module与moduleCollection你一定要会啊!Vuex源码学习(五)加工后的module
在组件中使用vuex的dispatch和commit的时候,我们只要把action、mutation注册好,通过dispatch、commit调用一下方法名就可以做到。
使用方式
vue组件内
//in vue component
this.$store.commit('setName',{name : 'xLemon'});
this.$store.commit('list/setName',{name : 'xLemon'});
vuex的mutation中
// in mutation.js
export const setName = function(state,payload){
state.name = payload.name;
}
// in list mutation.js 在名为list的模块下的mutation(有自己的命名空间)
export const setName = function(state,payload){
state.name = payload.name;
}
我们传递的只是一个字符串,commit是如何找到注册mutation时的同名方法的呢?有命名空间的这种mutation是如何被找到并且执行的呢?
上源码
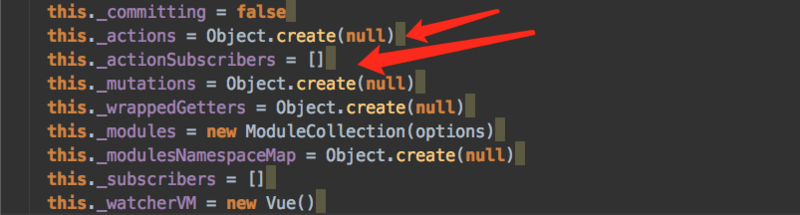
属性的意义
_actions用于存放所有注册的action
_mutations用于存放所有注册的mutation
被注册的action和mutation如何被放到对应的属性中的呢?
轮到installModule函数要出马了。
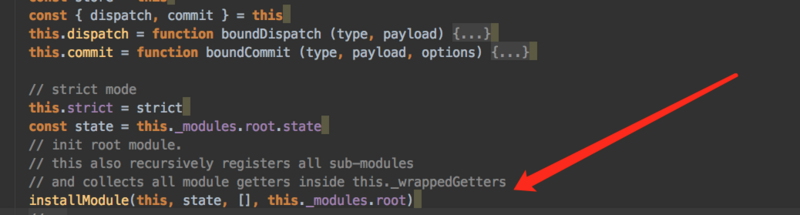
installModule的意义是初始化根模块然后递归的初始化所有模块,并且收集模块树的所有getters、actions、mutations、以及state。
看一下installModule的代码,installModule并不是在类的原型上,并不暴露出来,属于一个私有的方法,接收五个参数。
store(Vuex.store的实例对象。
rootState (根结点的state数据)。
path 被初始化模块的path(前两张讲过path的意义)。
module 被初始化的模块。
hot 热更新(并不关键)
function installModule (store, rootState, path, module, hot) {
const isRoot = !path.length
// 获取全名
const namespace = store._modules.getNamespace(path)
// register in namespace map
if (module.namespaced) {
// 设置命名空间对照map
store._modulesNamespaceMap[namespace] = module
//console.log(store._modulesNamespaceMap);
}
// set state
if (!isRoot && !hot) {
const parentState = getNestedState(rootState, path.slice(0, -1))
const moduleName = path[path.length - 1]
// 把子模块的state(数据)绑定到父模块上(按照层级)
store._withCommit(() => {
Vue.set(parentState, moduleName, module.state)
})
}
const local = module.context = makeLocalContext(store, namespace, path)
// 使用模块暴露出来的方法来注册mutation、action、getter
module.forEachMutation((mutation, key) => {
const namespacedType = namespace + key
registerMutation(store, namespacedType, mutation, local)
})
module.forEachAction((action, key) => {
const type = action.root ? key : namespace + key
const handler = action.handler || action
registerAction(store, type, handler, local)
})
module.forEachGetter((getter, key) => {
const namespacedType = namespace + key
registerGetter(store, namespacedType, getter, local)
})
module.forEachChild((child, key) => {
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(key), child, hot)
})
}
这个函数虽然只有40多行,但处于一个承上启下的关键点,这一章只会分析如何收集mutation与action其余的内容会再下一章讲述。
installModule首先获取一下这个模块的命名(我称之为全名)
依赖_modules(ModuleCollection实例对象)的getNamespace方法。
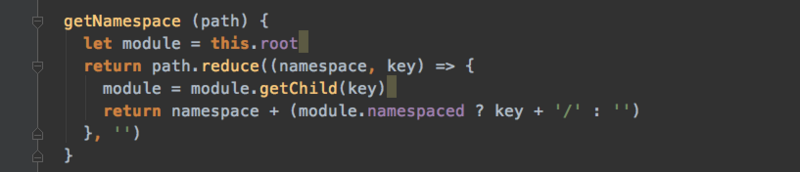
根据模块的path,path有从根结点到当前节点这条路径上按顺序排序的所有模块名(根结点没有模块名,并没有设置在path,所以根模块注册时是个空数组,他的子模块的path就是[子模块的名字])。那么Vuex如何整理模块名的呢?
效果:
如果这个模块有自己的命名空间(namespaced为true)这个模块的全名就是父模块的全名+自己的模块名,
如果这个模块没有自己的命名空间(namespaced为false)这个模块的全名就是父模块的全名
为什么会是这样?分析一下代码
getNamespace (path) {
let module = this.root //根模块
return path.reduce((namespace, key) => {
//根模块的path是个空数组不执行
// path的第一项是根模块的儿子模块。
// 获取儿子模块 并且将替换module (path的下一项就是儿子模块中的子模块了)
// 下次累加 就是这个module(轮到子模块了)去找它(子模块)的子模块
module = module.getChild(key)
// 查看儿子模块是不是设置了命名空间
//如果设置了这个模块的全名就增加自己的模块名和一个'/'分割后面的模块名,
//没有的话返回一个'',
// reduce累加可以把这个名称进行累加
return namespace + (module.namespaced ? key + '/' : '')
}, '')
}
获取完模块的全名了,之后我们看一下这两个函数
module.forEachAction
module.forEachMutation
在上一章节module提供了遍历自己内部的action、mutation的方法。
module.forEachMutation((mutation, key) => {
const namespacedType = namespace + key
registerMutation(store, namespacedType, mutation, local)
})
module.forEachAction((action, key) => {
const type = action.root ? key : namespace + key
const handler = action.handler || action
registerAction(store, type, handler, local)
})
const namespacedType = namespace + key
这句话 就是拼接出真正的mutation、action的名字
模块全名+mutation/action的名字。也就是一开始我举例的list/setName是这个mutation的全名(被调用的时候用)
this.$store.commit('list/setName',{name : 'xLemon'});
名称已经获取到了,下一步怎么办?
把这些函数按照对应名字放到之前说的_actions、_mutations属性中啊
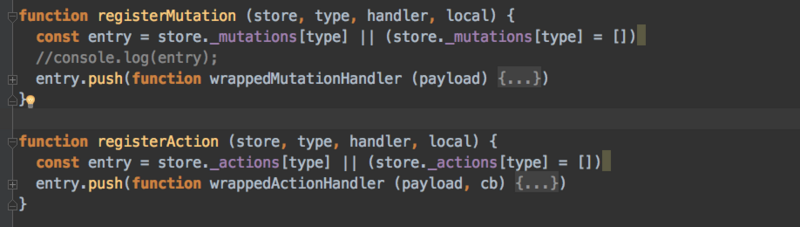
看一下这个名字的mutation有没有被注册过,没有就声明一下,然后push进去。
如果这个名字的mutation被注册过,就push进去。
action同理
小彩蛋 设置两个不同模块的同名mutation(全名一样哦)这两个mutation都会执行,action也是一样的。
总结
action和mutation在被dispatch和commit调用前,
首先遍历模块树获取每个模块的全名。
把模块内的action和mutation加上模块全名,整理成一个全新的名字放入_actions 、 _mutations属性中。
dispacth和commit如何调用aciton和mutation 的将在下章讲述
下一章:我们讨论action和mutation如何被调用的(调用篇)。
我是一个应届生,最近和朋友们维护了一个公众号,内容是我们在从应届生过渡到开发这一路所踩过的坑,已经我们一步步学习的记录,如果感兴趣的朋友可以关注一下,一同加油~






层进行压力测试)
)












