目录
一、vector的默认成员函数
1、vector类的大体结构
2、无参构造函数
3、拷贝构造函数
4、Swap(operator=需要用)
5、赋值重载operator=
6、析构函数
二、vector的三种遍历方式
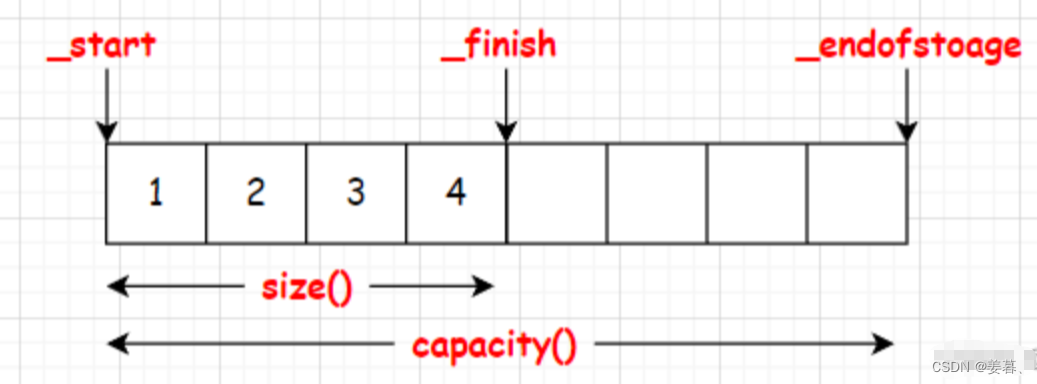
1、size和capacity(大小和容量)
2、 operator[]遍历
3、迭代器iterator遍历和范围for
三、vector相关的增容和删除
1、reserve (指定容量)
2、resize(指定大小)
3、push_back(尾插)
4、pop_back(尾删)
5、insert
6、erase
四、完整代码
vector.h:
test.cpp:
一、vector的默认成员函数
1、vector类的大体结构
vector的成员变量本质是由三个T类型(模板)的指针变量组成的,T是因为用了模板,因为vector具体存储什么类型的需要指定
namespace mz { using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string;template<class T>class vector{public:typedef T* iterator;typedef const T* const_iterator;private:iterator _start;iterator _finish;iterator _endofstorage;} }①、为什么要在新的命名空间中模拟实现vector?
防止与库里面的vector冲突,因为我们要自己模拟实现一个
②、iterator为什么要用两个版本(const和非const)?
因为迭代器遍历时我们要有只读和又能读又能写的状态,所以要有个const版本的
2、无参构造函数
vector():_start(nullptr),_finish(nullptr),_endofstorage(nullptr) {}
3、拷贝构造函数
注:此函数最好放最后面看,因为其内部调用了下文才讲的成员函数
①、正常版本
首先我们不自己实现,就是浅拷贝,会出现问题,故需我们自己实现深拷贝,v2(v1),即只要让v2拷贝一份新的数据即可(使v2和v1不是指向同一份数据)
②、现代版本
v2(v1),先让v2 reserve和v1一样的容量大小,防止频繁增容降低效率,再把v1中的每个数据尾插到v2中即可
为什么要const auto&e?
其是一种用于迭代容器元素的引用方式。它表示在循环过程中,我们用一个常量引用来访问容器中的元素。好处是不会对容器进行修改,并不会产生拷贝操作,可提高代码的效率。
在用范围for循环时,如果我们只是想读取容器中的元素而不对其进行修改,可以使用const auto&来声明循环变量。例如,当我们遍历一个vector或者数组时,可以使用const auto&来避免对容器进行修改操作。
例如,当我们遍历一个数组时,如果使用const auto&来声明循环变量,则不能修改数组中的元素。例如,对于以下代码:
int arr = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4};
for (const auto& a : arr) {
a = 1; // 错误,不能修改
cout << a << “\t”;
}由于使用了const auto&声明循环变量a,所以对a进行修改会导致编译错误。
//v2(v1) 正常版本的实现 /*vector(const vector<T>& v) {_start = new T[v.capacity()];_finish = _start;_endofstorage = _start + v.capacity();for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i){*_finish = v[i];++_finish;} }*///v2(v1) 现代版本的实现(更推荐) vector(const vector<T>& v):_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _endofstorage(nullptr) {reserve(v.capacity());for (const auto& e : v)push_back(e); }
4、Swap(operator=需要用)
为什么需要自己提供swap,而不调用库里提供的?
因为库里面提供的对于自定义类型代价极大,因为需要深拷贝,但对于内置类型用库函数里面的还好,所以应该自己写一个成员函数swap
void swap(vector<T>& v) {//调用全局的swap,交换指针,其为内置类型,无需深拷贝//代价相比于直接调用库里面函数交换比较小std::swap(_start, v._start);std::swap(_finish, v._finish);std::swap(_endofstorage, v._endofstorage); }
5、赋值重载operator=
①、正常版本
先要避免自己给自己赋值,先释放旧空间,再使_start指向一份自己新开辟的新空间,再把需要赋值的数据拷过去即可
②、现代版本(更推荐)
v是v3的临时拷贝,然后v会与v1交换,出了函数v就被销毁了,不用我们自己再销毁了,省力
//v1 = v3 正常版本的实现 /*vector<T>& operator=(const vector<T>& v) {if (this != &v){delete[] _start;_start = new T[v.capacity()];memcpy(_start, v._start, sizeof(T) * v.size());}return *this; }*///v1 = v3 现代版本 vector<T>& operator=(vector<T> v) {swap(v);//this->swap(v);return *this; }
6、析构函数
~vector() {if (_start){delete[]_start;_start = _finish = _endofstorage = nullptr;} }
二、vector的三种遍历方式
1、size和capacity(大小和容量)
原理:指针相减就是指针间的元素个数
size_t size()const{return _finish - _start;}size_t capacity()const{return _endofstorage - _start;}①、为什么要加const?
成员函数只要不改变成员变量的,最好都要加上const
2、 operator[]遍历
T& operator[](size_t i) {//确保范围的合法性assert(i < size());//记得引头文件assert.hreturn _start[i]; }const T& operator[](size_t i)const {assert(i < size());return _start[i]; }①、为什么要实现两个版本的operator[]?
直接把非const的operator[]加上const不行吗?不可以,因为operator[]访问完后,有两种状态:1、只读 2、可读可写 你直接加上const就只读了,万一我想改数据又不行了,故写两个版本的(const和非const版本)
3、迭代器iterator遍历和范围for
迭代器有只读的和可读可写的,故也要写两个版本
iterator begin() {return _start; }iterator end() {return _finish; }const_iterator begin()const {return _start; }const_iterator end()const {return _finish; }只要把迭代器写出来了,迭代器遍历和范围for遍历就都可以用了
测试operator[]和迭代器和范围for三种遍历
void test1() {vector<int>v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);cout << v.size() << endl;cout << v.capacity() << endl;vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();while (it != v.end()){*it += 1;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl; for (auto& e : v){e -= 1;cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i){cout << v[i] << " ";}cout << endl;运行结果:
三、vector相关的增容和删除
1、reserve (指定容量)
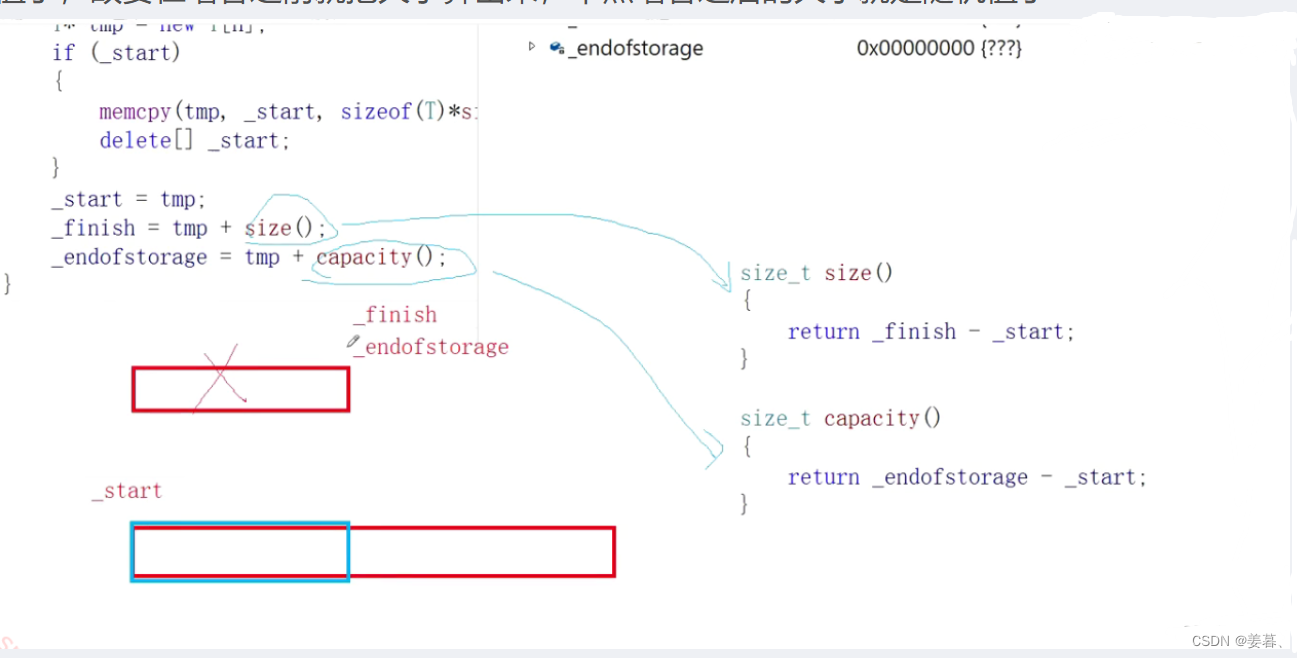
void reserve(size_t n) {if (n > capacity()){size_t sz = size();//大小要在增容前就算好T* tmp = new T[n];if (_start){//memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T) * sz);//按字节拷贝,浅拷贝//作深拷贝,使新旧空间指向自己对应的数据for (size_t i = 0; i < sz; ++i){tmp[i] = _start[i];//调用的是T的operator=,深拷贝}delete[]_start;}_start = tmp;_finish = tmp + sz;//不能写为=tmp + size()_endofstorage = tmp + n;} }①、为什么要在增容前就算出大小?
因为增容涉及新和旧空间的问题,比如_finish = tmp + size(),而size的求法是用_finish - _start,但_start已指向新空间,可_finish还是指向旧空间,两块不连续的空间相减就是随机值了,故要在增容之前就把大小算出来,不然增容之后的大小就是随机值了
②、为什么不能用memcpy拷贝数据?
测试时,当用string作为vector存储的类型时,程序崩溃了,为什么?
本质原因是因为增容中用了memcpy,memcpy导致了问题的出现,因为memcpy是按字节拷贝的,它本质上造成了浅拷贝问题, memcpy使新旧空间都指向了一份数据,旧空间释放后,它指向的对应数据也被释放,而新空间指针还是指向这份旧空间,这就造成非法访问,所以新空间与旧空间不应指向同一份数据,应该不用memcpy,写成深拷贝
解决(reserve的实现不用memcpy):
把旧空间的每个值赋值给新空间对应的每个值就好了,就能实现深拷贝了,指向不同的数据
2、resize(指定大小)
void resize(size_t n, const T& val = T())//因为不知道T的类型,故给T类型的缺省值 {if (n < size()){_finish = _start + n;}else{if (n > capacity()){reserve(n);}//填数据不能用memset//填数据while (_finish < _start + n){*_finish = val;++_finish;}} }①、填数据为什么不能用memset?
当对于a数组,设置为0时,没问题,但各设置为1和2时,就出现随机值了 ,因为memset只适合把所有值初始化为0,当初始化为1时,是把每个字节初始化为1
即00000001 00000001 00000001 00000001,这就不是整形的1了(2也同理,就初始化0可以)!memset连内置类型都处理不好,别说自定义类型了,问题会更大,本质上就是因为memxxx类函数都是按字节处理的,
即慎用memxxx,因为其按字节进行操作
②、const T& val = T()中的T()使什么意思?
因为不知道T的类型,故用T的缺省值
C++中内置类型也可以像自定义类型那样调用构造函数,严格来说,内置类型是没有构造函数的,但C++强行赋予了这个构造函数概念,是为了更好地支持模板
int i = int();//0int j = int(1);//1double d = double();//0.0000000000double e = double(1.1);//1.100000000
3、push_back(尾插)
void push_back(const T& x) {//方法一if (_finish == _endofstorage){size_t newcapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 2 : capacity() * 2;reserve(newcapacity);}*_finish = x;++_finish;//方法二、调用insert//insert(_finish, x); }
4、pop_back(尾删)
void pop_back() {//方法一assert(_start < _finish);--_finish;//方法二、复用eraseerase(_finish - 1); }
5、insert
void insert(iterator pos, const T& x) {assert(pos <= _finish);//pos == _finish时,相当于尾插//满了需要扩容if (_finish == _endofstorage){size_t n = pos - _start;//算出原pos距离size_t newcapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 2 : capacity() * 2;reserve(newcapacity);//增完容后要更新pos的位置,因为增容后原来的pos就失效了pos = _start + n;//新的_start + n}//插入之前需要往后挪动1个数据iterator end = _finish;while (end > pos){*end = *(end - 1);--end;}//插入数据*pos = x;++_finish; }为什么需要提前算出n?
有迭代器失效的问题,因为pos是迭代器类型,扩容前指向旧空间的某一位置,而reserve调用后会扩容,而我们是扩容完才插入数据的,此时pos无效,因为旧空间已经释放了,它这个迭代器还指向那里就失效了,故我们要更新pos位置,使它指向新空间,所以要先算n,即原pos的位置
6、erase
iterator erase(iterator pos) {assert(pos < _finish);iterator it = pos + 1;while (it < _finish){*(it - 1) = *it;++it;}--_finish;return pos;//返回被删除数据的下一位置,那就还是原位置,因为那个数据被删除了 }注意:erase是返回被删除数据的下一位置,当要被删除的数据被删除了,erase原地不动的话,就已自动指向了下一位置,因为那个数据被删除了
最后一个问题
如果T是字符串的话代码逻辑会不会忘掉'\0'?
不会,vector<char>末尾没有'\0',string才有,这也是他们的差别
四、完整代码
总共分为两个文件:vector.h和test.cpp
vector.h:
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
#include<string>namespace mz
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;template<class T>class vector{public:typedef T* iterator;typedef const T* const_iterator;vector():_start(nullptr),_finish(nullptr),_endofstorage(nullptr){}//v2(v1) 正常版本的实现/*vector(const vector<T>& v){_start = new T[v.capacity()];_finish = _start;_endofstorage = _start + v.capacity();for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i){*_finish = v[i];++_finish;}}*///v2(v1) 现代版本的实现(更推荐)vector(const vector<T>& v):_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _endofstorage(nullptr){reserve(v.capacity());for (const auto& e : v)push_back(e);}//v1 = v3 正常版本的实现/*vector<T>& operator=(const vector<T>& v){if (this != &v){delete[] _start;_start = new T[v.capacity()];memcpy(_start, v._start, sizeof(T) * v.size());}return *this;}*///v1 = v3 现代版本vector<T>& operator=(vector<T> v){swap(v);//this->swap(v);return *this;}void swap(vector<T>& v){//调用全局的swap,交换指针,其为内置类型,无需深拷贝//代价相比于直接调用库里面函数交换比较小std::swap(_start, v._start);std::swap(_finish, v._finish);std::swap(_endofstorage, v._endofstorage);}iterator begin(){return _start;}iterator end(){return _finish;}const_iterator begin()const{return _start;}const_iterator end()const{return _finish;}void reserve(size_t n){if (n > capacity()){size_t sz = size();//大小要在增容前就算好T* tmp = new T[n];if (_start){//memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T) * sz);//按字节拷贝,浅拷贝//作深拷贝,使新旧空间指向自己对应的数据for (size_t i = 0; i < sz; ++i){tmp[i] = _start[i];//调用的是T的operator=,深拷贝}delete[]_start;}_start = tmp;_finish = tmp + sz;//不能写为=tmp + size()_endofstorage = tmp + n;}}void resize(size_t n, const T& val = T())//因为不知道T的类型,故给T类型的缺省值{if (n < size()){_finish = _start + n;}else{if (n > capacity()){reserve(n);}//填数据不能用memset//填数据while (_finish < _start + n){*_finish = val;++_finish;}}}void push_back(const T& x){//方法一if (_finish == _endofstorage){size_t newcapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 2 : capacity() * 2;reserve(newcapacity);}*_finish = x;++_finish;//方法二、调用insert//insert(_finish, x);}void pop_back(){//方法一assert(_start < _finish);--_finish;//方法二、复用eraseerase(_finish - 1);}void insert(iterator pos, const T& x){assert(pos <= _finish);//pos == _finish时,相当于尾插//满了需要扩容if (_finish == _endofstorage){size_t n = pos - _start;//算出原pos距离size_t newcapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 2 : capacity() * 2;reserve(newcapacity);//增完容后要更新pos的位置,因为增容后原来的pos就失效了pos = _start + n;//新的_start + n}//插入之前需要往后挪动1个数据iterator end = _finish;while (end > pos){*end = *(end - 1);--end;}//插入数据*pos = x;++_finish;}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos < _finish);iterator it = pos + 1;while (it < _finish){*(it - 1) = *it;++it;}--_finish;return pos;//返回被删除数据的下一位置,那就还是原位置,因为那个数据被删除了}T& operator[](size_t i){//确保范围的合法性assert(i < size());//记得引头文件assert.hreturn _start[i];}const T& operator[](size_t i)const{assert(i < size());return _start[i];}size_t size()const{return _finish - _start;}size_t capacity()const{return _endofstorage - _start;}~vector(){if (_start){delete[]_start;_start = _finish = _endofstorage = nullptr;}}private:iterator _start;iterator _finish;iterator _endofstorage;};void print_vector(const vector<int>& v){vector<int>::const_iterator it = v.begin();while (it != v.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}void test1(){vector<int>v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);cout << v.size() << endl;cout << v.capacity() << endl;vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();while (it != v.end()){*it += 1;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl; for (auto& e : v){e -= 1;cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i){cout << v[i] << " ";}cout << endl;}void test2(){vector<int>v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(6);v.insert(v.begin(), 0);//头插0print_vector(v);//删除偶数vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();while (it != v.end()){if (*it % 2 == 0){it = v.erase(it);}else{++it;}}print_vector(v);}void test3(){vector<int>v;v.reserve(10);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(6);v.resize(4);print_vector(v);cout << v.size() << endl;cout << v.capacity() << endl;v.resize(8);print_vector(v);cout << v.size() << endl;cout << v.capacity() << endl;v.resize(12,int());print_vector(v);cout << v.size() << endl;cout << v.capacity() << endl;int i = int();//0int j = int(1);//1double d = double();//0.0000000000double e = double(1.1);//1.100000000}void test4(){vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);vector<int>v2(v1);for (size_t i = 0; i < v1.size(); ++i){cout << v1[i] << " ";}cout << endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < v2.size(); ++i){cout << v2[i] << " ";}cout << endl;vector<int>v3;v3.push_back(10);v3.push_back(20);v3.push_back(30);v3.push_back(40);v1 = v3;for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}void test5(){vector<string>v;v.push_back("111111111111111111111");v.push_back("222222222222222222222");v.push_back("333333333333333333333");v.push_back("444444444444444444444");for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}
}
test.cpp:
#include<iostream>
#include"vector.h"int main()
{mz::test1();//memxxx 按字节处理/*int a[10];memset(a, 0, sizeof(int) * 10);memset(a, 1, sizeof(int) * 10);memset(a, 2, sizeof(int) * 10);*/return 0;
}




















做毕设课设均可)


