目录
赋值运算符重载
运算符重载
赋值运算符重载
前置++和后置++重载
日期类的实现(前置后置++也在里面)
const 成员
编辑 取地址及const取地址操作符重载
赋值运算符重载
运算符重载
C++为了增强代码的可读性引入了运算符重载,运算符重载是具有特殊函数名的函数,也具有其
返回值类型,函数名字以及参数列表,其返回值类型与参数列表与普通的函数类似。
函数名字为:关键字operator后面接需要重载的运算符符号。
函数原型:返回值类型 operator操作符(参数列表)
需要注意的是:
- 不能通过连接其他符号来创建新的操作符:比如operator@
- 重载操作符必须有一个类类型参数
- 用于内置类型的运算符,其含义不能改变,例如:内置的整型+,不 能改变其含义
- 作为类成员函数重载时,其形参看起来比操作数数目少1,因为成员函数的第一个参数为隐
- 藏的this
- .* :: sizeof ?: . 注意以上5个运算符不能重载。
d1 - d2计算两个日期之间相差的天数有意义
d1+d2两个日期相加没有意义
d1*d2日期相乘没有意义
所以我们知道了一个类重载哪些运算符是看需求的,看重载有没有意义。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){static int arr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0){return 29;}return arr[month];}Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}//private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};bool operator==(const Date& d1 , const Date& d2)
{if (d1._year == d2._year){if (d1._month == d2._month){if (d1._day == d2._day){return true;}}}return false;
}int main()
{Date d1(2024, 4, 15);Date d2 = d1;Date d3;//显式调用operator==(d1, d2);//直接写,转换调用,编译器会转换operator==(d1, d2);d1 == d2;return 0;
}但是我们能看到这样写是不够好的 重载成全局函数无法访问私有成员 因此就可以重载为成员函数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){static int arr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0){return 29;}return arr[month];}Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}bool operator==(const Date& d1 , const Date& d2){if (d1._year == d2._year){if (d1._month == d2._month){if (d1._day == d2._day){return true;}}}return false;}//private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};//bool operator==(const Date& d1 , const Date& d2)
//{
// if (d1._year == d2._year)
// {
// if (d1._month == d2._month)
// {
// if (d1._day == d2._day)
// {
// return true;
// }
// }
// }
// return false;
//}int main()
{Date d1(2024, 4, 15);Date d2 = d1;Date d3;//显式调用operator==(d1, d2);//直接写,转换调用,编译器会转换operator==(d1, d2);d1 == d2;return 0;
}运算符重载和赋值运算符重载全部代码在后面
赋值运算符重载
赋值运算符重载格式
- 参数类型:const T&,传递引用可以提高传参效率
- 返回值类型:T&,返回引用可以提高返回的效率,有返回值目的是为了支持连续赋值
- 检测是否自己给自己赋值
- 返回*this :要复合连续赋值的含义
拷贝构造与赋值重载的区别:
赋值重载:一个已经存在的对象拷贝赋值给另一个已经存在的对象

为什么返回值类型是 类引用 而不是 void 呢?

如果是void 的话则会出现如下情况。所以我们需要一个返回值 *this .
接下来来看
为什么打印出来是随机值。
下面这个为什么是正确的

解释如下:

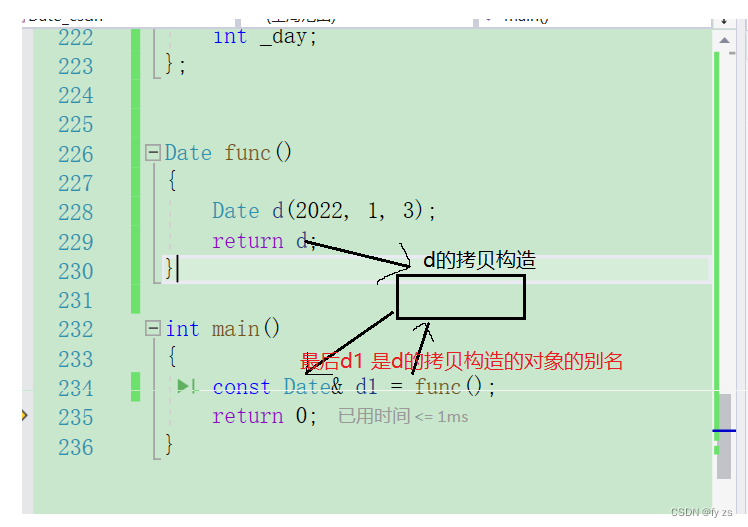
所以出了作用域,返回对象还在没有析构,那就可以引用返回,减少拷贝。
返回对象生命周期到了,会析构,传值返回。
返回对象生命周期没到,不会析构,传引用返回。
前置++和后置++重载
前置++:返回+1之后的结果
后置++:
前置++和后置++都是一元运算符,为了让前置++与后置++形成能正确重载
C++规定:后置++重载时多增加一个int类型的参数,但调用函数时该参数不用传递,编译器
自动传递
注意:后置++是先使用后+1,因此需要返回+1之前的旧值,故需在实现时需要先将this保存
一份,然后给this+1
日期类的实现(前置后置++也在里面)
class Date
{
public:int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){static int arr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0){return 29;}return arr[month];}Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}bool operator==(const Date& d){if (_year == d._year){if (_month == d._month){if (_day == d._day){return true;}}}return false;}Date& operator=(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;return *this;}bool operator>(const Date& d){if (_year > d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year){if (_month > d._month){return true;}else if (_month = d._month){if (_day > d._day){return true;}}}return false;}bool operator==(const Date& d){if (_year == d._year){if (_month == d._month){if (_day == d._day){return true;}}}return false;}bool operator>=(const Date& d){if (*this > d || *this == d){return true;}return false;}bool operator<(const Date& d){if (*this >= d){return false;}return true;}bool operator<=(const Date& d){if (*this > d){return false;}return true;}Date& operator+=(int i){_day += i;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month > 12){++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;}Date operator+(int i){Date tmp = *this;tmp += i;return tmp;}Date& operator-=(int i){_day -= i;while (_day <= 0){_day += GetMonthDay(_year, --_month);if (_month == 0){_year--;_month = 12;}}return *this;}Date operator-(int i){Date tmp = *this;tmp -= i;return tmp;}bool operator != (const Date& d){if (*this == d){return false;}return true;}Date& operator++(){*this += 1;return *this;}Date operator++(int){Date tmp = *this;*this += 1;return tmp;}Date& operator--(){*this -= 1;return *this;}Date operator--(int){Date tmp = *this;*this -= 1;return tmp;}int operator-(const Date& d){int flag = 1;int n = 0;Date d1 = *this;Date d2 = d;if (*this < d){Date d2 = *this;Date d1 = d;flag = -1;}while (d1 != d2){++d2;n++;}return n * flag;}void print(){cout << _year << ' ' << _month << ' ' << _day << endl;}~Date(){this->_year = -1;this->_month = -1;this->_day = -1;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};接下来又有一个问题:

由于cout 只能输出内置类型有没有什么办法能让他输出自定义内型呢!
我们可以定义如下运算符重载函数在类中。
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out)//这里需要+引用因为istream 和ostream不支持拷贝构造{out << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日" << endl;return out;}可是他还是不符合逻辑的:

因为this 指针的原因我们需要像下面这样输出,可这样是不符合逻辑的。


因为this 指针的原因我们需要把函数定义到全局中
这样的话又有了新的问题私有成员变量不可访问。

我们就可以通过友元函数声明来告诉编译器这个函数是我们的朋友可以调用。

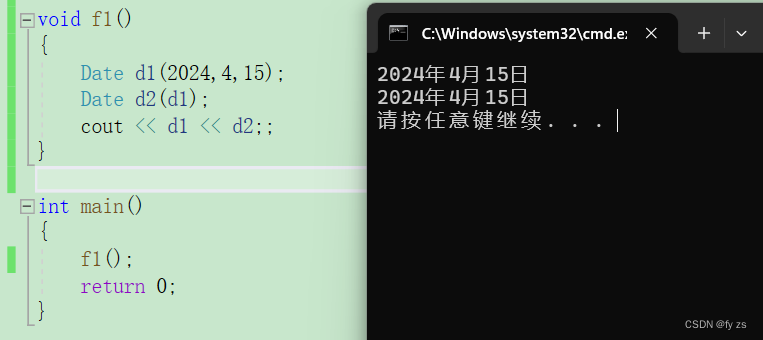
除了cout之外还有一个 cin 我们也可以来写一下。

const 成员
将const修饰的“成员函数”称之为const成员函数,const修饰类成员函数,实际修饰该成员函数
隐含的this指针,表明在该成员函数中不能对类的任何成员进行修改。

void print()const{cout << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日" << endl;} 取地址及const取地址操作符重载
取地址及const取地址操作符重载
这两个默认成员函数一般不用重新定义 ,编译器默认会生成。
这两个运算符一般不需要重载,使用编译器生成的默认取地址的重载即可,只有特殊情况,才需
要重载,比如想让别人获取到指定的内容!
class A
{
public:A* operator&(){return this;}const A* operator&() const{return this;}
private:int _a = 1;int _b = 1;int _c = 1;
};int main()
{A aa1;const A aa2;cout << &aa1 << endl;cout << &aa2 << endl;
}这两个默认成员函数编译器会自己实现一般不需要自己去实现。
感谢大家的观看!

【独一无二】)










控制一个电机转圈圈)





 Object Pascal 学习笔记---第9章第6节(嵌套异常和 InnerException机制))
