我的新书《Android App开发入门与实战》已于2020年8月由人民邮电出版社出版,欢迎购买。点击进入详情

有没有想过当您应用从低到高、从高到低或按字母顺序等过滤器时,亚马逊或任何其他电子商务网站中的产品如何排序?排序算法对于此类网站起着至关重要的作用,在这些网站中列出了大量产品,并且必须使客户交互变得轻松。
排序算法用于根据元素上的比较运算符重新排列给定数组或元素列表。比较运算符用于决定相应数据结构中元素的新顺序。主要使用了五种基本算法,并且可以利用这些基本算法衍生出多种算法。这些算法中的每一种都有一些优点和缺点,可以根据要处理的数据大小进行有效选择。
- 插入排序
- 选择排序
- 冒泡排序
- 归并排序
- 快速排序
如需完整的数据结构和算法速查表,请fork此GitHub存储库。
1.插入排序
插入排序是一种简单的排序算法,其工作原理类似于对手中的扑克牌进行排序。该数组实际上分为已排序部分和未排序部分。未排序部分的值被拾取并放置在已排序部分的正确位置。当问题规模较小(因为它的开销较低)或当数据接近排序时(因为它是自适应的),插入排序速度很快并且最适合。
示例: elements: 9, 6, 5, 0, 8, 2, 7, 1, 3, 4
i : 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
让我们循环 for i = 1(数组的第二个元素)到 9(数组的最后一个元素)
我=1。由于 6 小于 9,因此移动 9 并在 9 之前插入 6
6 , 9, 5, 0, 8, 2, 7, 1, 3, 4
我=2。由于 5 小于 6 和 9,因此将 5 移到 6 和 9 之前
5, 6, 9, 0, 8, 2, 7, 1, 3, 4
我=3。由于 0 小于 5,6 和 9,因此将 0 移到 5,6,9
0, 5, 6, 9, 8, 2, 7, 1, 3, 4之前
我=4。由于 8 小于 9,因此将 8 移到 9 之前
0, 5, 6, 8, 9, 2, 7, 1, 3, 4
我=5。由于 2 小于 5,6,8 和 9,因此将 2 移到 5,6,8,9
0, 2, 5, 6, 8, 9, 7, 1, 3, 4之前
我=6。0, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1, 3, 4
i=7。0, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 3, 4
i=8。0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 4
i=9。0、1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9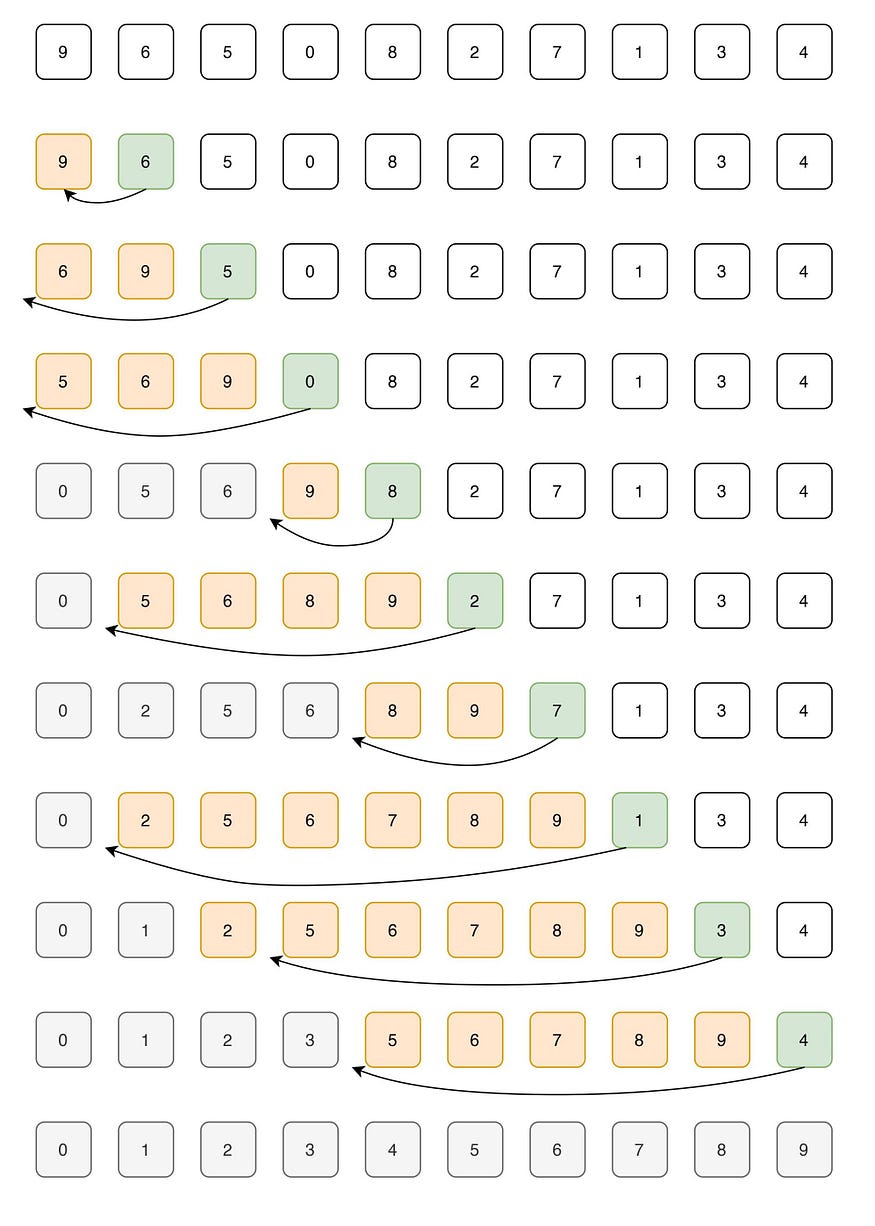
插入排序
算法:
插入排序(A)
{
for j=i to A.length key = A[i]; // 将 A[i] 插入已排序序列 A[1,2,3,..,i-1] j= i-1; while (j>0 且 A[j]>key) A[j+1] = A[j] j= j-1 A[j+1] = key
}// C program for insertion sort
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>/* Function to sort an array using insertion sort*/
void insertionSort(int arr[], int n)
{int i, key, j;for (i = 1; i < n; i++){key = arr[i];j = i - 1;/* Move elements of arr[0..i-1], that are greater than key, to one position ahead of their current position */while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key){arr[j + 1] = arr[j];j = j - 1;}arr[j + 1] = key;}
}// A utility function to print an array of size n
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < n; i++)printf("%d ", arr[i]);printf("\n");
}/* Driver program to test insertion sort */
int main()
{int arr[] = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6};int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);insertionSort(arr, n);printArray(arr, n);return 0;
}
2. 选择排序
选择排序算法通过从未排序的部分中重复查找最小元素(考虑升序)并将其放在开头来对数组进行排序。该算法在给定数组中维护两个子数组:
- 已经排序的子数组
- 剩余未排序的子数组
在选择排序的每次迭代/传递中,都会从未排序的子数组中选取最小元素(考虑升序)并将其移至已排序的子数组。选择排序具有最小化交换次数的特性。因此,当交换成本较高时,它是最佳选择。
示例:arr[]= 23 78 45 8 32 46
Pass 1// 找到arr[0...5]中的最小元素并将其放在开头
8 78 45 23 32 46
Pass 2// 找到arr[1...5]中的最小元素并将其放在arr[1...5]的开头
8 23 45 78 32 46
Pass 3// 找到arr[2...5]中的最小元素并将其放在arr[2...5]的开头
8 23 32 78 45 46
Pass 4// 找到arr[3...5]中的最小元素并将其放在arr[3...5]的开头
8 23 32 45 78 46
Pass 5// 找到arr[4...5]中的最小元素并将其放在arr[4...5]的开头
8 23 32 45 46 78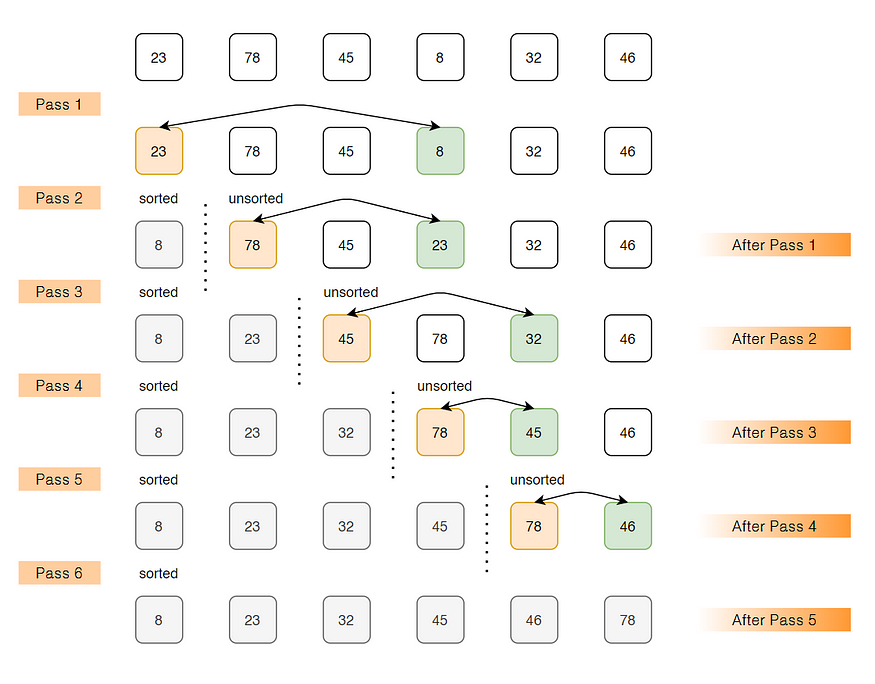
选择排序
算法:
void SelectionSort (int a[], int n)
{
int i,j, temp, min;
for (i=0; i<n-1; i++)
{ min = i; for (j=i+1; j<n; j++) if (a[j] < a[min]) { min = j; }温度 = a[i]; a[i] = a[min];a[分钟] = 温度;
}
}// C program for implementation of selection sort
#include <stdio.h>void swap(int *xp, int *yp)
{int temp = *xp;*xp = *yp;*yp = temp;
}void selectionSort(int arr[], int n)
{int i, j, min_idx;// One by one move boundary of unsorted subarrayfor (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){// Find the minimum element in unsorted arraymin_idx = i;for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])min_idx = j;// Swap the found minimum element with the first elementswap(&arr[min_idx], &arr[i]);}
}/* Function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < size; i++)printf("%d ", arr[i]);printf("\n");
}// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{int arr[] = {64, 25, 12, 22, 11};int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);selectionSort(arr, n);printf("Sorted array: \n");printArray(arr, n);return 0;
}
3.冒泡排序
冒泡排序是一种排序算法,如果相邻元素的顺序错误,则重复交换相邻元素。每次迭代或传递后,最大的元素到达末尾(在升序的情况下)或最小的元素到达末尾(在降序的情况下)。重复遍历列表直到列表被排序。该算法不适合大型数据集,因为其平均和最坏情况复杂度为 Ο(n^2),其中n是项目数
示例:64 34 25 12 22 11 90
迭代 1:( 64 34 25 12 22 11 90) -> ( 34 64 25 12 22 11 90),这里,算法比较前两个元素,并从 64 > 34 开始交换。
(34 64 25 12 22 11 90) - > (34 25 64 12 22 11 90),从 64 开始交换 > 25
(34 25 64 12 22 11 90) -> (34 25 12 64 22 11 90),从 64 开始交换 > 12
(34 25 12 64 22 11 90) ) -> (34 25 12 22 64 11 90),从 64 > 22 开始交换
(34 25 12 22 64 11 90) -> (34 25 12 22 11 64 90),从 64 > 11 开始交换
(34 25 12 22 11) 64 90 ) -> (34 25 12 22 11 64 90 ),现在,由于这些元素已经按顺序排列 (90 > 64),算法不会交换它们。
迭代 2:(34 25 12 22 11 64 90) -> ( 25 34 12 22 11 64 90),从 34 > 25 开始交换
( 25 34 12 22 11 64 90) -> (25 12 34 22 11 64 90),自 34 > 12 起交换(25 12 34 22 11 64 90) -> (25 12 22 34 11 64 90),自 34 > 22 起交换(25 12 22 34 11 64 90) -> (25 12 22 11 34 64 90) ),交换自 34 > 11(25 12 22 11 34 64 90) -> (25 12 22 11 34 64 90),现在,由于这些元素已经按顺序排列 (64 > 34),算法不会交换它们。迭代 3:( 25 12 22 11 34 64 90) -> ( 12 25 22 11 34 64 90),从 25 > 12 开始交换
(12 25 22 11 34 64 90) -> (12 22 25 11 34 64 90),自 25 > 22 起交换
(12 22 25 11 34 64 90) -> (12 22 11 25 34 64 90), 自 25 > 11 起交换
(12 22 11 25 34 64 90) -> (12 22 11 25 34 64 90) ),现在,由于这些元素已经按顺序排列 (34 > 25),算法不会交换它们。
迭代 4:( 12 22 11 25 34 64 90) -> ( 12 22 11 25 34 64 90)
(12 22 11 25 34 64 90) -> (12 11 22 25 34 64 90),从 22 > 11 开始交换
( 12 11 22 25 34 64 90) -> (12 11 22 25 34 64 90)
迭代 5:(12 11 22 25 34 64 90) -> ( 11 12 22 25 34 64 90),从 12 开始交换 > 11
(11 12 22 25 34 64 90) -> (11 12 22 25 34 64 90)
迭代 6:(11 12 22 25 34 64 90) -> ( 11 12 22 25 34 64 90)
现在,数组已经排序了,但是我们的算法不知道它是否已完成。该算法需要一整遍而不需要任何交换才能知道它已排序。
迭代7:( 11 12 22 25 34 64 90) -> ( 11 12 22 25 34 64 90)
(11 12 22 25 34 64 90) -> (11 12 22 25 34 64 90 ) ( 11 12 22 25 34 64 90) -> (11 12 22 25 34 64 90) (11 12 22 25 34 64 90) -> (11 12 22 25 34 64 90) (11 12 22 25 34 64 90) -> (11 12 22 25 34) 64 90) (11 12 22 25 34 64 90 ) -> (11 12 22 25 34 64 90 )

冒泡排序
算法:
Bubble_Sort(int a[], n)
{
int swapped, i, j;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{交换 = 0; for (j=0; j<ni-1; j++) { if (a[j] > a[j+1]) {交换 (a[j], a[j+1]); } 交换=1; if (交换== 0)中断 ; } }
// C program for implementation of Bubble sort
#include <stdio.h> void swap(int *xp, int *yp)
{ int temp = *xp; *xp = *yp; *yp = temp;
} // An optimized version of Bubble Sort
void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n)
{ int i, j; bool swapped; for (i = 0; i < n-1; i++) { swapped = false; for (j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) { swap(&arr[j], &arr[j+1]); swapped = true; } } // IF no two elements were swapped by inner loop, then break if (swapped == false) break; }
} /* Function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{ int i; for (i=0; i < size; i++) printf("%d ", arr[i]); printf("n");
} // Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{ int arr[] = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90}; int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]); bubbleSort(arr, n); printf("Sorted array: \n"); printArray(arr, n); return 0;
}
4. 归并排序
与上述三种排序算法不同,该算法基于分而治之技术。它将输入数组分为两半,为两半调用自身,然后合并已排序的两半。归并排序的核心是函数merge() ,用于合并两半。merge(A, p, q, r) 是一个关键过程,它假设 A[p..q] 和 A[q+1..r] 已排序,并将两个已排序的子数组合并为一个。
当您需要稳定且 O(N log N) 排序时,合并排序是唯一的选择。
合并()函数
合并过程也称为异地过程
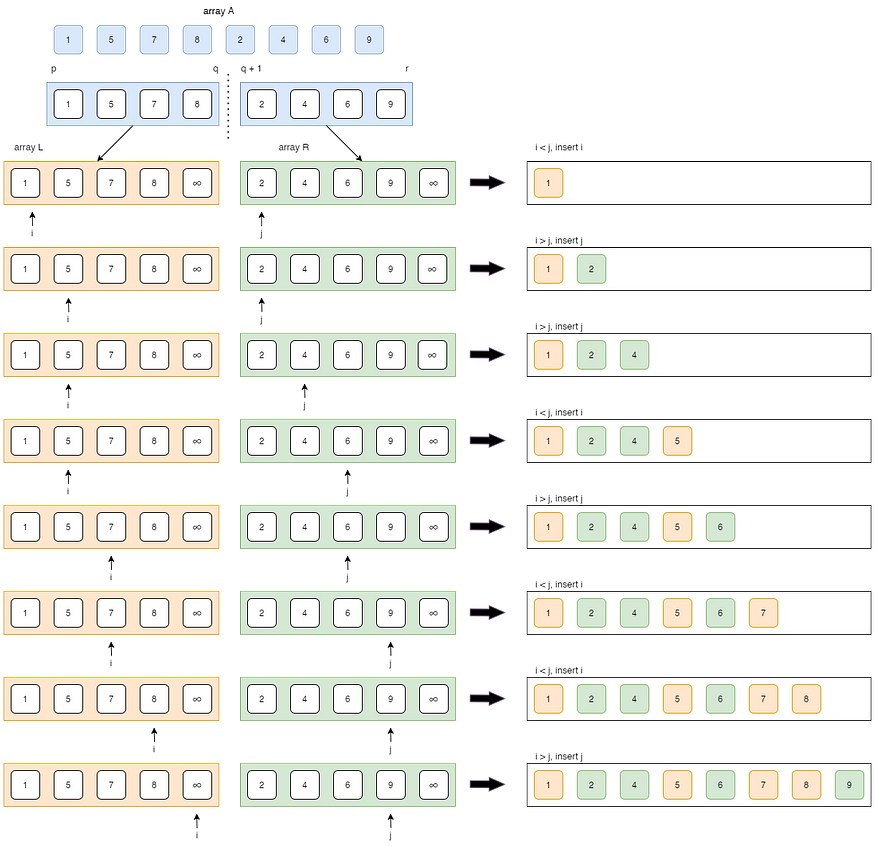
算法:
merge(A, p, q, r)
{ n1= q-p+1 n2= rq设 L[1:n+1] 和 R[1:n2+1] 为(i=1:n1) 的新数组L[i]= A[p+i-1] for (j=1:n2) R[j]= A[q+j] L[n1 + 1]= 无穷大R[n2 + 1]= 无穷大i= 1、j=1 for (k=p:r) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) A[k] = L[i] i= i+1 else A[k] = R[j ] j= j+1 }
}/* C program for Merge Sort */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>// Merges two subarrays of arr[].
// First subarray is arr[l..m]
// Second subarray is arr[m+1..r]
void merge(int arr[], int l, int m, int r)
{int i, j, k;int n1 = m - l + 1;int n2 = r - m;/* create temp arrays */int L[n1], R[n2];/* Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] */for (i = 0; i < n1; i++)L[i] = arr[l + i];for (j = 0; j < n2; j++)R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j];/* Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r]*/i = 0; // Initial index of first subarrayj = 0; // Initial index of second subarrayk = l; // Initial index of merged subarraywhile (i < n1 && j < n2){if (L[i] <= R[j]){arr[k] = L[i];i++;}else{arr[k] = R[j];j++;}k++;}/* Copy the remaining elements of L[], if there are any */while (i < n1){arr[k] = L[i];i++;k++;}/* Copy the remaining elements of R[], if there are any */while (j < n2){arr[k] = R[j];j++;k++;}
}/* l is for left index and r is right index of the
sub-array of arr to be sorted */
void mergeSort(int arr[], int l, int r)
{if (l < r){// Same as (l+r)/2, but avoids overflow for// large l and hint m = l + (r - l) / 2;// Sort first and second halvesmergeSort(arr, l, m);mergeSort(arr, m + 1, r);merge(arr, l, m, r);}
}/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to print an array */
void printArray(int A[], int size)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < size; i++)printf("%d ", A[i]);printf("\n");
}/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{int arr[] = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7};int arr_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);printf("Given array is \n");printArray(arr, arr_size);mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1);printf("\nSorted array is \n");printArray(arr, arr_size);return 0;
}
合并排序
整个归并排序按以下方式工作:
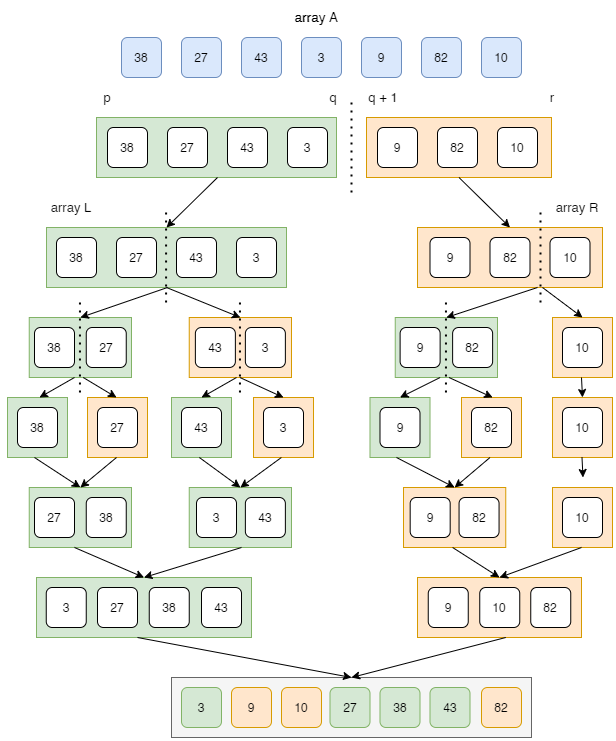
归并排序
算法:
Merge_Sort(A, p ,r)
{ if p<r q= [(p+r)/2] Merge_Sort(A, p ,q) Merge_Sort(A, q+1, r) merge(A, p, q, r)
}5. 快速排序
快速排序也是一种分治算法。它选择一个元素作为主元,并围绕所选主元对给定数组进行分区,以便所有较小的元素都位于主元的左侧,所有较大的元素都位于主元的右侧。QuickSort 有许多不同的版本,它们以不同的方式选择枢轴:
- 始终选择第一个元素作为枢轴。
- 始终选择最后一个元素作为基准(在下面实现)。
- 选择一个随机元素作为基准。
- 选择中位数作为枢轴。
快速排序的关键过程是partition()方法。分区的目标是,给定一个数组和数组中的一个元素 r 作为主元,将r放在排序数组中的正确位置,并将所有较小的元素(小于r)放在r之前,并将所有较大的元素(大于 r )放在 r 之前。比r ) 在r之后。所有这些都应该在线性时间内完成。
对于小输入,与合并排序相比,快速排序是最好的算法。当您不需要稳定的排序并且平均情况性能比最坏情况性能更重要时,请选择快速排序。我们先看看分区算法及其实现。
分区()算法
我们从最右边的元素开始,并跟踪较小(或等于)元素的索引r。
- 如果我们找到小于r的元素j,则我们增加i指针并交换 i 和 j 的元素。
- 如果我们找到一个大于r 的元素j,那么我们只需增加j指针即可。
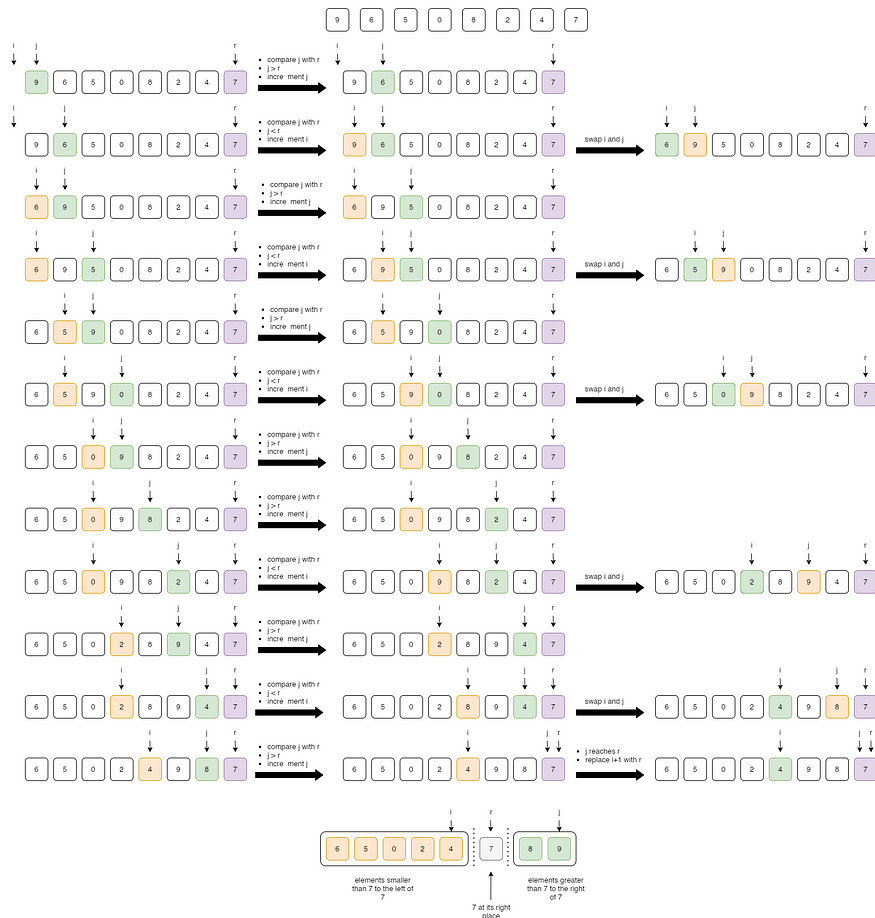
快速排序
算法:
分区(A, p, r)
{
x= A[r] i= p-1 for (j= p:r-1) { if (A[j] <= x) { i= i+1交换 A[ i] 与 A[j] } }将 A[i+1] 与 A[r] 交换,返回 i+1
}快速排序
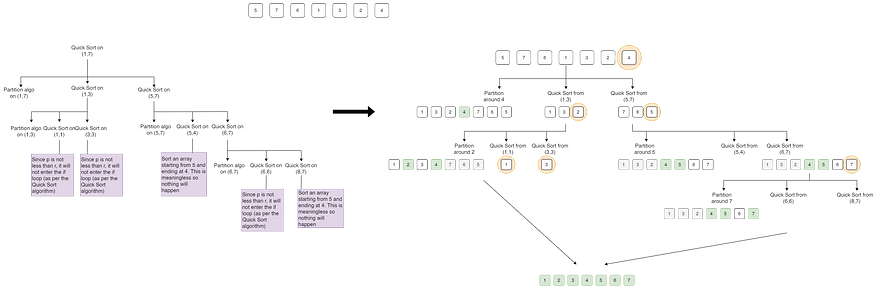
整个快速排序的工作原理如下:
- 它检查条件p < r。如果为 True,则进入 if 循环,否则退出循环
- 然后,应用分区算法来选择枢轴元素并将其放置在正确的位置。
- 经过分区算法后,整个数组被分为两半,所有小于主元元素的元素都在其左侧,所有大于主元元素的元素都在其右侧。
- 快速排序应用于两半。
- 整个循环继续将数组分成两部分,直到找到一个满足p > r的元素。
算法:
Quick_Sort(A, p ,r)
{ if (p<r) { q= 分区(A, p, r) Quick_Sort(A, p, q-1) Quick_Sort(A, q+1, r) }
}
快速排序
/* C implementation QuickSort */
#include <stdio.h>// A utility function to swap two elements
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{int t = *a;*a = *b;*b = t;
}/* This function takes last element as pivot, places the pivot element at its correct position in sorted array, and places all smaller (smaller than pivot) to left of pivot and all greater elements to right of pivot
*/
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high)
{int pivot = arr[high]; // pivotint i = (low - 1); // Index of smaller elementfor (int j = low; j <= high - 1; j++){// If current element is smaller than the pivotif (arr[j] < pivot){i++; // increment index of smaller elementswap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);}}swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);return (i + 1);
}/* The main function that implements QuickSort
arr[] --> Array to be sorted,
low --> Starting index,
high --> Ending index */
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high)
{if (low < high){/* pi is partitioning index, arr[p] is now at right place */int pi = partition(arr, low, high);// Separately sort elements before// partition and after partitionquickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);}
}/* Function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < size; i++)printf("%d ", arr[i]);printf("\n");
}// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{int arr[] = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1);printf("Sorted array: \n");printArray(arr, n);return 0;
}
)

对图像进行边缘检测)

)
![【笔记】正则表达式[1]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/【笔记】正则表达式[1])


)

,每组4位,然后把这4组数作为数当中的低4位分别放在AL,BL,CL,DL中。)


)

考点)



)