目录
- 单例模式
- 两种单例写法
- 饿汉式和懒汉式的区别
- Runtime
- Timer 计时器
- 两个线程间的通信
- 关键点:wait()线程等待 和 notify()随机唤醒等待的线程;
- 三个或三个以上间的线程通信
- 关键点:notifyAll()唤醒所有线程
- 线程间通信需要注意的问题
- JDK1.5的新特性互斥锁
- 线程组的概述和使用
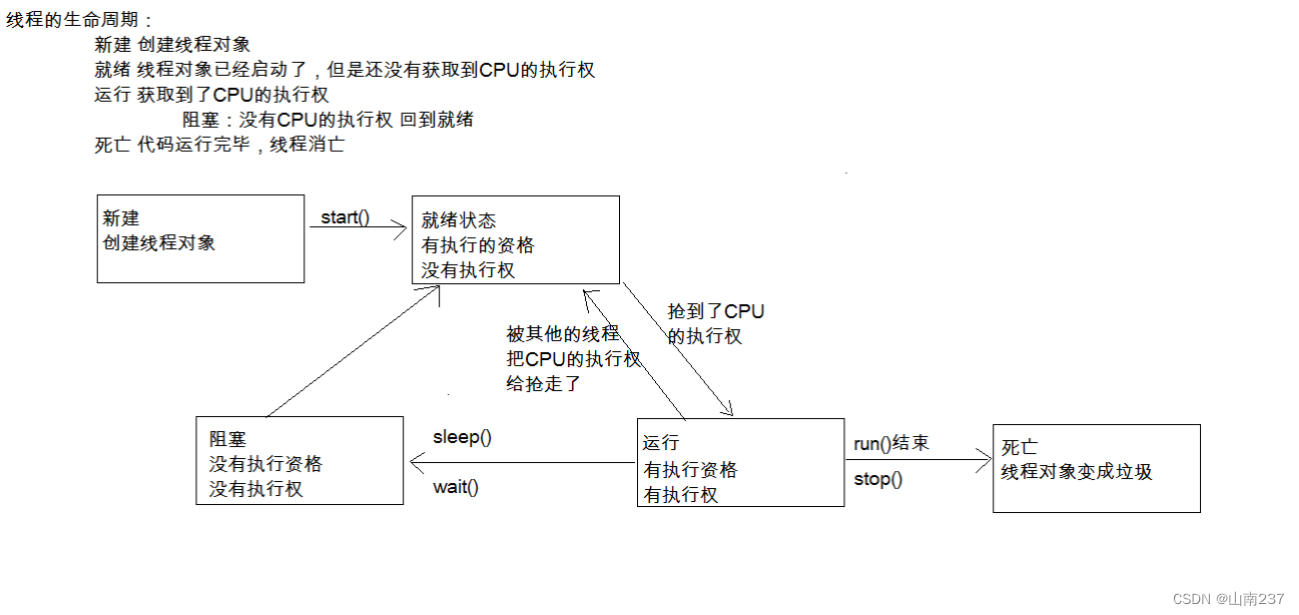
- 线程的五种状态
- 线程池的概述和使用
单例模式
-
单例设计模式:保证类在内存中只有一个对象。
-
如何保证类在内存中只有一个对象呢?
- (1)控制类的创建,不让其他类来创建本类的对象。private
- (2)在本类中定义一个本类的对象。Singleton s;
- (3)提供公共的访问方式。 public static Singleton getInstance(){return s}
两种单例写法
- 第一种单例写法
- 饿汉式
//饿汉式
class Singleton {//1、私有构造函数private Singleton() {}//2、创建本类对象private static Singleton singleton = new Singleton();//3、对外提供公共的访问方法public static Singleton getInstance() { //获取实例return singleton;}
}
- 第二种单例写法
- 懒汉式
//懒汉式
class Singleton1 {//1、私有构造函数private Singleton1() {}//2、声明一个本类的引用private static Singleton1 singleton1;//3、对外提供公共的访问方法public static Singleton1 getInstance() { //获取实例if (singleton1 == null) {singleton1 = new Singleton1();}return singleton1;}
}
饿汉式和懒汉式的区别
- 1、饿汉式是空间交换时间,懒汉式是时间交换空间
- 2、在多线程访问时,饿汉式不会创建多个对象,而懒汉式有可能会创建多个对象
Runtime
- Runtime类是一个单例类,可以获取运行时对象
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime(); //获取运行时对象//exec在单独的进程中执行指定的字符串命令//runtime.exec("shutdown -s -t 300"); //300秒后关机runtime.exec("shutdown -a"); //取消关机}
Timer 计时器
线程用其安排以后在后台线程中执行的任务,可安排任务执行一次或者定期重复执行
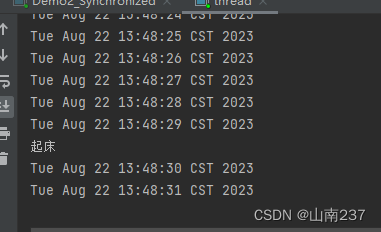
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {Timer timer = new Timer();//在指定时间安排指定任务//第一个参数,是安排的任务,第二个参数是执行的时间(执行时间需要当前年份减去1900,月份范围0-11),第三个参数是重复执行的间隔时间timer.schedule(new MyTimerTask(),new Date(123,7,22,13,49,30));while (true){Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(new Date());}
}class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("起床");}
}
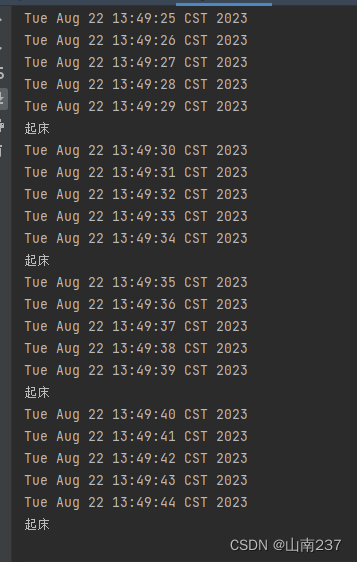
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {Timer timer = new Timer();//在指定时间安排指定任务//第一个参数,是安排的任务,第二个参数是执行的时间(执行时间需要当前年份减去1900,月份范围0-11),第三个参数是重复执行的间隔时间//下面是到了指定时间后每5秒执行一次timer.schedule(new MyTimerTask(),new Date(123,7,22,13,49,30),5000);while (true){Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(new Date());}}class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("起床");}
}
两个线程间的通信
关键点:wait()线程等待 和 notify()随机唤醒等待的线程;
- 1、什么时候需要通信
- 多个线程并发执行时, 在默认情况下CPU是随机切换线程的
- 如果我们希望他们有规律的执行, 就可以使用通信, 例如每个线程执行一次打印
- 2、怎么通信
- 如果希望线程等待, 就调用wait()
- 如果希望唤醒等待的线程, 就调用notify();
- 这两个方法必须在同步代码中执行, 并且使用同步锁对象来调用
public static void main(String[] agr) {final printer p = new printer();new Thread() {public void run() {while (true) {try {p.print1();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();new Thread() {public void run() {while (true) {try {p.print2();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();}/*** 非静态的同步方法的锁对象是this* 静态的同步方法的锁对象是该类的字节码对象*/
class printer {private int flag = 1 ;public void print1() throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this) {if (flag != 1){this.wait(); //当前线程等待}System.out.print("恩");System.out.print("施");System.out.print("大");System.out.print("峡");System.out.print("谷");System.out.print("\r\n");flag = 2;this.notify(); //随机唤醒单个等待的线程}}/** 非静态同步函数的锁是:this* 静态的同步函数的锁是:字节码对象*/public void print2() throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this) {if (flag != 2){this.wait(); //当前线程等待}System.out.print("屏");System.out.print("山");System.out.print("景");System.out.print("区");System.out.print("\r\n");flag = 1 ; //改变flag的值,让当前线程等待,唤醒其他等待的线程this.notify(); //随机唤醒单个等待的线程}}
}

三个或三个以上间的线程通信
关键点:notifyAll()唤醒所有线程
- 多个线程通信的问题
- notify()方法是随机唤醒一个线程
- notifyAll()方法是唤醒所有线程
- JDK5之前无法唤醒指定的一个线程
- 如果多个线程之间通信, 需要使用notifyAll()通知所有线程, 用while来反复判断条件
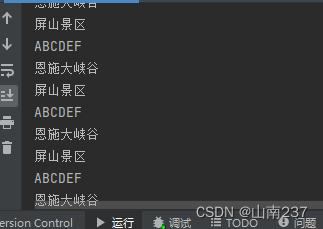
public class Synchronized {public static void main(String[] agr) {final printer p = new printer();new Thread() {public void run() {while (true) {try {p.print1();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();new Thread() {public void run() {while (true) {try {p.print2();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();new Thread() {public void run() {while (true) {try {p.print2();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();new Thread() {public void run() {while (true) {try {p.print3();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();}
}/*** 非静态的同步方法的锁对象是this* 静态的同步方法的锁对象是该类的字节码对象*/
class printer {private int flag = 1 ;public void print1() throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this) {while (flag != 1){this.wait(); //当前线程等待}System.out.print("恩");System.out.print("施");System.out.print("大");System.out.print("峡");System.out.print("谷");System.out.print("\r\n");flag = 2;this.notifyAll(); //随机唤醒单个等待的线程}}/** 非静态同步函数的锁是:this* 静态的同步函数的锁是:字节码对象*/public void print2() throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this) {while (flag != 2){this.wait(); //当前线程等待}System.out.print("屏");System.out.print("山");System.out.print("景");System.out.print("区");System.out.print("\r\n");flag = 3 ; //改变flag的值,让当前线程等待,唤醒其他等待的线程this.notifyAll(); //随机唤醒单个等待的线程}}public void print3() throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this) {while (flag != 3){ //while循环是循环判断,每次都会判断标记this.wait(); //当前线程等待}System.out.print("A");System.out.print("B");System.out.print("C");System.out.print("D");System.out.print("E");System.out.print("F");System.out.print("\r\n");flag = 1 ; //改变flag的值,让当前线程等待,唤醒其他等待的线程this.notifyAll(); //随机唤醒单个等待的线程}}
}
线程间通信需要注意的问题
- 在同步代码块中,用哪个对象锁,就用哪个对象调用wait方法
- 为什么wait方法和notify方法定义在object这个类中?
因为锁对象可以是任意对象,object是所有类的基类,所以wait方法和notify方法定义在object这个类中 - sleep方法和wait方法的区别
- sleep方法必须传入参数,参数就是时间,时间到了自动醒来
wait方法可以传入参数也可以不传入参数,传入参数就是在参数的时间结束后等待,不传入时间就是直接等待 - sleep方法在同步函数或同步代码块中,不释放锁
wait方法在同步函数或者同步代码块中,释放锁
JDK1.5的新特性互斥锁
- 1.同步
- 使用ReentrantLock类的lock()和unlock()方法进行同步
- 2.通信
- 使用ReentrantLock类的newCondition()方法可以获取Condition对象
- 需要等待的时候使用Condition的await()方法, 唤醒的时候用signal()方法
- 不同的线程使用不同的Condition, 这样就能区分唤醒的时候找哪个线程了
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;public class Synchronized {public static void main(String[] agr) {final printer p = new printer();new Thread() {public void run() {while (true) {try {p.print1();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();new Thread() {public void run() {while (true) {try {p.print2();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();new Thread() {public void run() {while (true) {try {p.print3();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();new Thread() {public void run() {while (true) {try {p.print3();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();}
}/*** 非静态的同步方法的锁对象是this* 静态的同步方法的锁对象是该类的字节码对象*/
class printer {private ReentrantLock r = new ReentrantLock();private Condition c1 = r.newCondition();private Condition c2 = r.newCondition();private Condition c3 = r.newCondition();private int flag = 1;public void print1() throws InterruptedException {r.lock(); //获取锁if (flag != 1) {c1.await(); //当前线程等待}System.out.print("恩");System.out.print("施");System.out.print("大");System.out.print("峡");System.out.print("谷");System.out.print("\r\n");flag = 2;c2.signal();r.unlock();}/** 非静态同步函数的锁是:this* 静态的同步函数的锁是:字节码对象*/public void print2() throws InterruptedException {r.lock();if (flag != 2) {c2.await(); //当前线程等待}System.out.print("屏");System.out.print("山");System.out.print("景");System.out.print("区");System.out.print("\r\n");flag = 3; //改变flag的值,让当前线程等待,唤醒其他等待的线程c3.signal();r.unlock();}public void print3() throws InterruptedException {r.lock();if (flag != 3) { c3.await(); //当前线程等待}System.out.print("A");System.out.print("B");System.out.print("C");System.out.print("D");System.out.print("E");System.out.print("F");System.out.print("\r\n");flag = 1; //改变flag的值,让当前线程等待,唤醒其他等待的线程c1.signal();r.unlock();}
}
线程组的概述和使用
A:线程组概述
- Java中使用ThreadGroup来表示线程组,它可以对一批线程进行分类管理,Java允许程序直接对线程组进行控制。
- 默认情况下,所有的线程都属于主线程组。
- public final ThreadGroup getThreadGroup()//通过线程对象获取他所属于的组
- public final String getName()//通过线程组对象获取他组的名字
- 给线程设置分组
- 1,ThreadGroup(String name) 创建线程组对象并给其赋值名字
- 2,创建线程对象
- 3,Thread(ThreadGroup?group, Runnable?target, String?name)
- 4,设置整组的优先级或者守护线程
public class ThreadGroup {public static void main(String[] agr) {//demo1();java.lang.ThreadGroup tg = new java.lang.ThreadGroup("我是一个新的线程组"); //创建新的线程组MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable(); //创建Runnable的子类对象Thread t1 = new Thread(tg,myRunnable,"张三"); //将线程t1放在组中Thread t2 = new Thread(tg,myRunnable,"李四"); //将线程t2放在组中System.out.println(t1.getThreadGroup().getName()); //获取名字System.out.println(t2.getThreadGroup().getName());//通过组名称设置后台线程,表示改组的线程都是后台线程tg.setDaemon(true);}private static void demo1() {MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();Thread t1 = new Thread(myRunnable, "线程1");Thread t2 = new Thread(myRunnable, "线程2");java.lang.ThreadGroup tg1 = t1.getThreadGroup();java.lang.ThreadGroup tg2 = t2.getThreadGroup();System.out.println(tg1.getName()); //默认是主程序System.out.println(tg2.getName());}
}class MyRunnable implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "....." + i);}}
}
线程的五种状态
线程池的概述和使用
- :线程池概述
- 程序启动一个新线程成本是比较高的,因为它涉及到要与操作系统进行交互。而使用线程池可以很好的提高性能,尤其是当程序中要创建大量生存期很短的线程时,更应该考虑使用线程池。线程池里的每一个线程代码结束后,并不会死亡,而是再次回到线程池中成为空闲状态,等待下一个对象来使用。在JDK5之前,我们必须手动实现自己的线程池,从JDK5开始,Java内置支持线程池
- B:内置线程池的使用概述
- JDK5新增了一个Executors工厂类来产生线程池,有如下几个方法
- public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)
- public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor()
- 这些方法的返回值是ExecutorService对象,该对象表示一个线程池,可以执行Runnable对象或者Callable对象代表的线程。它提供了如下方法
- Future<?> submit(Runnable task)
- Future submit(Callable task)
- 使用步骤:
- 创建线程池对象
- 创建Runnable实例
- 提交Runnable实例
- 关闭线程池
- JDK5新增了一个Executors工厂类来产生线程池,有如下几个方法
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class Demo5_Executors {public static void main(String[] agr) {ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); //创建线程池pool.submit(new MyRunnable()); //将线程放进线程池并执行pool.submit(new MyRunnable());pool.shutdown(); //关闭线程池}
}
集合的底层原理及应用场景)



 Developing with SAP Integration Suite)







:内存区域)




)

