文章目录
- 1.单词分析
- 1.代码
- 2.知识点
- 2.成绩统计
- 1.代码
- 2.知识点
- 1.如何四舍五入?
- 2.如何保留小数点后几位小数呢?
- 3.最短路
- 4.回文日期
- 1.代码
- 2.知识点
- 1.日期类
- 2.字符串细节
- 3.连等的细节
- 5.门牌制作
- 1.代码
- 6.卡片
- 1.代码
- 2.细节
- 7.数字三角形
- 1.代码
- 2.细节
- 8.成绩分析
- 1.代码
- 2.细节
- 9.购物单
- 1.代码
- 2.细节
- 10.空间
- 1.代码
- 2.细节
- 1.==MB --> KB --> 字节 --> bit==
- 2.整数溢出的问题
1.单词分析

1.代码
import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {//计算public static int[] count(int a[],String b){for (int i = 0; i < b.length(); i++) {char c = b.charAt(i);a[(int)c-97]++;}return a;}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);int[] ints = new int[26];String s = scan.next();int[] ints1 = count(ints,s);int index = 0;int val = ints1[0];for (int i = 1; i < ints1.length; i++) {if(ints1[i] > val){val = ints1[i];index = i;}}System.out.println((char)(index+97));System.out.println(val);}
}
2.知识点
一定要用调用函数的思想,保证一个模块干一件事
2.成绩统计

1.代码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;public class Main {public static void getPass(int ints1[],int n){int pass = 0;int goodpass = 0;for (int i = 0; i < ints1.length; i++) {if(ints1[i]>=60){if(ints1[i]>=85){goodpass++;}pass++;}}System.out.println(Math.round((pass/(n*1.0))*100) + "%");System.out.println(Math.round((goodpass/(n*1.0))*100) + "%");}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);int n = scan.nextInt();int[] ints = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {ints[i] = scan.nextInt();}getPass(ints,n);scan.close();}
}
2.知识点
成绩的问题可以考虑数组来解决问题,从而可以使其封装成函数
1.如何四舍五入?
result = d1 / d2;
int roundNum = (int) Math.round(result);//四舍五入
int ceilNum = (int) Math.ceil(result);//向上
int floorNum = (int) Math.floor(result);//向下
2.如何保留小数点后几位小数呢?
在java中可以使用和c语言相同的语法
result = d1 / d2;
System.out.printf("%.2f",d)
3.最短路
用眼看
4.回文日期

1.代码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.time.LocalDate;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);String str = scan.next();//接收八位整数int y = Integer.parseInt(str.substring(0, 4));int m = Integer.parseInt(str.substring(4, 6));int d = Integer.parseInt(str.substring(6, 8));//字符串转intLocalDate n = LocalDate.of(y, m, d);n = n.plusDays(1);
// System.out.println(n);String a = null;String b = null;boolean isFind = false;while (true) {String str1 = n.toString().replace("-", "");if (!isFind) {if(isHuiWen(str1)) {a = str1;isFind = true;}}if (isFind) {if (isABABBABA(str1)) {b = str1;break;}}n = n.plusDays(1);}System.out.println(a);System.out.println(b);scan.close();}public static boolean isHuiWen(String s) {boolean isFind = false;for (int i = 0; i < s.length() / 2; i++) {if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(s.length() - i - 1)) {break;}if (i == s.length() / 2 - 1) {isFind = true;}}return isFind;}public static boolean isABABBABA(String s) {boolean isFind = false;if (s.charAt(0) == s.charAt(2) && s.charAt(2) == s.charAt(5) && s.charAt(5) == s.charAt(7)&& s.charAt(1) == s.charAt(3) && s.charAt(3) == s.charAt(4) && s.charAt(4) == s.charAt(6)) {isFind = true;}return isFind;}
}
2.知识点
1.日期类
一般使用第三代日期类
====创建类====
LocalDate//日期 年月日
LocalTime//时间 时分秒
LocalDateTime//日期时间 年月日 时分秒
====获取时间====
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now() //获取当前时间
LocalDate ldt = LocalDate.of(y, m, d);//获取一个指定时间 其中ymd是int
====增减时间====
ldt = ldt.plusDays(1)//增加一天
ldt = ldt.minusDays(1)//减少一天
plusMonths plusWeeks plusYears //月 周 年
2.字符串细节
//获取字符串的子串
str.substring(0, 4)//后边类似切片,指定位置,前开后闭
//字符串转int
int y = Integer.parseInt(str.substring(0, 4));//如何记parse呢? 死记吧 貌似没有找到好的方法
//其他对象形式转字符串
toString()
LocalDate n = LocalDate.of(y, m, d);//返回的形式是y-m-d
String str1 = n.toString().replace("-", "");
//替换字符串中的某个具体字符
replace()
3.连等的细节
在java中没有连等,所以无法使用a == b == c,只用使用a == b && b == c
5.门牌制作

1.代码
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {int count = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= 2020; i++) {int k = i;while(k!=0){if(k%10==2){count++;}k /= 10;}}System.out.println(count);}
}
无注意细节
6.卡片

1.代码
public class kaPian_6 {public static void main(String[] args) {int num[] = new int[10];for (int i = 1; i < 4000; i++) {int k = i;while (k != 0) {num[k % 10]++;k /= 10;}for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {if (num[j] > 2021) {System.out.println(i - 1);break;}}}}
}2.细节
1.使用了个很大的数,作为循环条件
2.当前的数,一定是已经组装不了了,所以最后需要-1,才能满足题目要求
7.数字三角形

1.代码
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);int n = scan.nextInt();int arr[][] = new int[n+1][n+1];for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { //上左刚好多出来一行的思想!!!!记牢for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {arr[i][j] = scan.nextInt();}}//动态规划,求到每个数字路径的最大值,然后赋值给这个数字for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {arr[i][j] = arr[i][j] + Math.max(arr[i-1][j-1],arr[i-1][j]);}}if(n%2==0){System.out.println(Math.max(arr[n][n/2+1],arr[n][n/2]));}if(n%2!=0){System.out.println(arr[n][n/2+1]);}scan.close();}
}
2.细节
1.上方和左方多一行的思想!方便操作 数字三角形
2.动态规划,从底向上记录值
3.关于向左向右步数不能相差1的理解:
说明最后在最后一层一定会落到中间
所以只需判断最后一层为奇数:中位数
偶数:中间两个取最大即可
8.成绩分析

1.代码
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);int n = scan.nextInt();int m[] = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int score = scan.nextInt();m[i] = score;}int max = m[0];int min = m[0];double sum = m[0];for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {if(m[i]>max){max = m[i];}if(m[i]<min){min = m[i];}sum += m[i];}double avg = sum / (double)n;
// avg = (Math.round(avg*100))/100.0;System.out.println(max);System.out.println(min);System.out.printf("%.2f",sum/n);scan.close();}
}
2.细节
1.转double可以使用*1.0的操作
2.小数点后几位四舍五入,使用c思想 System.out.printf(“%.2f”,sum/n);
9.购物单
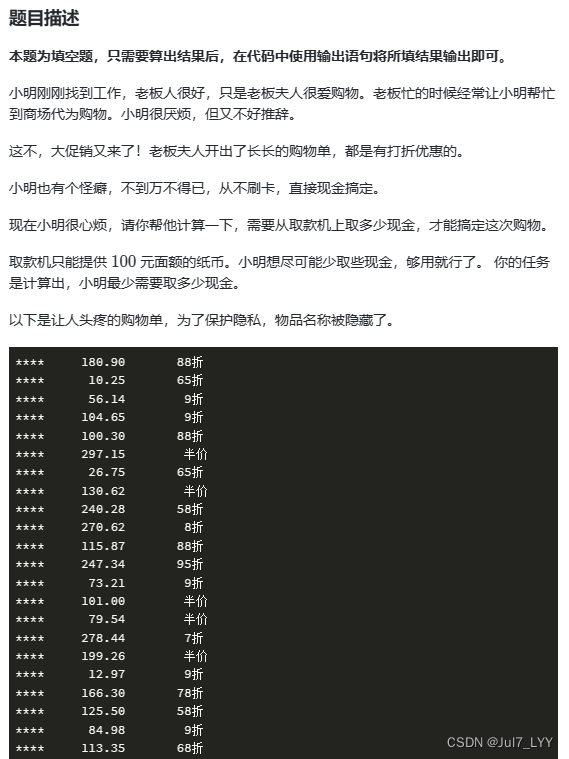
1.代码
public class Main{public static void main(String []args){int n = 50;Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);double sum = 0;while (n>0){String a = scan.next();double b = scan.nextDouble();String c = scan.next();sum += price(b,c);n--;}System.out.println((((int)sum + 100)/100*100));}public static double price(double b,String c){return b * zhekou(c);}public static double zhekou(String c){int p = 0;if(c.length()<=0){return 0;}if(c.length()==2){if(c.equals("半价")){p = 50;}else {String s = c.substring(0,1);p = Integer.parseInt(s);p *= 10;}}if(c.length() == 3){String s = c.substring(0,2);p = Integer.parseInt(s);}return p / 100.0;}scan.close;
}
2.细节
1.取整百的思想:System.out.println((((int)sum + 100)/100*100));
2.根据字符串的长度来分类
10.空间

1.代码
package lanqiao1_10;public class NeiCun_10 {
// 首先,将 256MB 转换为比特(bits),因为 32位整数占用 32 比特。
// 然后,将结果除以 32,以确定可以容纳多少个 32位整数。
// 256MB 等于 256 * 1024 * 1024 字节,因为 1MB 等于 1024KB,1KB 等于 1024字节。所以:
//
// 256MB = 256 * 1024 * 1024 字节 = 268435456 字节
//
// 接下来,将字节数转换为比特:
//
// 268435456 字节 * 8 比特/字节 = 2147483648 比特
//
// 现在,将这个结果除以 32位:
//
// 2147483648 比特 / 32 比特/整数 = 67108864 个整数
//
// 因此,256MB 可以存储 67108864 个 32位二进制整数。// MB --> 字节 --> bit 1字节 = 8bit
}2.细节
1.MB --> KB --> 字节 --> bit
1字节 = 8bit 32位就代表32个bit
2.整数溢出的问题
System.out.println(25610241024*8/32);//计算出来是负数,因为是大整数,使用L表示long类型
System.out.println(256L * 1024 * 1024 * 8 / 32);


docker:建立oracle数据库)


)









-亲测过)



