功能,以便在AOP拦截器链中获取当前代理对象。
AspectJAroundAdvice、MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor、AspectJAfterAdvice、AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor、AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice就是我们的@Around、@Before、@After、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing。
重点来了,接下来将逐一分析ReflectiveMethodInvocation、AspectJAroundAdvice、MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor、AspectJAfterAdvice、AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor、AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice。
ReflectiveMethodInvocation
这段代码是ReflectiveMethodInvocation类中的proceed方法,这个proceed()方法是Spring框架中的ReflectiveMethodInvocation类的一个重要方法。在AOP(面向切面编程)中,拦截器用于在方法调用之前、之后或者周围执行特定的操作。这个proceed()方法在方法调用过程中起到关键作用。我来分解一下提供的代码:
-
this.currentInterceptorIndex表示当前拦截器的索引。开始时,索引值为-1,然后提前递增。 -
这个条件语句检查当前拦截器索引是否等于拦截器列表的最后一个索引。如果是,说明已经到达了拦截器链的末尾,调用
invokeJoinpoint()方法执行实际的方法调用,并返回其结果。 -
如果当前拦截器索引不是最后一个,就获取下一个拦截器或者拦截器通知(
interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice)。 -
接下来的条件语句检查
interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice的类型。如果是InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher类型,说明它是一个动态方法匹配的拦截器。- 该拦截器的动态方法匹配器在这里被评估(已经在静态部分被评估并确定是匹配的)。
- 如果方法匹配成功,调用该拦截器的
invoke(this)方法,并返回结果。 - 如果方法匹配失败,跳过当前拦截器,继续调用下一个拦截器,通过递归调用
proceed()方法实现。
-
如果
interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice是普通的拦截器(MethodInterceptor类型),直接调用它的invoke(this)方法。
这个方法的逻辑实现了拦截器链的调用和动态方法匹配的过程,确保在方法调用前后可以执行相应的逻辑。
@Override@Nullablepublic Object proceed() throws Throwable {// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {return invokeJoinpoint();}Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have// been evaluated and found to match.InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);}else {// Dynamic matching failed.// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.return proceed();}}else {// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);}}
AspectJAroundAdvice
AspectJAroundAdvice类的invoke方法是一个用于执行环绕通知(around advice)的方法。环绕通知是AOP中一种类型的通知,在目标方法调用前后都能执行特定逻辑。
下面是对AspectJAroundAdvice的invoke方法进行的分析:
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {// 检查传入的MethodInvocation是否是Spring的ProxyMethodInvocation的实例if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) {// 如果不是,抛出IllegalStateException异常throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi);}// 将传入的MethodInvocation强制转换为ProxyMethodInvocation类型ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation) mi;// 获取ProceedingJoinPoint对象,这是Spring AOP中特定于环绕通知的接口ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi);// 获取JoinPointMatch对象,用于匹配切点JoinPointMatch jpm = getJoinPointMatch(pmi);// 调用invokeAdviceMethod方法执行环绕通知的逻辑// 参数为ProceedingJoinPoint、JoinPointMatch以及null、nullreturn invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, null, null);
}
分析:
-
类型检查:首先,方法检查传入的
MethodInvocation对象是否是ProxyMethodInvocation的实例。如果不是,说明传入的对象不是Spring代理方法调用的实例,抛出IllegalStateException异常。 -
类型转换:如果
MethodInvocation对象是ProxyMethodInvocation的实例,就将其强制转换为ProxyMethodInvocation类型,为后续的操作做准备。 -
获取ProceedingJoinPoint和JoinPointMatch:通过
pmi对象获取ProceedingJoinPoint对象和JoinPointMatch对象。ProceedingJoinPoint是Spring AOP中特定于环绕通知的接口,它包含了目标方法的信息。JoinPointMatch对象用于匹配切点。 -
调用环绕通知逻辑:最后,调用
invokeAdviceMethod方法,执行环绕通知的逻辑。invokeAdviceMethod方法可能包含了环绕通知的具体实现,它接受ProceedingJoinPoint、JoinPointMatch以及额外的参数,然后执行通知逻辑并返回结果。
总的来说,这个invoke方法的目的是将Spring AOP中的代理方法调用转换为AspectJ中的ProceedingJoinPoint对象,并执行相应的环绕通知逻辑。
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor的invoke方法是用于执行"前置通知"(before advice)的关键部分。前置通知是AOP中的一种通知类型,在目标方法执行之前执行特定逻辑。以下是该方法的分析:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {// 在目标方法执行前调用通知的before方法this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());// 继续执行目标方法return mi.proceed();
}
分析:
-
调用前置通知的
before方法:首先,在目标方法执行前,通过this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis())调用了前置通知(MethodBeforeAdvice接口的实现类)的before方法。这个方法通常用于执行前置逻辑,比如日志记录、权限检查等。before方法接受目标方法(mi.getMethod())、方法参数(mi.getArguments())和目标对象(mi.getThis())作为参数。 -
继续执行目标方法:之后,通过
mi.proceed()方法继续执行目标方法。这个方法调用会使得程序流程进入被代理的实际目标方法。
这个invoke方法的逻辑非常简单,但是非常重要。它确保了前置通知在目标方法执行前被触发,然后再允许目标方法继续执行。这种机制允许开发者在不修改目标方法的情况下,在方法执行前插入自定义逻辑。
AspectJAfterAdvice
AspectJAfterAdvice的invoke方法是用于执行"后置通知"(after advice)的关键部分。后置通知是AOP中的一种通知类型,在目标方法执行之后执行特定逻辑。以下是该方法的分析:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {try {// 继续执行目标方法return mi.proceed();} finally {// 在目标方法执行后,通过invokeAdviceMethod执行后置通知逻辑invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);}
}
分析:
-
继续执行目标方法:首先,使用
mi.proceed()方法继续执行目标方法。这个方法调用会使得程序流程进入被代理的实际目标方法。 -
执行后置通知逻辑:使用
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null)在finally块中执行后置通知的逻辑。getJoinPointMatch()方法用于获取匹配的连接点(Join Point)。在这里,AspectJAfterAdvice可能会使用该连接点信息执行后置逻辑。finally块保证无论目标方法是否抛出异常,后置通知的逻辑都会被执行。
这个invoke方法的逻辑非常清晰:它确保了在目标方法执行前后分别执行前置和后置逻辑。在这个方法中,后置通知的逻辑被放在了finally块中,以确保在目标方法执行后无论是否发生异常,都会执行后置通知。这样,开发者可以在方法执行后插入自定义的逻辑,而不需要修改目标方法的代码。
AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor
AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor的invoke方法是用于执行"返回后通知"(after returning advice)的关键部分。返回后通知是AOP中的一种通知类型,在目标方法正常执行并返回后执行特定逻辑。以下是该方法的分析:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {// 调用目标方法,并获取其返回值Object returnValue = mi.proceed();// 在目标方法返回后,调用通知的afterReturning方法this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());// 返回目标方法的返回值return returnValue;
}
分析:
-
调用目标方法:首先,使用
mi.proceed()方法调用目标方法。这个方法调用会使得程序流程进入被代理的实际目标方法,并获取其返回值。 -
执行返回后通知逻辑:在目标方法返回后,使用
this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis())调用通知的afterReturning方法。这个方法通常用于执行返回后的逻辑,比如日志记录、结果处理等。afterReturning方法接受目标方法的返回值(retVal)、目标方法(mi.getMethod())、方法参数(mi.getArguments())和目标对象(mi.getThis())作为参数。 -
返回目标方法的返回值:最后,将目标方法的返回值返回给调用者。
这个invoke方法的逻辑确保了在目标方法正常返回后,执行自定义的返回后逻辑。这种机制允许开发者在目标方法执行后对其返回值进行处理或记录。
AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice
AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice的invoke方法是用于执行"异常抛出后通知"(after throwing advice)的关键部分。异常抛出后通知是AOP中的一种通知类型,在目标方法抛出异常后执行特定逻辑。以下是该方法的分析:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {try {// 调用目标方法return mi.proceed();} catch (Throwable ex) {// 捕获目标方法抛出的异常// 如果满足特定条件,调用通知的invokeAdviceMethod方法if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) {invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex);}// 重新抛出捕获到的异常throw ex;}
}
分析:
-
调用目标方法:首先,使用
mi.proceed()方法调用目标方法。这个方法调用会使得程序流程进入被代理的实际目标方法。 -
捕获异常:使用
try-catch块捕获目标方法抛出的异常(Throwable ex)。 -
判断是否调用通知:在
catch块内部,通过shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)方法判断是否满足特定条件,如果满足,调用通知的invokeAdviceMethod方法。这个方法可能会包含了异常抛出后通知的具体逻辑。如果不满足条件,则不执行通知的逻辑。 -
重新抛出异常:最后,无论是否调用了通知,都会重新抛出捕获到的异常。这样做是为了保持异常的传播,使得上层调用者可以处理该异常或者继续传播异常。
总的来说,这个invoke方法的逻辑确保了在目标方法抛出异常后,根据特定条件执行相应的通知逻辑,并且保持异常的传播。这种机制允许开发者在目标方法抛出异常时执行自定义的逻辑。
ThamNotVeryUsefulAspect
QhyuAspectService配合ThamNotVeryUsefulAspect,查看所有advice的执行顺序。直接启动QhyuApplication的main方法。
tham around before
tham Before 方法调用前
执行我的方法
tham afterReturning
tham After 方法调用前
tham around after
下面这个图整理的就是整个调用逻辑。
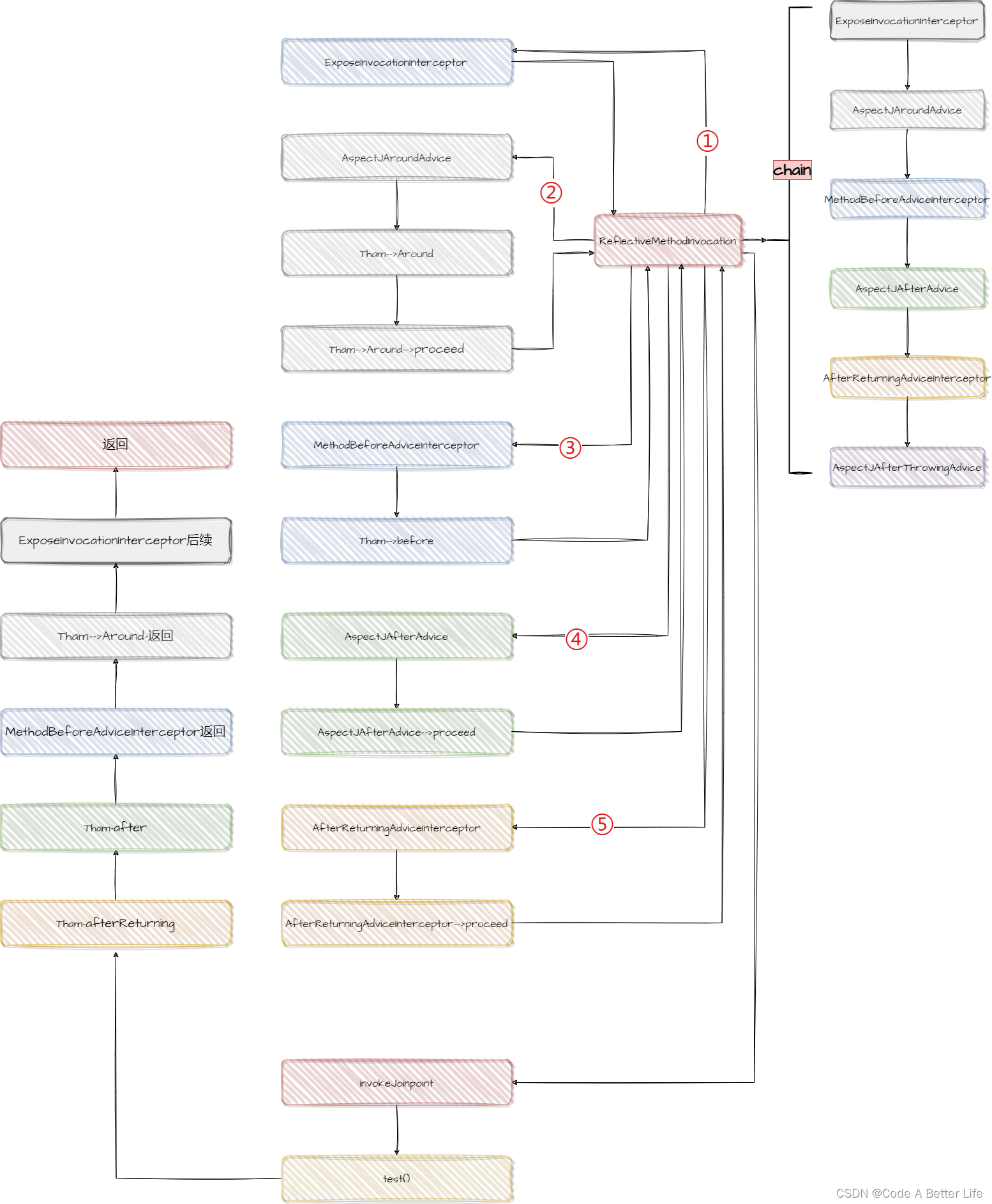
然后我创建了一个NotVeryUsefulAspect,@Order让其先执行,查看整体执行流程
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(99)
public class NotVeryUsefulAspect {@Pointcut("execution(* com.qhyu.cloud.aop.service.QhyuAspectService.*(..))") // the pointcut expressionprivate void anyOldTransfer() {} // the pointcut signature@Before("anyOldTransfer()")public void before(){System.out.println("not Before 方法调用前");}@After("anyOldTransfer()")public void after(){System.out.println("not After 方法调用前");}@AfterReturning("anyOldTransfer()")public void afterReturning(){System.out.println("not afterReturning");}@AfterThrowing("anyOldTransfer()")public void afterThrowing(){System.out.println("not AfterThrowing");}@Around("anyOldTransfer()")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{// start stopwatchSystem.out.println("not around before");Object retVal = pjp.proceed();// stop stopwatchSystem.out.println("not around after");return retVal;}
}
not around before
not Before 方法调用前
tham around before
tham Before 方法调用前
执行我的方法
tham afterReturning
tham After 方法调用前
tham around after
not afterReturning
not After 方法调用前
not around after
注意:
@AfterReturning 和 @AfterThrowing 通知确实是互斥的,它们中只有一个会在目标方法执行完成后执行。具体取决于目标方法的执行结果:
-
@AfterReturning通知:会在目标方法成功返回时执行,即使目标方法返回值为null也会执行。 -
@AfterThrowing通知:会在目标方法抛出异常时执行。
如果目标方法成功返回,@AfterReturning 通知会被执行;如果目标方法抛出异常,@AfterThrowing 通知会被执行。这两者之间不会同时执行,只有其中一个会根据目标方法的结果被触发。
)


)
,好用免费的数据库管理工具)









)

![[蓝桥杯-610]分数](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[蓝桥杯-610]分数)


、Jakarta XML Web Services Eclipse 实现)