基础知识
- Linux 内核当中有 3 种调度策略:
- SCHED_OTHER 分时调度策略;
- SCHED_FIFO 实时调度策略,先到先服务;
- SCHED_RR 实时调度策略,时间片轮转。
如果有相同优先级的实时进程(根据优先级计算的调度权值是一样的)已经准备好,FIFO 时必须等待该进程主动放弃之后才可以运行这个优先级相同的任务。而 RR 可以每个任务都执行一段时间。
- 获取线程设置的最高和最低优先级函数
int sched_get_priority_max(int policy)获取实时优先级的最大值;int sched_get_priority_min(int policy)获取实时优先级的最小值;
SCHED_OTHER它 不 支 持 优 先 级 使 用 , 而SCHED_RR/SCHED_FIFO 支持优先级使用,它们分别为 1-99,数值越大优先级越高。
实时调度策略(SCHED_FIFO/SCHED_RR)优先级最大值为99;普通调度策略
(SCHED_NORMAL/SCHED_BATCH/SCHED_IDLE),始终返回0,即普通任务调度的函数。
-
设置和获取优先级的2个主要核心参数
int pthread_attr_setschedparam(pthread_attr_t* attr, const struct sched_param* param);设置线程优先级;int pthread_attr_getschedparam(pthread_attr_t* attr, const struct sched_param* param);获取线程优先级;
struct sched_param {int __sched_priority; // 所有设定的线程优先级 }param.sched_priority = 11; // 设置优先级 -
当操作系统创建线程时,默认线程是 SCHED_OTHER,我们也可以通过改变调度策略,使用如下函数:
int pthread_attr_setschedpolicy(pthread_attr_t* attr, int policy);设置线程调度策略;
基础案例分析
- 操作系统所支持优先级测试程序分析:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <assert.h>static int GetThreadPolicyFunc(pthread_attr_t *pAttr)
{int iPlicy;int igp=pthread_attr_getschedpolicy(pAttr,&iPlicy);assert(igp==0);switch (iPlicy){case SCHED_FIFO:printf("Policy is --> SCHED_FIFO.\n");break;case SCHED_RR:printf("Policy is --> SCHED_RR.\n");break;case SCHED_OTHER:printf("Policy is --> SCHED_OTHER.\n");break;default:printf("Policy is --> Unknown.\n");break;}return iPlicy;
}static void PrintThreadPriorityFunc(pthread_attr_t *pAttr,int iPolicy)
{int iPriority=sched_get_priority_max(iPolicy); assert(iPriority!=-1);printf("Max_priority is : %d\n",iPriority);iPriority=sched_get_priority_min(iPolicy); assert(iPriority!=-1);printf("Min_priority is : %d\n",iPriority);
}static int GetThreadPriorityFunc(pthread_attr_t *pAttr)
{struct sched_param sParam;int irs=pthread_attr_getschedparam(pAttr,&sParam);assert(irs==0);printf("Priority=%d\n",sParam.__sched_priority);return sParam.__sched_priority;
}static void SetThreadPolicyFunc(pthread_attr_t *pAttr,int iPolicy)
{int irs=pthread_attr_setschedpolicy(pAttr,iPolicy);assert(irs==0);GetThreadPolicyFunc(pAttr);
}int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{pthread_attr_t pAttr;struct sched_param sched;int irs=pthread_attr_init(&pAttr);assert(irs==0);int iPlicy=GetThreadPolicyFunc(&pAttr);printf("\nExport current Configuration of priority.\n");PrintThreadPriorityFunc(&pAttr,iPlicy);printf("\nExport SCHED_FIFO of prioirty.\n");PrintThreadPriorityFunc(&pAttr,SCHED_FIFO);printf("\nExport SCHED_RR of prioirty.\n");PrintThreadPriorityFunc(&pAttr,SCHED_RR);printf("\nExport priority of current thread.\n");int iPriority=GetThreadPriorityFunc(&pAttr);printf("Set thread policy.\n");printf("\nSet SCHED_FIFO policy.\n");SetThreadPolicyFunc(&pAttr,SCHED_FIFO);printf("\nSet SCHED_RR policy.\n");SetThreadPolicyFunc(&pAttr,SCHED_RR);printf("\nRestore current policy.\n");SetThreadPolicyFunc(&pAttr,iPlicy);irs=pthread_attr_destroy(&pAttr);assert(irs==0);return 0;
}

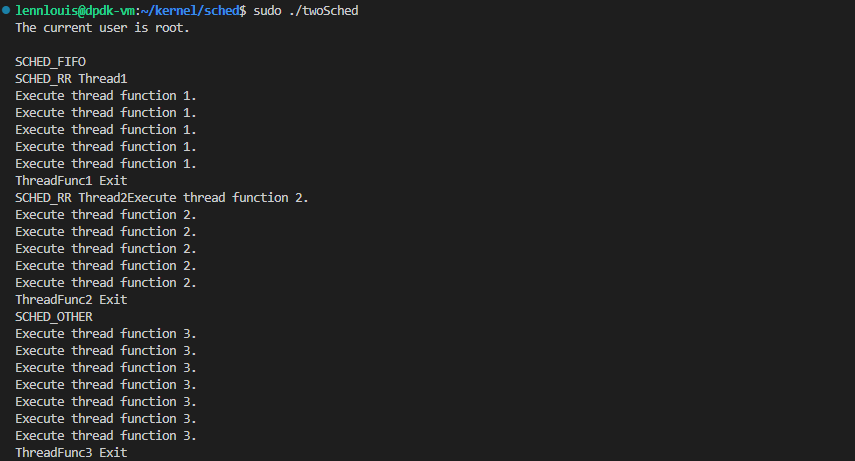
- 简单线程调度策略,我们创建三个线程,默认创建的线程它的调度策略为SCHED_OTHER,另外两个线程调度策略为 SCHED_RR/FIFO:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>void ThreadFunc1() {sleep(1);int i, j;int policy;struct sched_param param;pthread_getschedparam(pthread_self(), &policy, ¶m);switch (policy) {case SCHED_OTHER:printf("SCHED_OTHER\n");break;case SCHED_FIFO:printf("SCHED_FIFO\n");case SCHED_RR:printf("SCHED_RR Thread1\n");default:break;}for(i = 1; i <= 5; i++){for(j = 1; j <= 5000000; j++){}printf("Execute thread function 1.\n");}printf("ThreadFunc1 Exit\n");
}void ThreadFunc2() {sleep(2);int policy;struct sched_param param;pthread_getschedparam(pthread_self(), &policy, ¶m);switch(policy) {case SCHED_OTHER:printf("SCHED_OTHER\n");break;case SCHED_FIFO:printf("SCHED_FIFO\n");break;case SCHED_RR:printf("SCHED_RR Thread2");break;}for(int i = 1; i <= 6; i++){for(int j = 1; j <= 6000000; j++){}printf("Execute thread function 2.\n");}printf("ThreadFunc2 Exit\n");
}void ThreadFunc3() {sleep(3);int policy;struct sched_param param;pthread_getschedparam(pthread_self(), &policy, ¶m);switch(policy) {case SCHED_OTHER:printf("SCHED_OTHER\n");break;case SCHED_FIFO:printf("SCHED_FIFO\n");break;case SCHED_RR:printf("SCHED_RR\n");break;}for(int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) {for(int j = 0; j <= 7000000; j++){}printf("Execute thread function 3.\n");}printf("ThreadFunc3 Exit\n");
}int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {int i = 0;i = getuid();if(i == 0) {printf("The current user is root.\n\n");}else {printf("The current user is not root.\n\n");}pthread_t pid1, pid2, pid3;struct sched_param param;pthread_attr_t attr1, attr2, attr3;pthread_attr_init(&attr1);pthread_attr_init(&attr2);pthread_attr_init(&attr3);param.sched_priority = 31;pthread_attr_setschedpolicy(&attr2, SCHED_RR);pthread_attr_setschedparam(&attr2, ¶m);pthread_attr_setinheritsched(&attr2, PTHREAD_EXPLICIT_SCHED);param.sched_priority = 11;pthread_attr_setschedpolicy(&attr1, SCHED_FIFO);pthread_attr_setschedparam(&attr1, ¶m);pthread_attr_setinheritsched(&attr1, PTHREAD_EXPLICIT_SCHED);pthread_create(&pid3, &attr3, (void*)ThreadFunc3, NULL);pthread_create(&pid2, &attr2, (void*)ThreadFunc2, NULL);pthread_create(&pid1, &attr1, (void*)ThreadFunc1, NULL);pthread_join(pid3, NULL);pthread_join(pid2, NULL);pthread_join(pid1, NULL);pthread_attr_destroy(&attr3);pthread_attr_destroy(&attr2);pthread_attr_destroy(&attr1);return 0;
}
- 超级用户运行








)


代码实践 -计算机视觉-37微调)
五千字好文)






![[保姆级教程]uniapp自定义导航栏](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[保姆级教程]uniapp自定义导航栏)