
文章目录
- 二叉树创建字符串
- 二叉树分层遍历(从前开始)
- 二叉树分层遍历(从后开始)
- 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 二叉搜索树与双向链表
- 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 二叉树的前序遍历(非递归)
- 二叉树的中序遍历(非递归)
- 二叉树的后续遍历
二叉树创建字符串
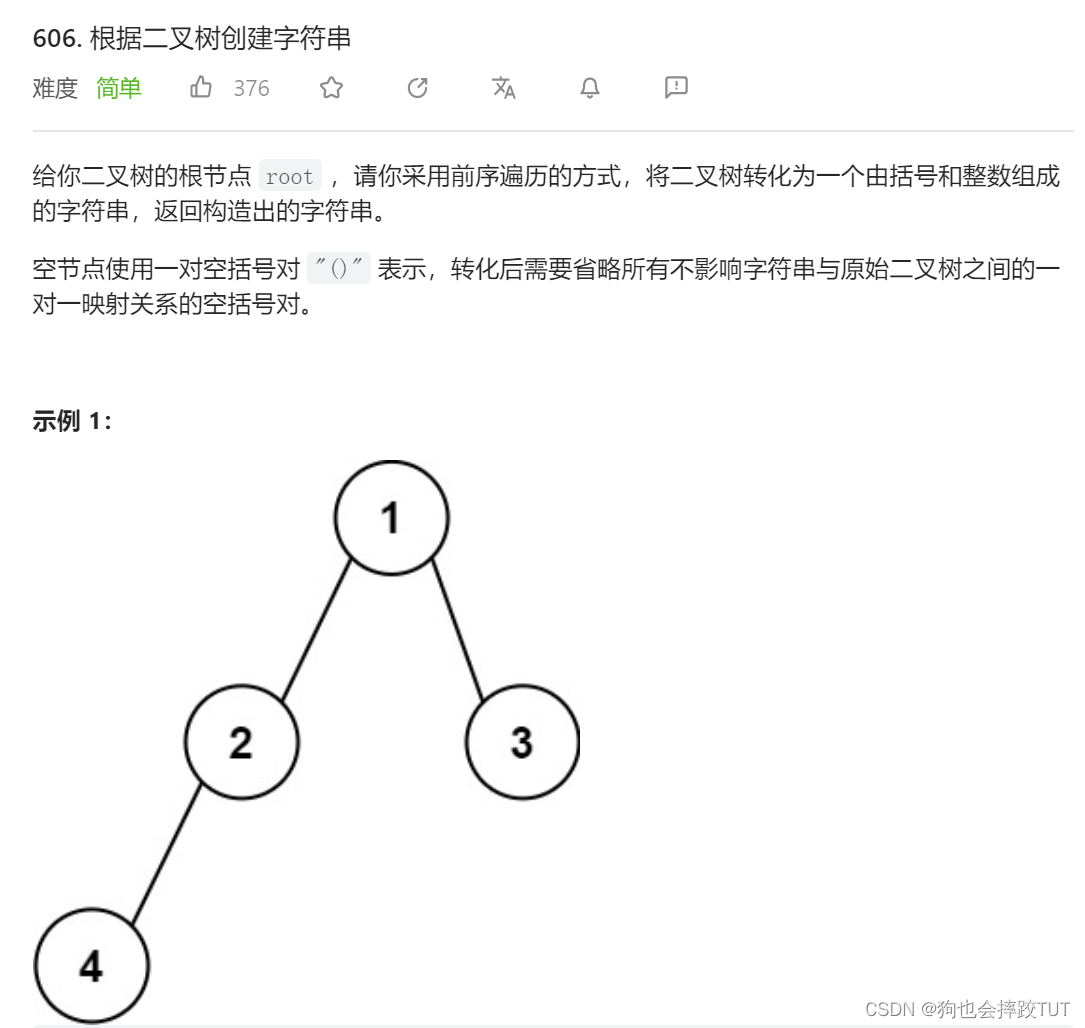

思路: 该题需要注意的细节就是当节点的左子树为空,而右子树却不为空的情况,就需要特殊处理,也是需要加上
(),而节点的左子树不为空,右子树为空就是不需要加上()。if(root->left||root->right)该语句就是实现左子树的字符和(),之后再去处理右子树。
//C++
class Solution {
public:string tree2str(TreeNode* root) {if(root==nullptr){return "";}string str=to_string(root->val);if(root->left||root->right){str+='(';str+=tree2str(root->left);str+=')';}if(root->right){str+='(';str+=tree2str(root->right);str+=')';}return str;}
};
二叉树分层遍历(从前开始)
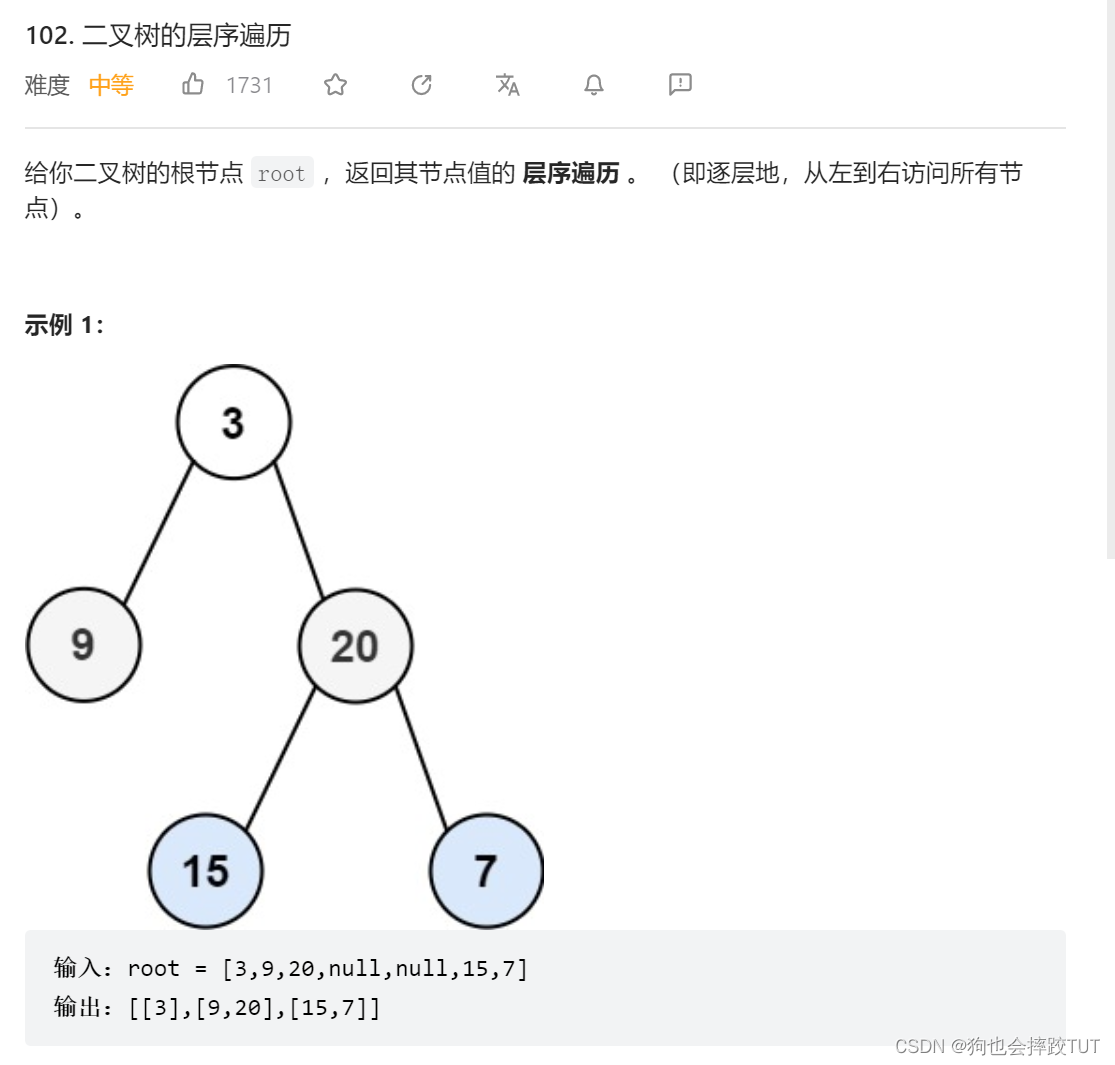

**思路:**创建一个队列,将遍历的数据存入到里面,在创建一个计数器用来记录每层的数据个数。
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {queue<TreeNode*> q;vector<vector<int>> vv; int levelsize=0;if(root){q.push(root);levelsize=1;}while(!q.empty()){vector<int> v;while(levelsize--){TreeNode* front=q.front();q.pop();v.push_back(front->val);if(front->left){q.push(front->left);}if(front->right){q.push(front->right);} }vv.push_back(v);levelsize=q.size();}return vv;}
};
二叉树分层遍历(从后开始)


**思路:**其实他就和上一个题的思路是一样的,只需要加个翻转就可以了。
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {queue<TreeNode*> q;vector<vector<int>> vv; int levelsize=0;if(root){q.push(root);levelsize=1;}while(!q.empty()){vector<int> v;while(levelsize--){TreeNode* front=q.front();q.pop();v.push_back(front->val);if(front->left){q.push(front->left);}if(front->right){q.push(front->right);} }vv.push_back(v);levelsize=q.size();}reverse(vv.begin(),vv.end());return vv;}
};
二叉树的最近公共祖先


思路:
1、使用三叉链(有父节点)转换为链表相交问题,其中长的一条先走gap。
2、就是进行判断确定一个数在自己的左边,另一个在自己的右边。不在用一边就说明现在的节点就是最近的公共祖先,在同一边就需要继续向下找。
class Solution {
public:bool Isintree(TreeNode* root,TreeNode* in){if(root==nullptr){return false;}if(root==in){return true;}else{return Isintree(root->left,in) || Isintree(root->right,in);}}TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {if(root==nullptr){return nullptr;}if(p==root || q==root){return root;}bool pinleft=Isintree(root->left,p);bool pinright=!pinleft;bool qinleft=Isintree(root->left,q);bool qinright=!qinleft;if((pinleft && qinright) || (pinright && qinleft)){return root;}else if(pinleft&&qinleft){return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);}else{return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);}}
};
注意: 上面的写法是属于性能较低的,他所用的时间是较长的。时间复杂度是
O(N^2)。在他最坏的情况下会出现歪脖子树。也就是确定一次两个数在哪边(递归一边查找,歪脖子树),共要向下递归N次。
思路: 下面的思路就是找到两条路径,用找链表的公共节点的方法来找最近公共节点。需要注意的就是在放入栈之后要进行判断下面没有就要进行出栈。
class Solution {
public:bool Getpath(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* g,stack<TreeNode*>& path){if(root==nullptr){return false;}path.push(root);//只要不是空就放进来if(root==g){return true;}if(Getpath(root->left,g,path)){return true;}if(Getpath(root->right,g,path)){return true;}path.pop();return false;}TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {stack<TreeNode*> qpath,ppath;Getpath(root,p,ppath);Getpath(root,q,qpath);while(ppath.size()!=qpath.size()){if(ppath.size()>qpath.size()){ppath.pop();}else{qpath.pop();}}while(ppath.top()!=qpath.top()){ppath.pop();qpath.pop();}return ppath.top();}
};
二叉搜索树与双向链表

思路: 该题目要求了空间复杂度,要是不要求的话,直接就中序遍历就好了。将节点prev指向空,cur为4的指针,这里要注意成员函数prev的引用,是必须要带上的,不带会影响整个结构的。将cur以递归的路径进行,prev跟上cur之前的节点。通过cur->left=prev,prev->right=cur。
class Solution {
public:void InorderConvert(TreeNode* cur,TreeNode*& prev){if(cur==nullptr){return;}InorderConvert(cur->left,prev);cur->left=prev;if(prev){prev->right=cur;}prev=cur;InorderConvert(cur->right,prev);}TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {TreeNode* prev=nullptr;InorderConvert(pRootOfTree,prev);TreeNode* root=pRootOfTree;while(root&&root->left){root=root->left;}return root;}
};从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树

思路: 将中序遍历的数组进行划区域处理,ibegin,iend,iroot,中序前序两个数组比较这进行。具体看代码。
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder,int& prei,int ibegin,int iend){if(ibegin>iend){return nullptr;}TreeNode* root=new TreeNode(preorder[prei]);int iroot=ibegin;while(iroot<=iend){if(preorder[prei]==inorder[iroot]){break;}else{iroot++;}}prei++;root->left= _buildTree(preorder,inorder,prei,ibegin,iroot-1);root->right= _buildTree(preorder,inorder,prei,iroot+1,iend);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {int prei=0;return _buildTree(preorder,inorder,prei,0,preorder.size()-1);}
};
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
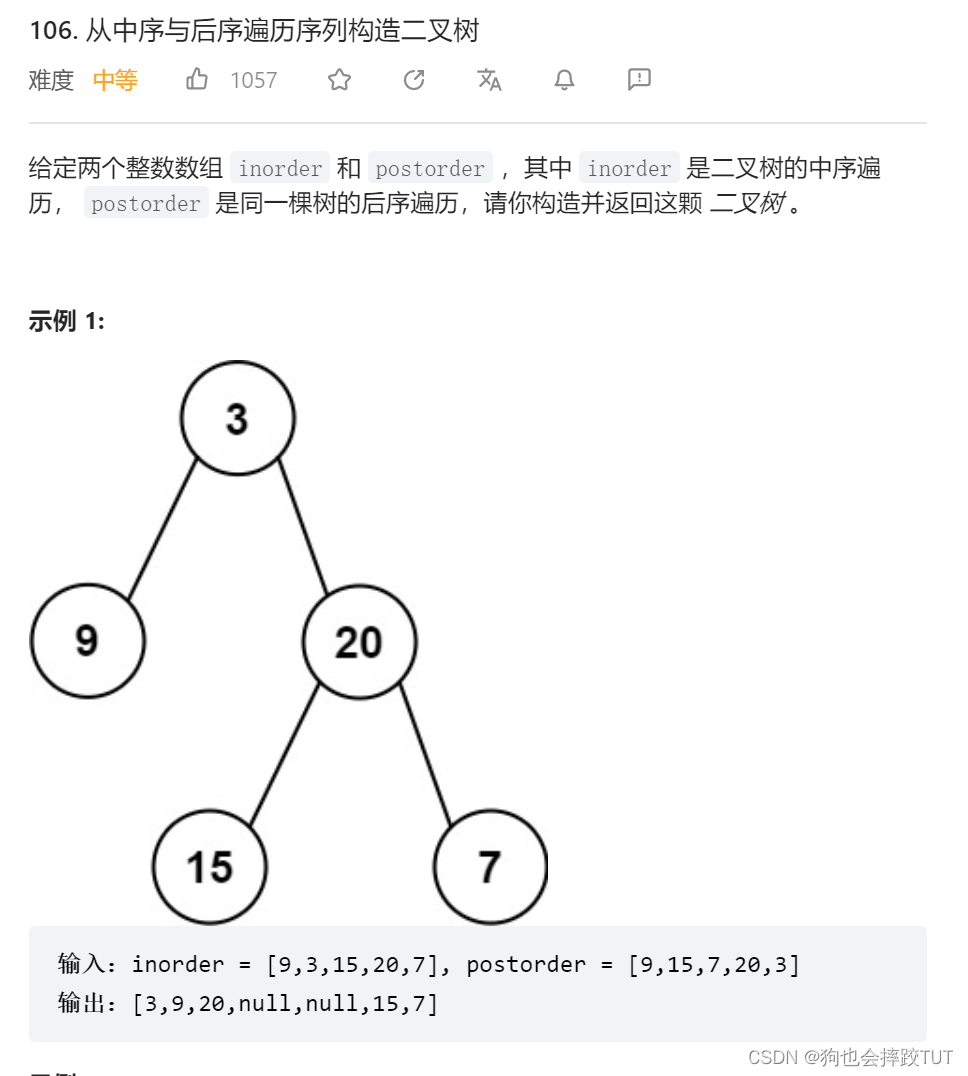
思路: 该题和上一个题的思路是相同的,就是将前序改为后序了,所以就是prei改为从后开始遍历。
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder,int& prei,int ibegin,int iend){if(ibegin>iend){return nullptr;}TreeNode* root=new TreeNode(preorder[prei]);int iroot=ibegin;while(iroot<=iend){if(preorder[prei]==inorder[iroot]){break;}else{iroot++;}}prei--;root->right= _buildTree(preorder,inorder,prei,iroot+1,iend);root->left= _buildTree(preorder,inorder,prei,ibegin,iroot-1);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {int prei=postorder.size()-1;return _buildTree(postorder,inorder,prei,0,postorder.size()-1);}
};
二叉树的前序遍历(非递归)
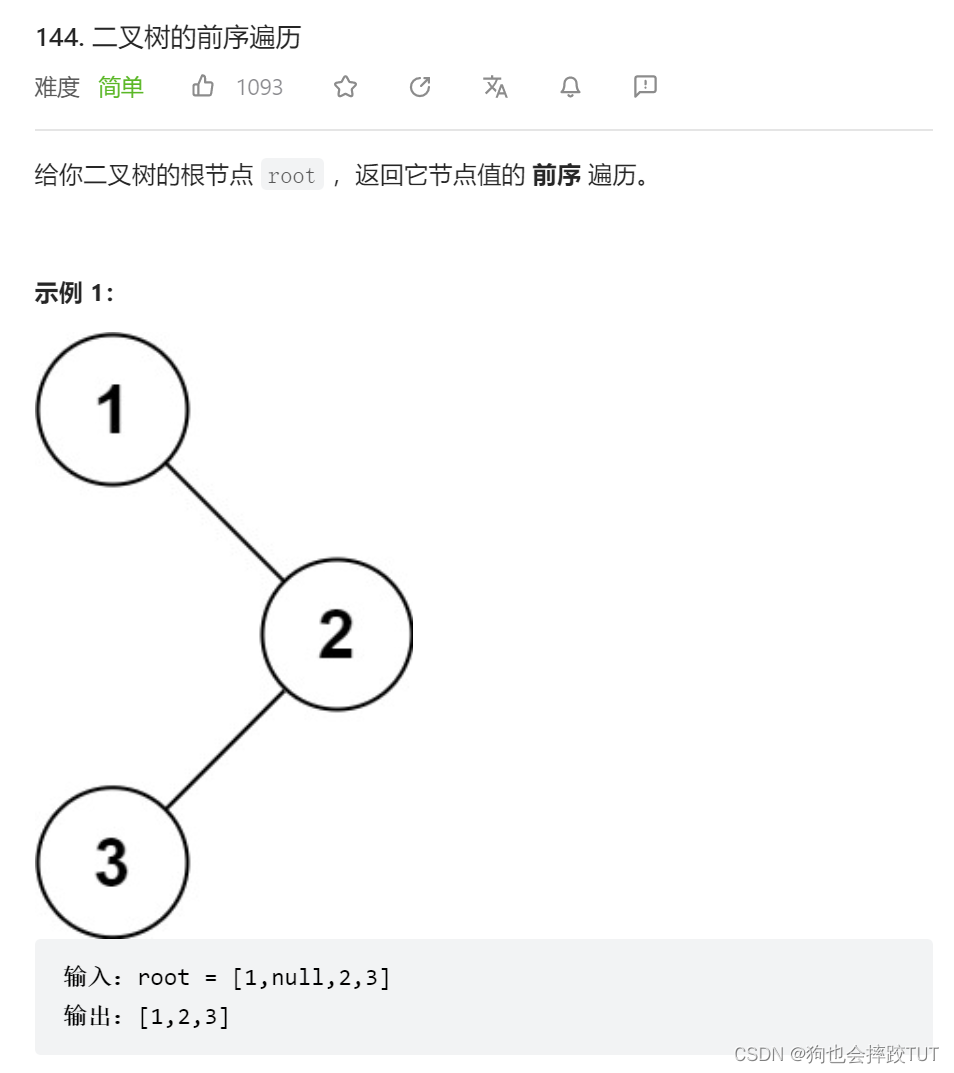
思路: 创建一个数组和一个找,是将树的左子树先进行都先进入数组按顺序。并且将前面进入数组的节点放入栈当中,之后进行对右子树的遍历,这时要将指向右子树的这颗节点进行删除在栈当中。
class Solution {
public:vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> v;stack<TreeNode*> s;TreeNode* cur=root;while(cur || !s.empty()){while(cur){v.push_back(cur->val);s.push(cur);cur=cur->left;}TreeNode* top=s.top();s.pop();cur=top->right;}return v;}
};
二叉树的中序遍历(非递归)
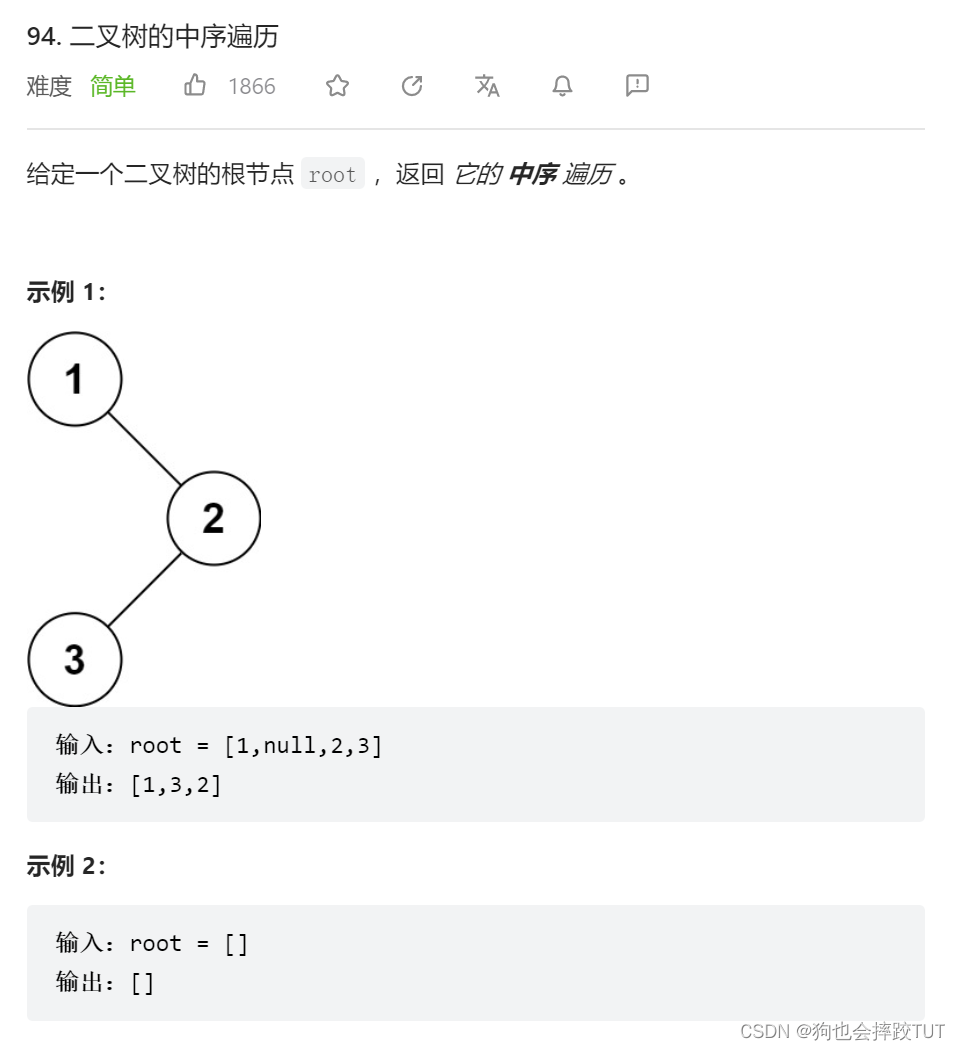
思路: 它的思路是和上一道题的解法是相同的,就是将pop出的节点,挨个放入数组。
class Solution {
public:vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> v;stack<TreeNode*> s;TreeNode* cur=root;while(cur || !s.empty()){while(cur){s.push(cur);cur=cur->left;}TreeNode* top=s.top();v.push_back(top->val);s.pop();cur=top->right;}return v;}
};
二叉树的后续遍历
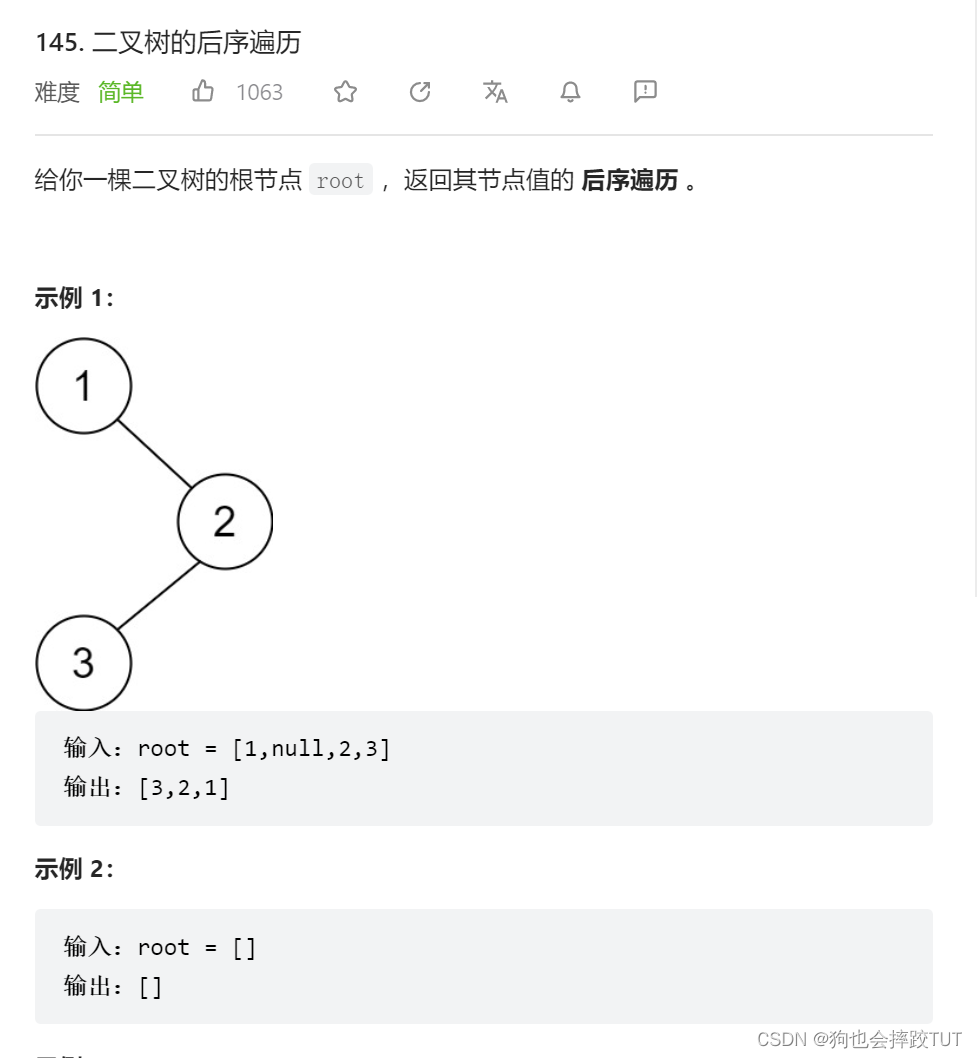
思路: 他与上述的问题差距就是如何让右子树在节点的前面输出,而采用的方法就是创建一个变量,用于判断是否右子树已经在父节点前面输出了。
class Solution {
public:vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> v;stack<TreeNode*> s;TreeNode* cur=root;TreeNode* pre=nullptr;while(cur || !s.empty()){while(cur){s.push(cur);cur=cur->left;}TreeNode* top=s.top();if(top->right==nullptr || pre==top->right){v.push_back(top->val);pre=top;s.pop();}else{cur=top->right;} }return v;}
};






![[React]常见Hook实现之useUpdateLayoutEffect](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[React]常见Hook实现之useUpdateLayoutEffect)

|第二节:超高产文本生成机,传媒营销人必备神器)
![[SQL挖掘机] - 字符串函数 - concat](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[SQL挖掘机] - 字符串函数 - concat)

)


(未完))



)
