题目链接
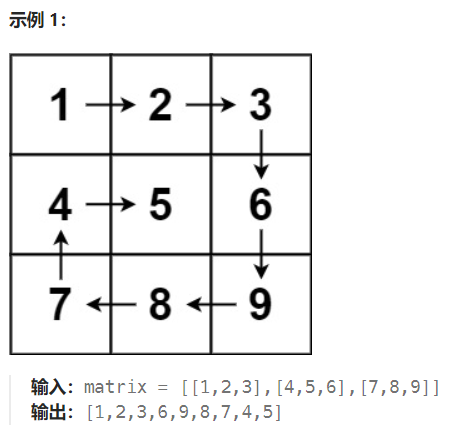
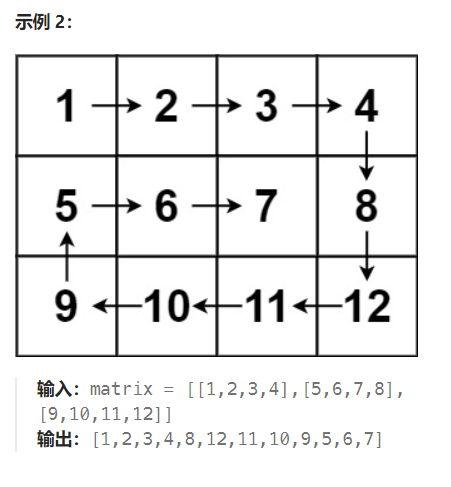

注意边界 和 方向变化
文章目录
Python3
方法一: 计算每个元素 下一个元素的下标 ⟮ O ( m n ) 、 O ( m n ) ⟯ \lgroup O(mn)、O(mn) \rgroup ⟮O(mn)、O(mn)⟯
模拟 螺旋矩阵 的路径。
初始位置是矩阵的左上角,初始方向是向右,当路径超出界限或者进入之前访问过的位置时,顺时针旋转,进入下一个方向。



class Solution:def spiralOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:rows, cols = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])visited = [[False] * cols for _ in range(rows)]ans = []directions = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]] # 和 螺旋矩阵 的行列变化一致directionsIndex = 0 ## 位于 整个 圈的 哪一侧, 0 1 2 3 顶 右 下 左i, j = 0, 0for _ in range(rows * cols): # 每个元素读一遍ans.append(matrix[i][j])visited[i][j] = TruenextRow, nextCol = i + directions[directionsIndex][0], j + directions[directionsIndex][1] # 计算 下一个 读取元素的位置,这显然与 方向有关系## 判断是否 需要换方向, 每读一个元素 都要判断一次,显然冗余if nextRow < 0 or nextRow >= rows or nextCol < 0 or nextCol >= cols or visited[nextRow][nextCol]: # 越界 或 读过 ——> 换方向 directionsIndex = (directionsIndex + 1) % 4 # 换方向i += directions[directionsIndex][0]j += directions[directionsIndex][1]return ans
方法二:按层模拟 ⟮ O ( m n ) 、 O ( 1 ) ⟯ \lgroup O(mn)、O(1) \rgroup ⟮O(mn)、O(1)⟯
将矩阵看成若干层,首先输出最外层的元素,其次输出次外层的元素,直到输出最内层的元素。

class Solution:def spiralOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:rows, cols = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])ans = []left, right, top, bottom = 0, cols-1, 0, rows-1while left <= right and top <= bottom:for col in range(left, right + 1): # 注意 这四个参数是下标 , range为左闭右开ans.append(matrix[top][col])for row in range(top+1,bottom+1): # 注意交界处,读过了直接跳过ans.append(matrix[row][right])if left < right and top < bottom: # 还有列 和 行for col in range(right - 1, left, -1):ans.append(matrix[bottom][col])for row in range(bottom, top, -1): # 注意不要重复,也不要遗漏ans.append(matrix[row][left])left, right, top, bottom = left + 1, right -1, top + 1, bottom -1return ansC++
方法一: 计算每个元素 下一个元素的下标
class Solution {
public:vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {int rows = matrix.size(), cols = matrix[0].size();vector<vector<bool>> visited(rows, vector<bool>(cols));int total = rows * cols;vector<int> ans(total);int i = 0, j = 0;int directions[4][2] = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};int directionsIndex = 0;for (int loop = 0; loop < total; ++loop){ans[loop] = matrix[i][j];visited[i][j] = true;int nextRow = i + directions[directionsIndex][0], nextCol = j + directions[directionsIndex][1];if (nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= rows || nextCol < 0 || nextCol >= cols || visited[nextRow][nextCol]) { //越界或 读过了——> 换方向directionsIndex = (directionsIndex + 1) % 4;}i += directions[directionsIndex][0];j += directions[directionsIndex][1];}return ans;}
};
方法二:按层模拟
class Solution {
public:vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {int rows = matrix.size(), cols = matrix[0].size();vector<int> ans;int left = 0, right = cols - 1, top = 0, bottom = rows - 1;while (left <= right && top <= bottom){for (int col = left; col <= right; ++col){ans.emplace_back(matrix[top][col]);}for (int row = top + 1; row <= bottom; ++row){ans.emplace_back(matrix[row][right]);}if (left < right && top < bottom){for (int col = right - 1; col > left; --col){ans.emplace_back(matrix[bottom][col]);}for (int row = bottom; row > top; --row){ans.emplace_back(matrix[row][left]);}}left ++; right --; top ++; bottom --;}return ans;}
};













)





