文件系统
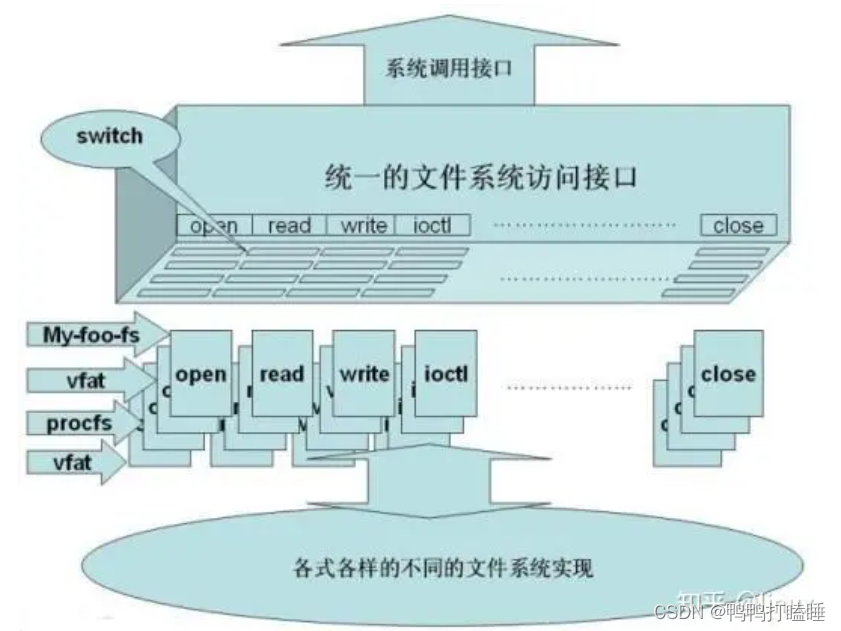
Linux将文件系统分为了两层:VFS(虚拟文件系统)、具体文件系统,如下图所示:
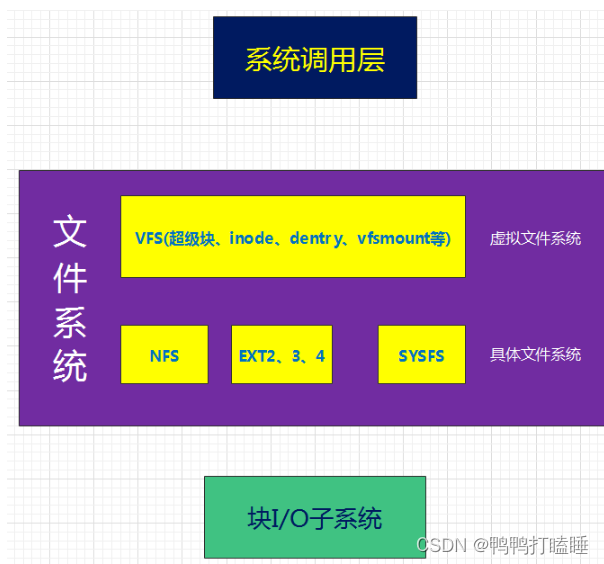
VFS(Virtual Filesystem Switch)称为虚拟文件系统或虚拟文件系统转换,是一个内核软件层,在具体的文件系统之上抽象的一层,用来处理与Posix文件系统相关的所有调用,表现为能够给各种文件系统提供一个通用的接口,使上层的应用程序能够使用通用的接口访问不同文件系统,同时也为不同文件系统的通信提供了媒介。
VFS并不是一种实际的文件系统,它只存在于内存中,不存在任何外存空间,VFS在系统启动时建立,在系统关闭时消亡。
Linux系统中存在很多的文件系统,例如常见的**ext2,ext3,ext4,sysfs,rootfs,proc...**等等。
从用户的使用角度,Linux下的文件系统中宏观上主要分为三层:
1.上层的文件系统的系统调用(System-call ,产生软中断);2.虚拟文件系统VFS(Virtual File System)层,3.挂载到VFS中的各种实际文件系统。
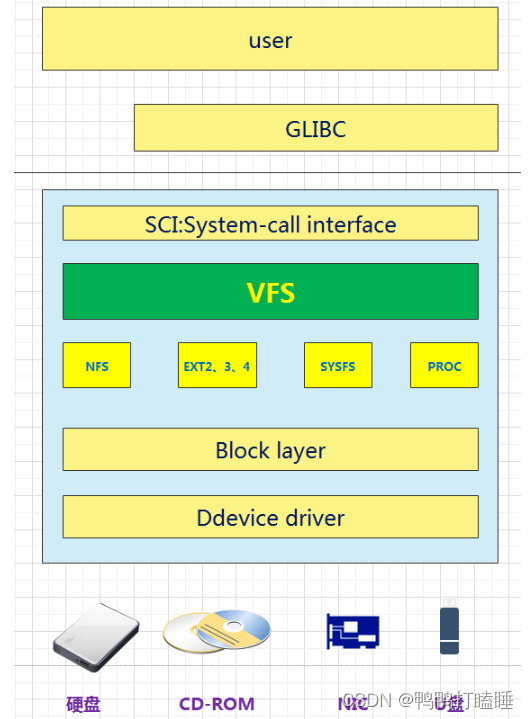
Linux系统的User使用GLIBC啥fopen等函数(POSIX标准、GUN C运行时库)作为应用程序的运行时库,然后通过操作系统,将其转换为系统调用SCI(system-call interface),SCI是操作系统内核定义的系统调用接口,这层抽象允许用户程序的I/O操作转换为内核的接口调用。此时触发0x80软中断进入内核态 再控制VFS进行后续的操作
2. 用户如何透明的去处理文件?
我们知道每个文件系统是独立的,有自己的组织方法,操作方法。那么对于用户来说,不可能所有的文件系统都了解,那么怎么做到让用户透明的去处理文件呢?
例如:我想写文件,那就直接read就OK,不管你是什么文件系统,具体怎么去读!这里就需要引入虚拟文件系统。
所以虚拟文件系统就是:对于一个system,可以存在多个“实际的文件系统”,例如:ext2,ext3,fat32,ntfs...例如我现在有多个分区,对于每一个分区我们知道可以是不同的“实际文件系统”。
例如现在三个磁盘分区分别是:ext2,ext3,fat32,那么每个“实际的文件系统”的操作和数据结构肯定不一样,那么,用户怎么能透明使它们呢?
这个时候就需要VFS作为中间一层!用户直接和VFS打交道。
VFS是一种软件机制,只存在于内存中,每次系统初始化期间Linux都会先在内存中构造一棵VFS的目录树(也就是源码中的namespace)。
VFS主要的作用是对上层应用屏蔽底层不同的调用方法,提供一套统一的调用接口,二是便于对不同的文件系统进行组织管理。
VFS提供了一个抽象层,将POSIX API接口与不同存储设备的具体接口实现进行了分离,使得底层的文件系统类型、设备类型对上层应用程序透明。
例如read,write,那么映射到VFS中就是sys_read,sys_write,那么VFS可以根据你操作的是哪个“实际文件系统”(哪个分区)来进行不同的实际的操作!这个技术也是很熟悉的“钩子结构”技术来处理的。
其实就是VFS中提供一个抽象的struct结构体,然后对于每一个具体的文件系统要把自己的字段和函数填充进去,这样就解决了异构问题(内核很多子系统都大量使用了这种机制)。
Linux虚拟文件系统7大对象
为了对文件系统进行统一的管理与组织,Linux创建了一个公共根目录和全局文件系统树。要访问一个文件系统中的文件,必须先将这个文件系统挂载在全局文件系统树的某个根目录下,这一挂载过程被称作文件系统的挂载,所挂载的目录称为挂载点。
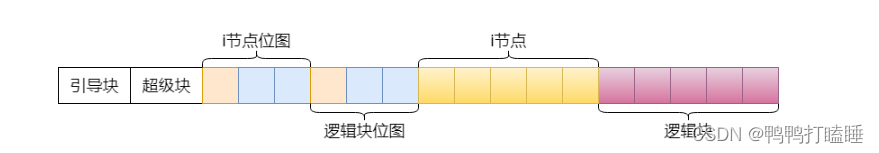
传统的文件系统在磁盘上的布局如下:
文件系统拿取磁盘数据详细分析: 上面这个图,和inode和文件和磁盘的对应关系
磁盘分成了一个个块,上面每个格子都是块,都有自己的块id,那我们的文件系统要读取哪一个块,直接放松对应的块id
就能拿到相应的数据内容
每一个块的大小是固定的,我们先假定为4kb,一个id的大小为64位,那大小就是8字节
如果所有文件大小都不超过4kb,那就能用磁盘块id作为文件名字
但目前情况每个文件大小不确定,需要多个块才能保存,所以就有了inode数据结构,记录了文件和多个块id的对应关系
一个块是4kb,颗粒度有些粗,不可能所有文件都是4kb的倍数给inode记录
所以在inode记录了这个文件对应磁盘的多个块和文件的大小(单位byte)和元数据
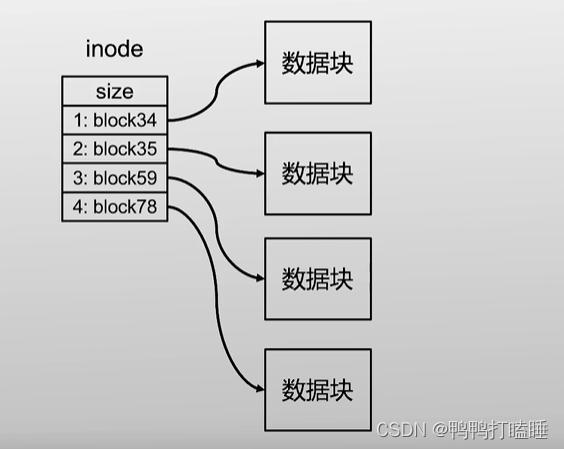
同时每个inode应该占多少块呢 inode不能太小,不然存的数据也小,也会限制到文件的大小
假设一个文件有4GB:这个文件就用了100万个块(一个块4kb,块id大小8字节),那存储id就8MB了
如果每个inode预留8MB,其实不划算
所以inode指向多级inode再指向数据块
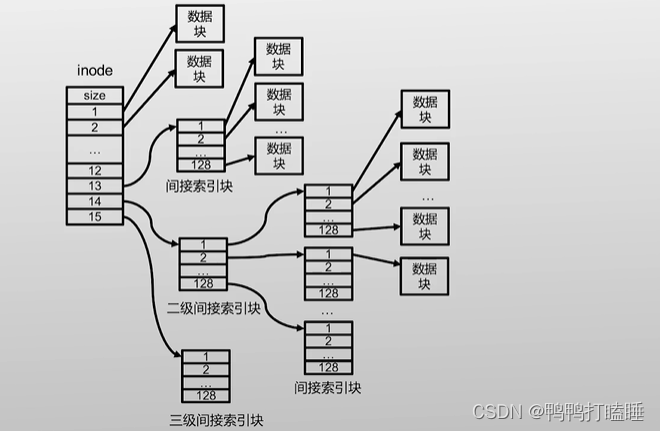
所有inode都放在一起,保存在磁盘头部的inode表,这个表就像一个大数组每一项都对应一个inode,每个inode都大小一样
这样每个inode都用数组对应的下表作为这个inode的名字:第一个inoded就是inode0,第二个inode就是inode1
这个索引也叫inode号(inode number)
所以看得出来 磁盘中inode号就能表示一个文件
在inode中增加另一个字段来表示这个是目录inode还是普通inode,
把inode号对应的字符串名字记录在它的上级目录中,就形成了目录树
tips:inode大小和块大小完全没关系,通常一个快里面放了多个inode
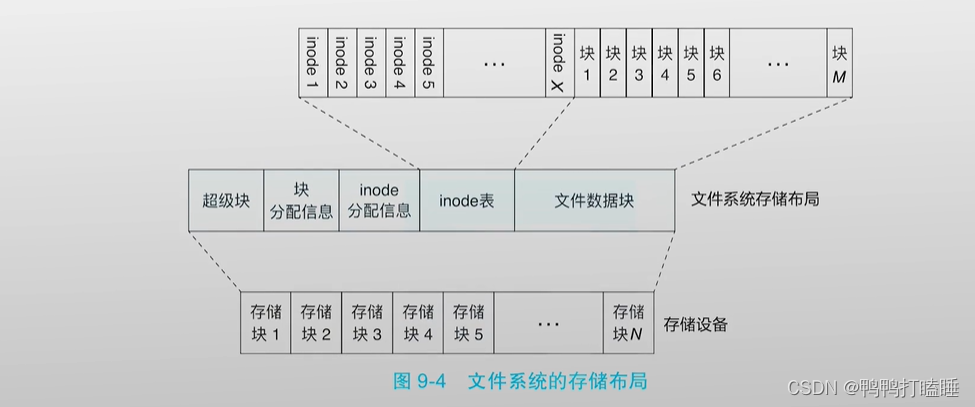
图片9-4和上面的布局一一对应,超级快后面的分配信息也叫节点位图,说明了哪个块没被使用,哪个inode没被使用仅此而已
小结一下:如果要找/bin/app_run这个文件时候
1.文件系统找到根目录的inode,通常在inode表的第一个
2.根据inode找到对应文件的块id
3.读取磁盘块id获得数据,找到 bin 字符串,通过字符串找到inode号 (这时候理解还在/目录)
4.根据bin的inode号,就能知道bin的目录inode在哪 (这时候理解进入bin目录)
5.同理根据bin的inode知道了bin的数据,分析字符串app_run的inode_Id在哪
6.获得了app_run的数据
上面得知了 文件名是存在它的父目录的 ,和自身的inode没有关系
继续介绍
由上图可知,文件系统的开头通常是由一个磁盘扇区所组成的引导块,该部分的主要目的是用于对操作系统的引导。一般只在启动操作系统时使用。
随后是超级块,超级块主要存放了该物理磁盘中文件系统结构的相关信息,并且对各个部分的大小进行说明,记录了后面四个区的位置。
操作系统mount磁盘的时候也是首先读取超级块来确定后面的位置
最后由i节点位图,逻辑块位图、i节点、逻辑块这几部分分布在物理磁盘上。
Linux为了对超级块,i节点,逻辑块这三部分进行高效的管理,Linux创建了几种不同的数据结构,分别是文件系统类型、inode、dentry等几种。
超级块则是反映了文件系统整体的控制信息。超级块能够以多种的方式存在,对于基于磁盘的文件系统,它以特定的格式存在于磁盘的固定区域(取决于文件系统类型)上。在挂载文件系统时,该超级块中的内容被读入磁盘中,从而构建出位于内存中的新的超级块。
inode则反映了文件系统对象中的一般元数据信息。
dentry则是反映出某个文件系统对象在全局文件系统树中的位置(没有磁盘实体只在内存中)。
linux怎么把不同的分区进行链接呢
我们在linux输入ls可以看见下面的各种目录结构
它其实是一棵目录树(没有画全):
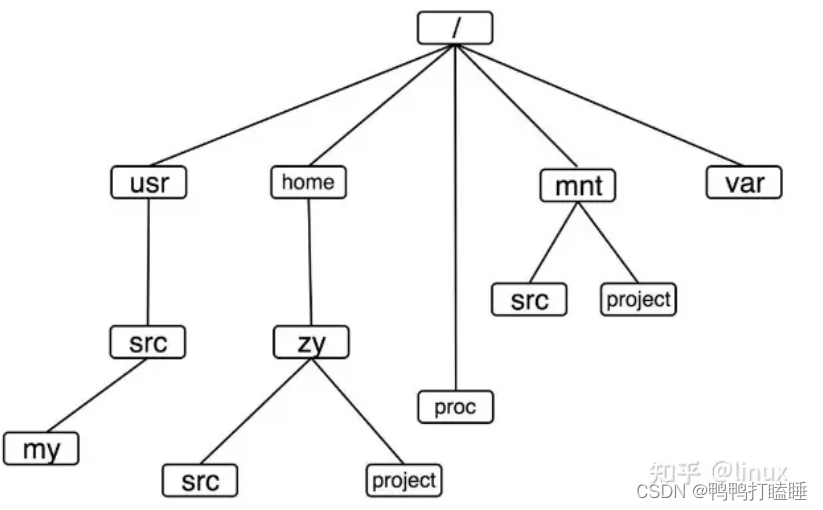
对于linux怎么把各种有不同文件系统的分区进行链接
现在只要记住两个重要链表:
1文件系统链表
2每一个文件系统的mount挂载点链表。
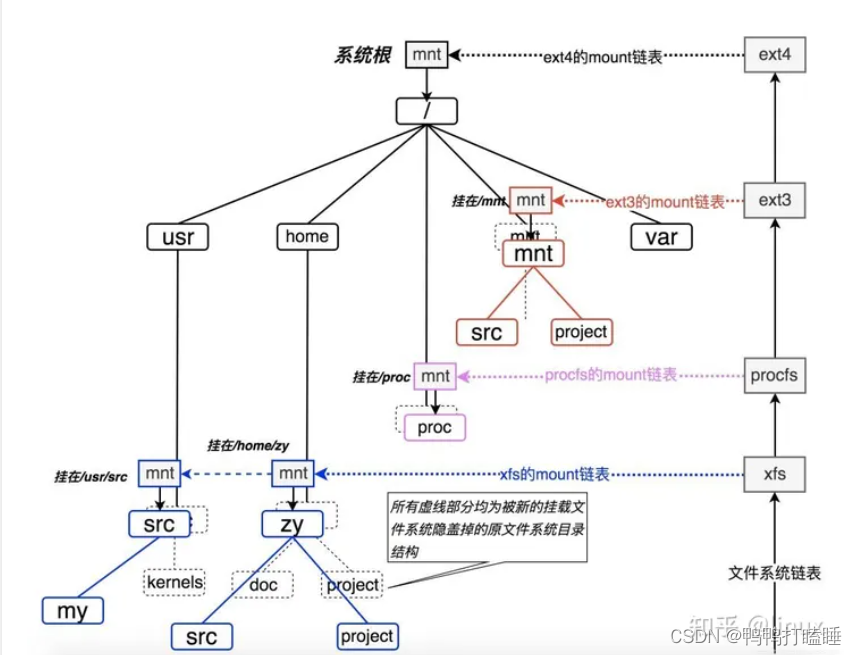
我们看到,Linux系统的文件目录树就是靠上图中的这一系列的链表穿针引线给串在一起的,就像缝制一件衣服一样,最终的成衣就是我们看到的Linux系统目录树,而缝制这件成衣的线以及指导走线的规则便是VFS本身了。
VFS之所有可以将机制大相径庭的完全不同的文件系统对外统一成一个样子,完全就是依靠了它的统一的对POSIX文件调用的接口,该接口的结构看上去是下面的样子:
结构体关系1. 超级块(super block)
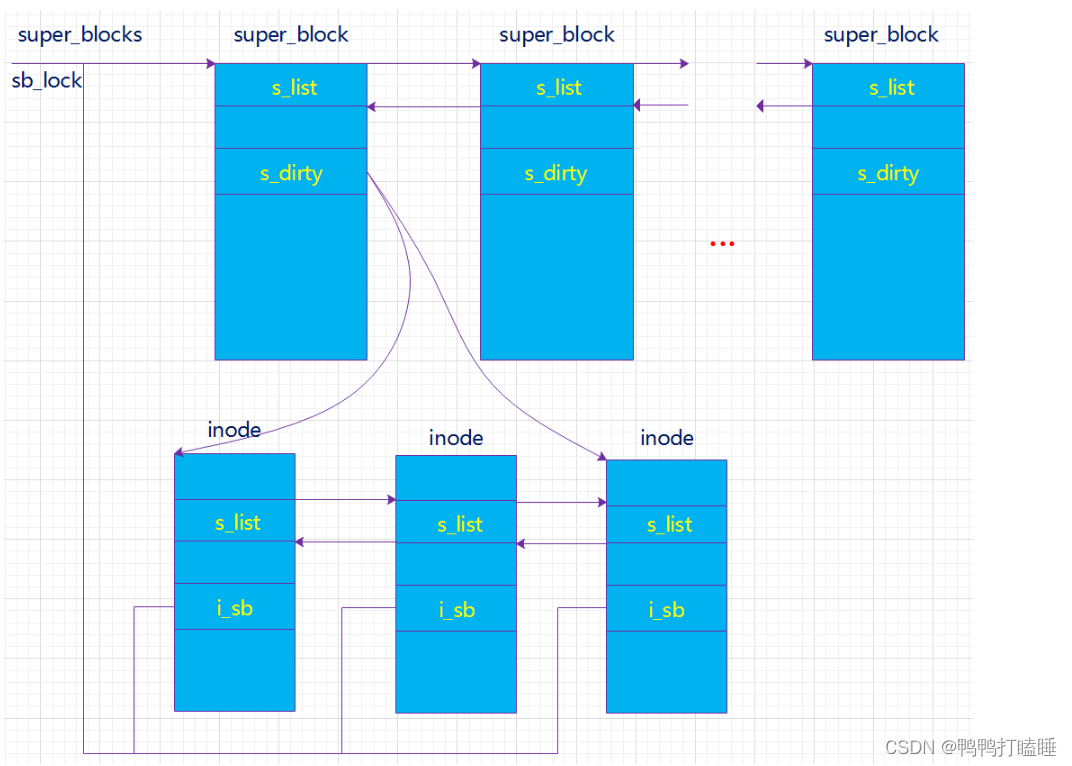
超级块:一个超级块对应一个文件系统(已经安装的文件系统类型如ext2,此处是实际的文件系统,不是VFS)。
之前我们已经说了文件系统用于管理这些文件的数据格式和操作之类的,系统文件有系统文件自己的文件系统,同时对于不同的磁盘分区也有可以是不同的文件系统。那么一个超级块对于一个独立的文件系统。保存文件系统的类型、大小、状态等等。
(“文件系统”和“文件系统类型”不一样!一个文件系统类型下可以包括很多文件系统即很多的super_block) 就是之前的图文件系统链表
既然我们知道对于不同的文件系统有不同的super_block,那么对于不同的super_block的操作肯定也是不同的,所以我们在下面的super_block结构中可以看到上面说的抽象的struct结构(例如下面的:struct super_operations):
(linux内核3.14)1246 struct super_block {
1247 struct list_head s_list;//指向超级块链表指针,把所有超级快链接
1248 dev_t s_dev; search index;//块设备的设备号等
1249 unsigned char s_blocksize_bits;
1250 unsigned long s_blocksize;
1251 loff_t s_maxbytes; Max file size
1252 struct file_system_type *s_type;//这个文件系统的文件类型(fat32,ext32)
1253 const struct super_operations *s_op;//指向具体的文件系统用于对超级块的函数操作集合
1254 const struct dquot_operations *dq_op;//某个特定的具体文件系统用于限额操作的函数集合
1255 const struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop;//于配置磁盘限额的的方法
1256 const struct export_operations *s_export_op;
1257 unsigned long s_flags;
1258 unsigned long s_magic;
1259 struct dentry *s_root;
1260 struct rw_semaphore s_umount;
1261 int s_count;
1262 atomic_t s_active;
1263 #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
1264 void *s_security;
1265 #endif
1266 const struct xattr_handler **s_xattr;
1267
1268 struct list_head s_inodes; all inodes
1269 struct hlist_bl_head s_anon; anonymous dentries for (nfs) exporting
1270 struct list_head s_mounts; list of mounts; _not_ for fs use1271 struct block_device *s_bdev;
1272 struct backing_dev_info *s_bdi;
1273 struct mtd_info *s_mtd;
1274 struct hlist_node s_instances;
1275 struct quota_info s_dquot; Diskquota specific options
1276
1277 struct sb_writers s_writers;
1278
1279 char s_id[32]; Informational name
1280 u8 s_uuid[16]; UUID
1281
1282 void *s_fs_info; Filesystem private info
1283 unsigned int s_max_links;
1284 fmode_t s_mode;
1285
1286 Granularity of c/m/atime in ns.
1287 Cannot be worse than a second
1288 u32 s_time_gran;
1289
1290
1291 * The next field is for VFS *only*. No filesystems have any business
1292 * even looking at it. You had been warned.
1293
1294 struct mutex s_vfs_rename_mutex; Kludge
1295
1296
1297 * Filesystem subtype. If non-empty the filesystem type field
1298 * in /proc/mounts will be "type.subtype"
1299
1300 char *s_subtype;
1301
1302
1303 * Saved mount options for lazy filesystems using
1304 * generic_show_options()
1305
1306 char __rcu *s_options;
1307 const struct dentry_operations *s_d_op; default d_op for dentries
1308
1309
1310 * Saved pool identifier for cleancache (-1 means none)
1311
1312 int cleancache_poolid;
1313
1314 struct shrinker s_shrink; per-sb shrinker handle
1315
1316 Number of inodes with nlink == 0 but still referenced
1317 atomic_long_t s_remove_count;
1318
1319 Being remounted read-only
1320 int s_readonly_remount;
1321
1322 AIO completions deferred from interrupt context
1323 struct workqueue_struct *s_dio_done_wq;
1324
1325
1326 * Keep the lru lists last in the structure so they always sit on their
1327 * own individual cachelines.
1328
1329 struct list_lru s_dentry_lru ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
1330 struct list_lru s_inode_lru ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
1331 struct rcu_head rcu;
1332 };
针对上面的操作超级块的函数操作集
struct super_operations {//该函数在给定的超级块下创建并初始化一个新的索引节点对象struct inode *(*alloc_inode)(struct super_block *sb);//释放指定的索引结点 。
void (*destroy_inode)(struct inode *);//VFS在索引节点被修改时会调用此函数。void (*dirty_inode) (struct inode *, int flags);// 将指定的inode写回磁盘。
int (*write_inode) (struct inode *, struct writeback_control *wbc);//删除索引节点。
int (*drop_inode) (struct inode *);void (*evict_inode) (struct inode *);//用来释放超级块
void (*put_super) (struct super_block *);//使文件系统的数据元素与磁盘上的文件系统同步,wait参数指定操作是否同步。
int (*sync_fs)(struct super_block *sb, int wait);
int (*freeze_fs) (struct super_block *);
int (*unfreeze_fs) (struct super_block *);//获取文件系统状态。把文件系统相关的统计信息放在statfs中
int (*statfs) (struct dentry *, struct kstatfs *);
int (*remount_fs) (struct super_block *, int *, char *);
void (*umount_begin) (struct super_block *);int (*show_options)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
int (*show_devname)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
int (*show_path)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
int (*show_stats)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
#ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA
ssize_t (*quota_read)(struct super_block *, int, char *, size_t, loff_t);
ssize_t (*quota_write)(struct super_block *, int, const char *, size_t, loff_t);
#endif
int (*bdev_try_to_free_page)(struct super_block*, struct page*, gfp_t);
long (*nr_cached_objects)(struct super_block *, int);
long (*free_cached_objects)(struct super_block *, long, int);
};
结构体关系2. 索引节点(inode)
索引节点inode:保存的其实是实际的数据的一些信息,这些信息称为“元数据”(也就是对文件属性的描述)
例如:文件大小,设备标识符,用户标识符,用户组标识符,文件模式,扩展属性,文件读取或修改的时间戳,链接数量,指向存储该内容的磁盘区块的指针,文件分类等等。
真实数据放在数据块里,可以通过索引节点找到数据块( 注意数据分成:元数据+数据本身 )
同时注意:inode有两种,一种是VFS的inode,一种是具体文件系统的inode。前者在内存中,后者在磁盘中。所以每次其实是将磁盘中的inode调进填充内存中的inode,这样才是算使用了磁盘文件inode。
inode怎样生成的?
每个inode节点的大小,一般是128字节或256字节。inode节点的总数,在格式化时就给定(现代OS可以动态变化),一般每2KB就设置一个inode。
一般文件系统中很少有文件小于2KB的,所以预定按照2KB分,一般inode是用不完的。所以inode在文件系统安装的时候会有一个默认数量,后期会根据实际的需要发生变化。
注意inode号:inode号是唯一的,表示不同的文件。其实在Linux内部的时候,访问文件都是通过inode号来进行的,所谓文件名仅仅是给用户容易使用的。
当我们打开一个文件的时候,首先,系统找到这个文件名对应的inode号;然后,通过inode号,得到inode信息,最后,由inode找到文件数据所在的block,现在可以处理文件数据了。
inode和文件的关系?
当创建一个文件的时候,就给文件分配了一个inode。一个inode只对应一个实际文件,一个文件也会只有一个inode。inodes最大数量就是文件的最大数量。
接下来看看inode的结构体
527 struct inode {
528 umode_t i_mode; 访问权限控制
529 unsigned short i_opflags;
530 kuid_t i_uid; 使用者的id
531 kgid_t i_gid; 使用组id
532 unsigned int i_flags; 文件系统标志
533
534 #ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACL
535 struct posix_acl *i_acl;
536 struct posix_acl *i_default_acl;
537 #endif
538
539 const struct inode_operations *i_op; 索引节点操作表
540 struct super_block *i_sb; 相关的超级块
541 struct address_space *i_mapping; 相关的地址映射
542
543 #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
544 void *i_security;
545 #endif
546
547 Stat data, not accessed from path walking
548 unsigned long i_ino; 索引节点号
549
550 * Filesystems may only read i_nlink directly. They shall use the
551 * following functions for modification:
552 *
553 * (set|clear|inc|drop)_nlink
554 * inode_(inc|dec)_link_count
555
556 union {
557 const unsigned int i_nlink;
558 unsigned int __i_nlink; 硬连接数
559 };
560 dev_t i_rdev; 实际设备标识符号
561 loff_t i_size;
562 struct timespec i_atime; 最后访问时间
563 struct timespec i_mtime; 最后修改时间
564 struct timespec i_ctime; 最后改变时间
565 spinlock_t i_lock; i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size
566 unsigned short i_bytes; 使用的字节数
567 unsigned int i_blkbits;
568 blkcnt_t i_blocks; 文件的块数
569
570 #ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDERED
571 seqcount_t i_size_seqcount;572 #endif
573
574 Misc
575 unsigned long i_state;
576 struct mutex i_mutex;
577
578 unsigned long dirtied_when; jiffies of first dirtying 首次修改时间
579
580 struct hlist_node i_hash; hash值,提高查找效率
581 struct list_head i_wb_list; backing dev IO list
582 struct list_head i_lru; inode LRU list 未使用的inode
583 struct list_head i_sb_list; 链接一个文件系统中所有inode的链表
584 union {
585 struct hlist_head i_dentry; 目录项链表
586 struct rcu_head i_rcu;
587 };
588 u64 i_version;
589 atomic_t i_count; 引用计数
590 atomic_t i_dio_count;
591 atomic_t i_writecount; 写者计数
592 const struct file_operations *i_fop; former ->i_op->default_file_ops 文件操作
593 struct file_lock *i_flock; 文件锁链表
594 struct address_space i_data; 表示被inode读写的页面
595 #ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA
596 struct dquot *i_dquot[MAXQUOTAS]; 节点的磁盘限额
597 #endif
598 struct list_head i_devices; 设备链表(共用同一个驱动程序的设备形成的链表。)
599 union {
600 struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe; 管道信息
601 struct block_device *i_bdev; 块设备驱动节点
602 struct cdev *i_cdev; 字符设备驱动节点
603 };
604
605 __u32 i_generation; 索引节点版本号
606
607 #ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
608 __u32 i_fsnotify_mask; all events this inode cares about
609 struct hlist_head i_fsnotify_marks;
610 #endif
611
612 #ifdef CONFIG_IMA
613 atomic_t i_readcount; struct files open RO
614 #endif
615 void *i_private; fs or device private pointer 用户私有数据
616 };
对inode操作的函数操作集
目前感觉是看后面的图 这些结构体的关系
进程先通过 file_struct结构体找 在进程的哪个fd[]中,找到对应file结构体
再找到dentry结构体再找到inode结构体,调用里面的i_fop的函数,触发系统调用的80软中断
最后碰到了内核态和VFS
节点方法struct inode_operations {//lookup()查找指定文件的dentry
struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, unsigned int);
void * (*follow_link) (struct dentry *, struct nameidata *);
int (*permission) (struct inode *, int);
struct posix_acl * (*get_acl)(struct inode *, int);int (*readlink) (struct dentry *, char __user *,int);
void (*put_link) (struct dentry *, struct nameidata *, void *);int (*create) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, umode_t, bool);//create()如果该inode描述一个目录文件,那么当在该目录下创建或打开一个文件时,内核必须为这个文件创建一个inode。//VFS通过调用该inode的i_op->create()函数来完成上述新inode的创建。// 该函数的第一个参数为该目录的 inode,第二个参数为要打开新文件的dentry,//第三个参数是对该文件的访问权限。如果该inode描述的是一个普通文件,那么该inode永远都不会调用这个create函数
int (*link) (struct dentry *,struct inode *,struct dentry *);//link()用于在指定目录下创建一个硬链接。这个link函数最终会被系统调用link()调用。//该函数的第一个参数是原始文件的dentry,第二个参数即为上述指定目录的inode,第三个参数是链接文件的dentry。
int (*unlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);
int (*symlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,const char *);//symlink ()在某个目录下新建mkdir()在指定的目录下创建一个子目录,当前目录的inode会调用i_op->mkdir()。该函数会被系统调用mkdir()调用。//第一个参数即为指定目录的inode,第二个参数为子目录的dentry,第三个参数为子目录权限;
int (*mkdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,umode_t);//mknod()在指定的目录下创建一个特殊文件,比如管道、设备文件或套接字等。
int (*rmdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);//rmdir ()从inode所描述的目录中删除一个指定的子目录时,该函数会被系统调用rmdir()最终调用
int (*mknod) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,umode_t,dev_t);
int (*rename) (struct inode *, struct dentry *,struct inode *, struct dentry *);
int (*rename2) (struct inode *, struct dentry *,struct inode *, struct dentry *, unsigned int);
int (*setattr) (struct dentry *, struct iattr *);
int (*getattr) (struct vfsmount *mnt, struct dentry *, struct kstat *);
int (*setxattr) (struct dentry *, const char *,const void *,size_t,int);
ssize_t (*getxattr) (struct dentry *, const char *, void *, size_t);
ssize_t (*listxattr) (struct dentry *, char *, size_t);
int (*removexattr) (struct dentry *, const char *);
int (*fiemap)(struct inode *, struct fiemap_extent_info *, u64 start,u64 len);
int (*update_time)(struct inode *, struct timespec *, int);
int (*atomic_open)(struct inode *, struct dentry *,struct file *, unsigned open_flag,umode_t create_mode, int *opened);
int (*tmpfile) (struct inode *, struct dentry *, umode_t);
int (*set_acl)(struct inode *, struct posix_acl *, int);
} ____cacheline_aligned;
结构体关系3.目录项(dentry)
目录项是描述文件的逻辑属性,只存在于内存中,并没有实际对应的磁盘上的描述,更确切的说是存在于内存的目录项缓存,为了提高查找性能而设计。
注意不管是文件夹还是最终的文件,都是属于目录项,所有的目录项在一起构成一颗庞大的目录树。
例如:open一个文件/home/xxx/yyy.txt,那么/、home、xxx、yyy.txt都是一个目录项,VFS在查找的时候,根据一层一层的目录项找到对应的每个目录项的inode,那么沿着目录项进行操作就可以找到最终的文件。
注意:目录也是一种文件(所以也存在对应的inode)。打开目录,实际上就是打开目录文件。
108 struct dentry {
109 RCU lookup touched fields
110 unsigned int d_flags; protected by d_lock
111 seqcount_t d_seq; per dentry seqlock
112 struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; lookup hash list
113 struct dentry *d_parent; parent directory 父目录
114 struct qstr d_name;
115 struct inode *d_inode; Where the name belongs to - NULL is
116 * negative 与该目录项关联的inode
117 unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN]; small names 短文件名
118
119 Ref lookup also touches following
120 struct lockref d_lockref; per-dentry lock and refcount
121 const struct dentry_operations *d_op; 目录项操作
122 struct super_block *d_sb; The root of the dentry tree 这个目录项所属的文件系统的超级块(目录项树的根)
123 unsigned long d_time; used by d_revalidate 重新生效时间
124 void *d_fsdata; fs-specific data 具体文件系统的数据
125
126 struct list_head d_lru; LRU list 未使用目录以LRU 算法链接的链表
127
128 * d_child and d_rcu can share memory
129
130 union {
131 struct list_head d_child; child of parent list 目录项通过这个加入到父目录的d_subdirs中
132 struct rcu_head d_rcu;
133 } d_u;
134 struct list_head d_subdirs; our children 本目录的所有孩子目录链表头
135 struct hlist_node d_alias; inode alias list 索引节点别名链表
136 };
一个有效的dentry结构必定有一个inode结构,这是因为一个目录项要么代表着一个文件,要么代表着一个目录,而目录实际上也是文件。
所以,只要dentry结构是有效的,则其指针d_inode必定指向一个inode结构。但是inode却可以对应多个。
整个结构其实就是一棵树,目录其实就是文件(kobject、inode)再加上一层封装,这里所谓的封装主要就是增加两个指针,一个是指向父目录,一个是指向该目录所包含的所有文件(普通文件和目录)的链表头。
这样才能有我们的目录操作(比如回到上次目录,只需要一个指针步骤【…】,而进入子目录需要链表索引需要多个步骤)
下面的dentry相关的操作函数集(inode里面已经包含了mkdir,rmdir,mknod之类的操作了)
struct dentry_operations {该函数判断目录对象是否有效。VFS准备从dcache中使用一个目录项时,会调用该函数.
int (*d_revalidate)(struct dentry *, unsigned int);
int (*d_weak_revalidate)(struct dentry *, unsigned int);该目录生成散列值,当目录项要加入到散列表时,VFS要调用此函数。
int (*d_hash)(const struct dentry *, struct qstr *); 该函数来比较name1和name2这两个文件名。使用该函数要加dcache_lock锁。
int (*d_compare)(const struct dentry *, const struct dentry *,unsigned int, const char *, const struct qstr *);当d_count=0时,VFS调用次函数。使用该函数要叫 dcache_lock锁。
int (*d_delete)(const struct dentry *);当该目录对象将要被释放时,VFS调用该函数。
void (*d_release)(struct dentry *);
void (*d_prune)(struct dentry *);当一个目录项丢失了其索引节点时,VFS就掉用该函数。
void (*d_iput)(struct dentry *, struct inode *);
char *(*d_dname)(struct dentry *, char *, int);
struct vfsmount *(*d_automount)(struct path *);
int (*d_manage)(struct dentry *, bool);
} ____cacheline_aligned;
结构体关系4.文件对象(file)
文件对象描述的是进程已经打开的文件。因为一个文件可以被多个进程打开,所以一个文件可以存在多个文件对象。但是由于文件是唯一的,那么inode就是唯一的,目录项也是定的!
进程其实是通过文件描述符来操作文件的,每个文件都有一个32位的数字来表示下一个读写的字节位置,这个数字叫做文件位置。
一般情况下打开文件后,打开位置都是从0开始,除非一些特殊情况。Linux用file结构体来保存打开的文件的位置,所以file称为打开的文件描述。file结构形成一个双链表,称为系统打开文件表。
结构体:file
775 struct file {
776 union {
777 struct llist_node fu_llist; 每个文件系统中被打开的文件都会形成一个双链表
778 struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead;
779 } f_u;
780 struct path f_path;
781 #define f_dentry f_path.dentry
782 struct inode *f_inode; cached value
783 const struct file_operations *f_op; 指向文件操作表的指针
784
785
786 * Protects f_ep_links, f_flags.
787 * Must not be taken from IRQ context.
788
789 spinlock_t f_lock;
790 atomic_long_t f_count; 文件对象的使用计数
791 unsigned int f_flags; 打开文件时所指定的标志
792 fmode_t f_mode; 文件的访问模式(权限等)
793 struct mutex f_pos_lock;
794 loff_t f_pos; 文件当前的位移量
795 struct fown_struct f_owner;
796 const struct cred *f_cred;
797 struct file_ra_state f_ra; 预读状态
798
799 u64 f_version; 版本号
800 #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
801 void *f_security; 安全模块
802 #endif
803 needed for tty driver, and maybe others
804 void *private_data; 私有数据
805
806 #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
807 Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file
808 struct list_head f_ep_links;
809 struct list_head f_tfile_llink;
810 #endif #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
811 struct address_space *f_mapping; 页缓存映射
812 #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_WRITECOUNT
813 unsigned long f_mnt_write_state;
814 #endif
815 } __attribute__((aligned(4))); lest something weird decides that 2 is OK
重点解释一些重要字段:
首先,f_flags、f_mode和f_pos代表的是这个进程当前操作这个文件的控制信息。
这个非常重要,因为对于一个文件,可以被多个进程同时打开,那么对于每个进程来说,操作这个文件是异步的,所以这个三个字段就很重要了。
对于引用计数f_count,当我们关闭一个进程的某一个文件描述符时候,其实并不是真正的关闭文件,仅仅是将f_count减一,当f_count=0时候,才会真的去关闭它。
对于dup,fork这些操作来说,都会使得f_count增加,具体的细节,以后再说。f_op也是很重要的!是涉及到所有的文件的操作结构体。例如:用户使用read,最终都会调用file_operations中的读操作,而file_operations结构体是对于不同的文件系统不一定相同。里面一个重要的操作函数式release函数,当用户执行close时候,其实在内核中是执行release函数,这个函数仅仅将f_count减一,这也就解释了上面说的,用户close一个文件其实是将f_count减一。只有引用计数减到0才关闭文件。
注意:对于“正在使用”和“未使用”的文件对象分别使用一个双向链表进行管理。
另一个结构体 files_struct
上面的file只是对一个文件而言,对于一个进程(用户)来说,可以同时处理多个文件,所以需要另一个结构来管理所有的files!
即:用户打开文件表--->files_struct
172 struct files_struct {
173 atomic_t count;
174 rwlock_t file_lock; Protects all the below members. Nests inside tsk->alloc_lock
175 int max_fds;
176 int max_fdset;
177 int next_fd;
178 struct file ** fd; current fd array
179 fd_set *close_on_exec;
180 fd_set *open_fds;
181 fd_set close_on_exec_init;
182 fd_set open_fds_init;
183 struct file * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT];
184 };
解释一些字段:
字段描述count引用计数file_lock锁,保护下面的字段max_fds当前文件对象的最大的数量max_fdset文件描述符最大数next_fd已分配的最大的文件描述符+1fd指向文件对象指针数组的指针,一般就是指向最后一个字段fd_arrray,当文件数超过NR_OPEN_DEFAULT时候,就会重新分配一个数组,然后指向这个新的数组指针!close_on_exec执行exec()时候需要关闭的文件描述符open_fds指向打开的文件描述符的指针close_on_exec_init执行exec()时候需要关闭的文件描述符初始化值open_fds_init文件描述符初值集合fd_array文件对象指针的初始化数组fs_struct
那同时因为打开了文件 也会有对应的操作函数file_operations
file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);
ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);
ssize_t (*read_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
ssize_t (*write_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
int (*iterate) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*fsync) (struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int datasync);
int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync);
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int);
int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int);
unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);
int (*check_flags)(int);
int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int);
int (*setlease)(struct file *, long, struct file_lock **);
long (*fallocate)(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset,loff_t len);
int (*show_fdinfo)(struct seq_file *m, struct file *f);
};
应该是用户空间的调用总结:
每个进程都有自己的namespace。
fs_struct用于表示进程与文件系统之间的结构关系,比如当前的工作目录,进程的根目录等等。
files_struct 用于表示当前进程打开的文件。
而对于每一个打开的文件,由file对象来表示。
Linux中,常常用文件描述符(file descriptor)来表示一个打开的文件,这个描述符的值往往是一个大于或等于0的整数。而这个整数,其实就是在files_struct中file数组fd的下标。对于所有打开的文件, 这些文件描述符会存储在open_fds的位图中。
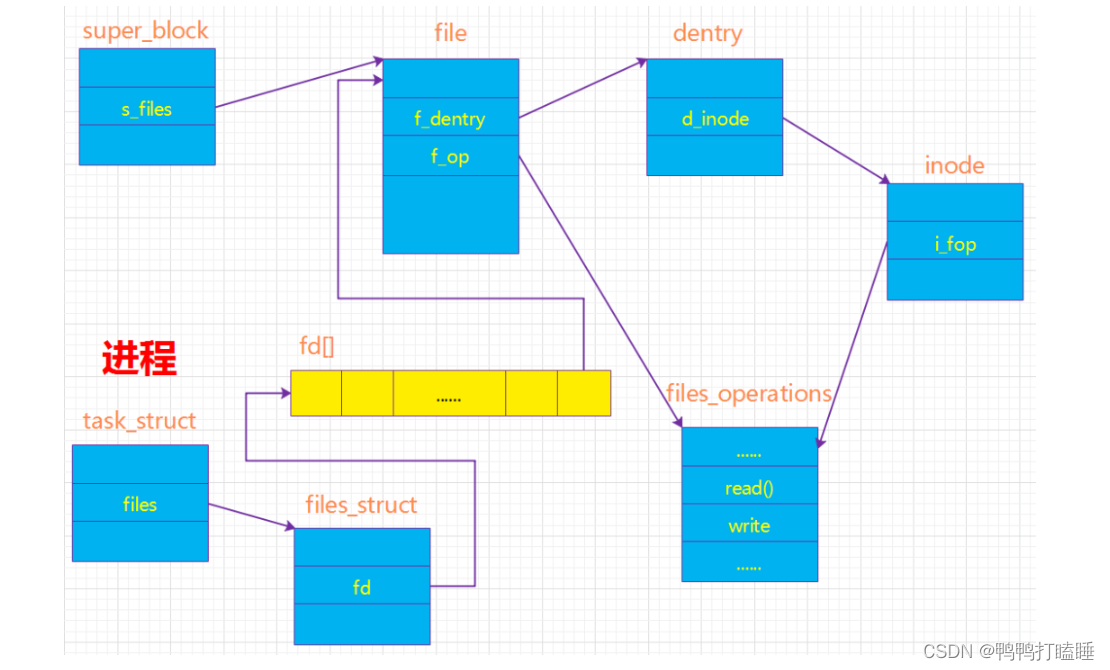
从图中可知:进程通过task_struct中的一个域files->files_struct 来了解它当前所打开的文件对象;而我们通常所说的文件描述符其实是进程打开的文件对象数组的索引值。文件对象通过域f_dentry找到它对应的dentry对象,再由dentry对象的域d_inode找到它对应的索引节点(通过索引节点又可以得到超级块的信息,也就可以得到最终操作文件的方法,在open文件的时候就是使用这样一个过程),这样就建立了文件对象与实际的物理文件的关联。文件对象所对应的文件操作函数列表是通过索引节点的域i_fop得到的,而i_fop最终又是通过struct super_operations *s_op来初始化的。
VFS文件系统中的inode和dentry与实际文件系统的inode和dentry有一定的关系,但不能等同。
真实磁盘文件的inode是存在于物理外存上的,但VFS中的inode和dentry是存在于内存中的,系统读取外存中的inode信息进行一定加工后,生成内存中的inode和dentry。
虚拟的文件系统也具有inode和dentry结构,只是这是系统根据相应的规则生成的,不存在于实际外存中。
用户空间和内核空间和系统调用和泽呢么知道这个文件的file_operation
http://wed.xjx100.cn/news/162453.html?action=onClick 目前还在看这个文章
https://blog.csdn.net/marlos/article/details/130234691
上面这个文章是vfs文件系统,怎么被应用open调用再调用到不同的文件系统的
估计还要从之前 迅维的文档看看驱动创建的时候 有个file_opeartion是不是能关联起来
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45172832/article/details/129242285
https://blog.csdn.net/wenfengliaoshuzhai/article/details/131776900
上面两个文章都是说驱动文件的open怎么和应用程序的open对应起来
https://blog.csdn.net/uunubt/article/details/127278292
上面是主要参考的文章
分手了时间真多





——从数据资产谈起 MySQL的DOS命令、常用数据类型、SQL语句的分类 SQL函数)

)








)


